Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2015–2051) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The combination of biological (bDMARDs) and targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) has emerged as a promising approach to improve clinical outcomes in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs), particularly in refractory or complex cases where simultaneous targeting of multiple inflammatory pathways may be beneficial. However, this strategy raises concerns regarding safety, adverse events, and optimal drug selection. The objectives of this study are to describe the clinical characteristics of IMID patients receiving dual targeted therapy (DTT) with two bDMARDs or a bDMARD plus a tsDMARD, to identify the most commonly used combinations and main adverse events and to evaluate clinical response to DTT.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational study including IMID patients treated with bDMARD and/or tsDMARD combinations at Hospital Universitario La Paz from October 2019 to December 2024. We collected clinical data, details of DTT combinations, treatment duration, reasons for discontinuation, and disease activity assessed by DAS28, ASDAS, and DAPSA at baseline and at discontinuation or end of follow-up.
Results: Nineteen patients with 28 DTT cycles were included; 68.4% were women, with a mean age at DTT initiation of 42.9±19.4 years. Diagnoses included spondyloarthritis (SpA, 36.8%), rheumatoid arthritis (RA, 21.1%), psoriatic arthritis (PsA, 15.8%), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA, 10.5%), polyarthritis of possible genetic cause (10.5%), and Behçet syndrome (5.3%). A second IMID treated with bDMARD/tsDMARD was associated in 57.9% of patients: 63.3% with bowel disease (IBM), 27.3% with psoriasis, 18.2% with chronic urticaria and 9.1% with chronic angioedema. Extra-musculoskeletal manifestations were present in 21.2%: 1 case of interstitial lung disease, 1 sicca syndrome, 2 uveitis and 1 with neurological involvement. Patients had received a median of five prior DMARDs. Thirteen patients (68.4%) had a single DTT cycle, while six (31.6%) had ≥1 prior DTT cycles. The main indications for DTT initiation were active musculoskeletal disease (63%), active IBD (11.1%), combined active MSK/IBD disease (7.4%), and psoriasis (7.4%). Most frequently used combinations were TNF inhibitor (TNFi)+JAK inhibitor (JAKi, 32.1%), TNFi+vedolizumab (25.0%), and TNFi+anti-IL23 (10.7%). Median DTT duration was 10.3 months (range 0.7–60.3 months). The most common adverse events were infections (25.0%) and hypertransaminasemia (10.7%). Discontinuation occurred in 57.1% of DTT cycles, mainly due to inefficacy (31.1%) and infections (7.1%). At the end of the study, 57.9% of patients maintained TDD and clinical improvement was observed in 52.6%, as assessed by disease activity indices and clinical reports (see Table 1).
Conclusion: DTT appears to be a viable option for refractory IMID patients, achieving clinical improvement in over half of the cases. Nonetheless, the high rate of adverse events and treatment discontinuation underscores the importance of careful patient selection and close monitoring. Further research is needed to refine patient selection, optimize drug combinations, and improve risk management strategies.
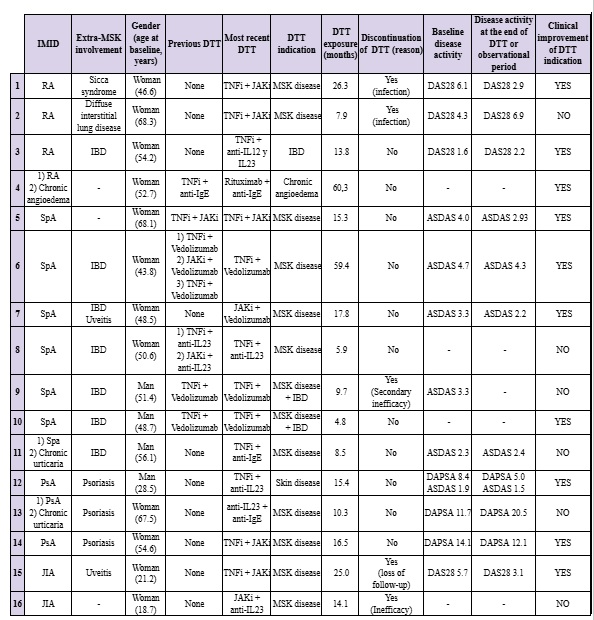 Clinical characteristics, DTTs used, duration of treatment, reason for discontinuation and disease activity and status at baseline (beginning of most recent DTT) and at discontinuation of treatment or at the end of the study of the included patients.
Clinical characteristics, DTTs used, duration of treatment, reason for discontinuation and disease activity and status at baseline (beginning of most recent DTT) and at discontinuation of treatment or at the end of the study of the included patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lopez Juanes N, Ureta C, Novella-Navarro M, Monjo Henry I, Peiteado D, Villalba A, Nuño L, Navarro-Compan V, Sanz M, Gonzalez M, Suarez C, Remesal A, Alcobendas R, udaondo C, Sendagorta E, Balsa A, de Miguel E, Plasencia-Rodríguez C. Safety and Effectiveness of the Use of Combined Therapy with bDMARDS and tsDMARDs in Immune-mediated Inflammatory Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-the-use-of-combined-therapy-with-bdmards-and-tsdmards-in-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-the-use-of-combined-therapy-with-bdmards-and-tsdmards-in-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases/
