Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To examine humoral and cellular immune responses induced by a live attenuated herpes zoster (HZ) vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared with osteoarthritis (OA) patients.
Methods: we performed an observational study of a live attenuated HZ vaccine in 41 RA patients receiving conventional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and/or low-dose glucocorticoids (median 60 years-old, 92.7% female), 28 OA patients (median 62 years-old, 85.7% female). Blood samples were obtained before and at 12 weeks after HZ vaccination. Immunogenicity was assessed using varicella zoster virus (VZV)-specific interferon gamma (IFN-¥ã) enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assays and an in-house enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
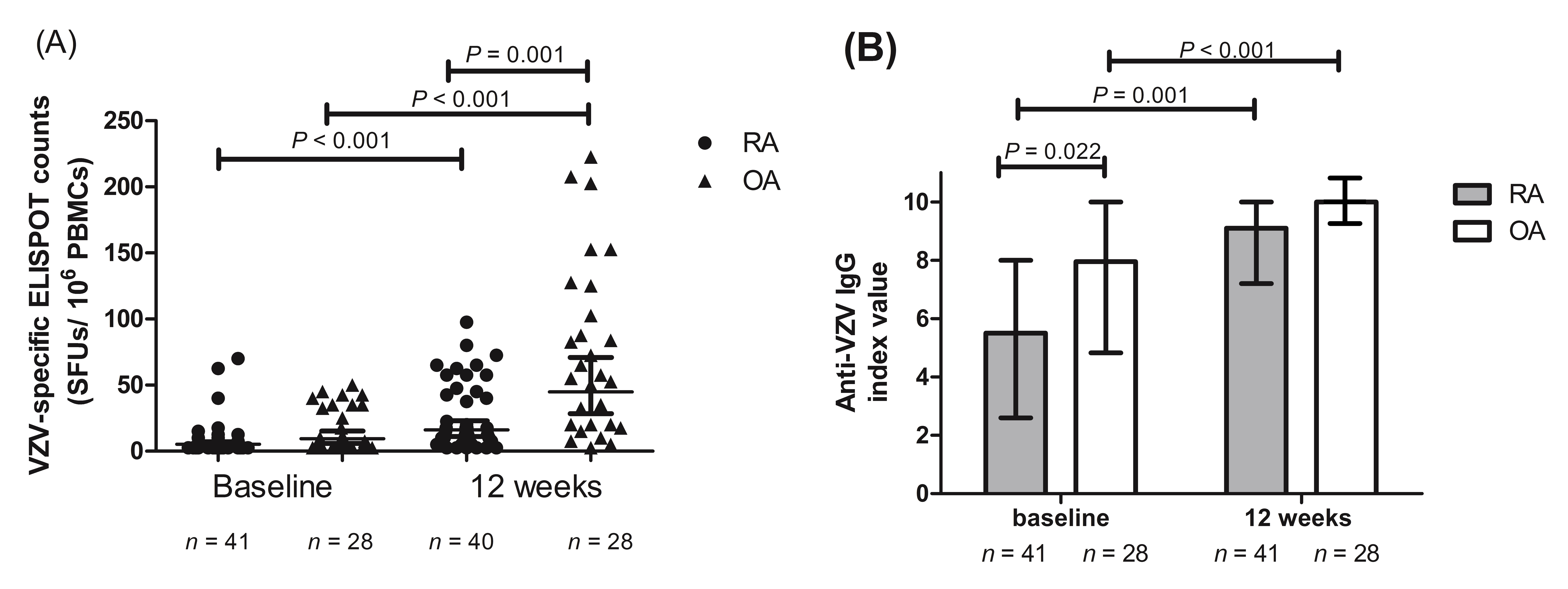
Results: No vaccinated patients developed HZ during the follow-up period (median, 1.6 years). The HZ vaccine induced a significant increase in the VZV-specific ELISPOT spot-forming units and anti-VZV immunoglobulin G antibodies in both RA and OA patients. The number of spot-forming units was lower in RA patients than in OA patients both at baseline and at 12 weeks after vaccination (Figure). The disease activity score 28 (DAS28) was similar at baseline and at 12 weeks after vaccination. However, six RA patients (15%) experienced a flare-up (increase in DAS28 > 1.2) during the 12 weeks. The HZ vaccine induced VZV-specific cellular and humoral responses in RA patients.
Conclusion: Although RA patients showed a weaker vaccine-induced VZV-specific cellular immune response than OA patients, the HZ vaccine may be considered in RA patients receiving conventional DMARDs and/or low dose glucocorticoids.
Figure. Vaccine-induced cellular and humoral immune response to varicella zoster virus (VZV) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA).
(A) Number of interferon-¥ã enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) spot-forming units (SFU) for VZV stimulation (according to time point) for patients with RA (circle) and OA (triangle) after herpes zoster vaccination.
(B) Assay of anti-VZV immunoglobulin G antibodies in serum from RA and OA patients at baseline and at 12 weeks after vaccination.
Data are expressed as the median and interquartile range. Statistical significance was calculated using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Mann-Whitney U test as appropriate. n, number of subjects who had tested.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koh J, Kim JW, Kwok SK, Ju JH, Park SH. Safety and Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immune Responses to Herpes Zoster Vaccine in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-humoral-and-cell-mediated-immune-responses-to-herpes-zoster-vaccine-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-humoral-and-cell-mediated-immune-responses-to-herpes-zoster-vaccine-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/