Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: This study aimed to characterize the impact of pt advocacy group membership and its association with NPTM frequency and clinical parameters in axSpA pts. EULAR recently recommended the implementation of self-management strategies, such as participation in patient (pt) organizations to improve pt self-management and participation1. Non-pharmacological treatment modalities (NPTM)2 are recommended in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) treatment guidelines3, and are part of ASAS quality standards4. Evidence regarding improvements in pt participation in NPTM associated with membership in pt advocacy groups is limited.
Methods: Pts with a physician-judged axSpA diagnosis were enrolled in the multicenter, observational ATTENTUS-axSpA survey, conducted across Germany (11-2019 to 07-2020). Prescribed NPTM measures were assessed to study the effect of membership in pt advocacy groups. Demographics, clinical parameters and pt-related data were collected electronically.
Results: In total, 787 axSpA pts were enrolled in ATTENTUS; this analysis was conducted on the overall population (n=770) and working population (n=695), which was based on pre-defined criteria of working staus5. Overall, 12.2% (n=85) pts were members of a pt advocacy group and 87.8% (n=610) were not. Pt advocacy group members were older, had higher Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) scores, increased functional impairment (BASFI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index) and higher impact of axSpA on health (ASAS-HI, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society-Health Index) (Table 1). Despite worse prognostic factors, there was no significant difference in Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) score [40.6 (27.0) for pt advocacy group members vs 36.8 (29.9) for non-members; p=0.380]. Importantly, membership in a pt advocacy group was associated with increased prescribed, supervised NPTM (57.6% [n=49] vs 34.4% [n=210]) and increased likelihood of having ever received medicinal rehabilitation (78.8% [n=67] vs 53.8% [n=328]) vs non-members. Pts reported to have ever received 2.6 rehabilitation measures in total, and ≥3.0 different rehabilitation NPTM measures. Cumulatively, 25.0% (N=654) of rehabilitation measures were physiotherapy, 8.0% (N=209) were rehabilitation sport and 5.5% (N=143) functional training (Figure 1). Importantly, there was no difference between self-applied regular physical training between groups (89.4% [n=76] vs 84.4% [n=515]).
Conclusion: Pt advocacy group membership was associated with increased prescribed NPTM in axSpA. Our data provide evidence for a significant role of patient organizations in the implementation of guideline-supported treatments, as well as improvement of self-management strategies in pts with axSpA, which may have an influence on important health domains such as work participation.
References
1. Nikiphorou E, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;0:1–8
2. Rausch Osthoff A-K, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:1251–1260
3. van der Heijde D, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:978–991
4. Kiltz U, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:193–201
5. Kiltz et al. 2021. EULAR eposter; POS0983
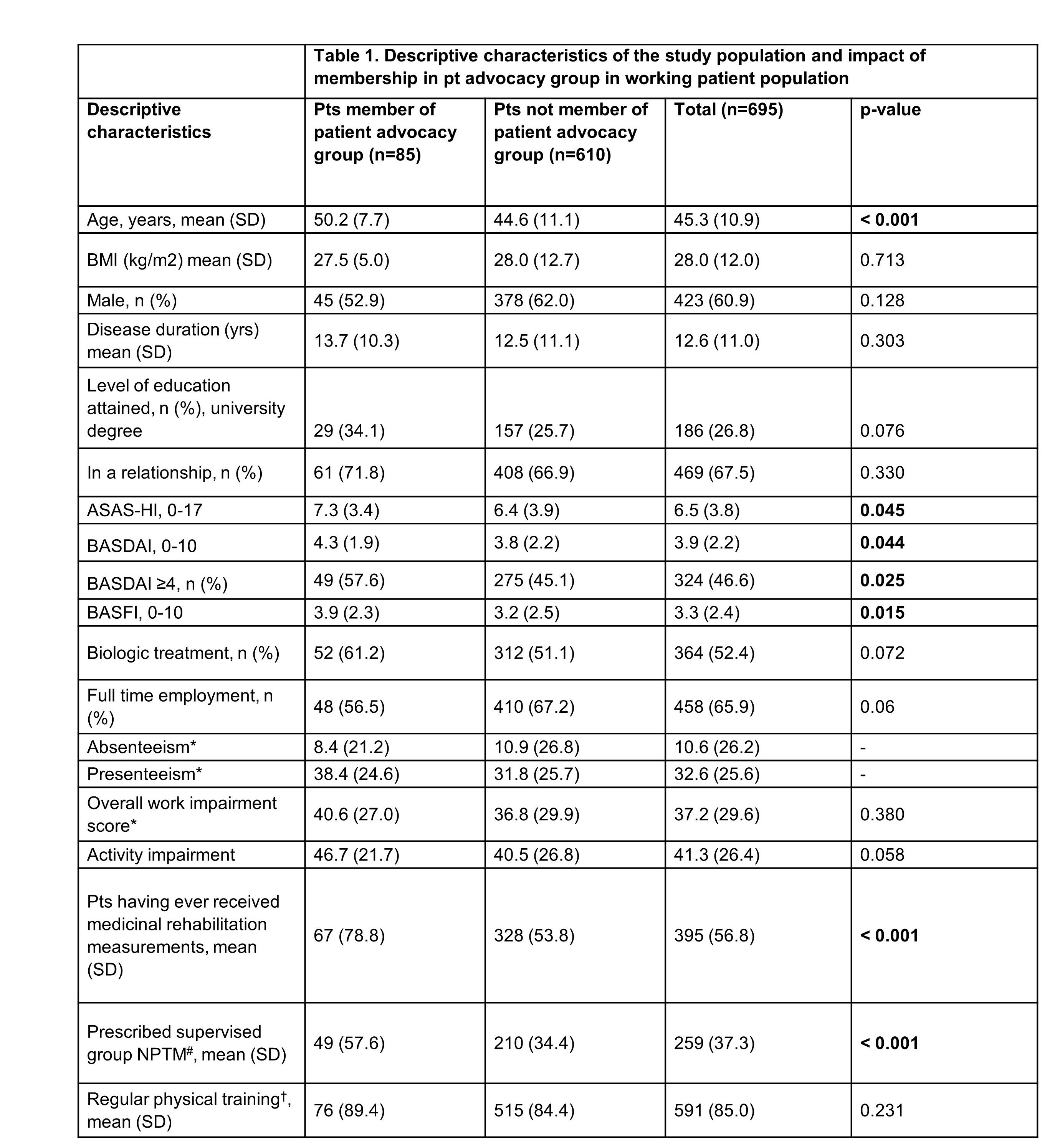 *Work-related questions of WPAI-score have been calculated for pts stated being employed (Nf340); †Regular physical training in the context of their axSpA; #rehabilitation sport/functional training or both. ASAS-HI, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society-Health Index; BASDAI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BASFI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index; BMI, Body Mass Index; n, number of pts; pts, patients; SD, Standard Deviation; WPAI, Work Productivity and Activity Impairment; yrs, years.
*Work-related questions of WPAI-score have been calculated for pts stated being employed (Nf340); †Regular physical training in the context of their axSpA; #rehabilitation sport/functional training or both. ASAS-HI, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society-Health Index; BASDAI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BASFI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index; BMI, Body Mass Index; n, number of pts; pts, patients; SD, Standard Deviation; WPAI, Work Productivity and Activity Impairment; yrs, years.
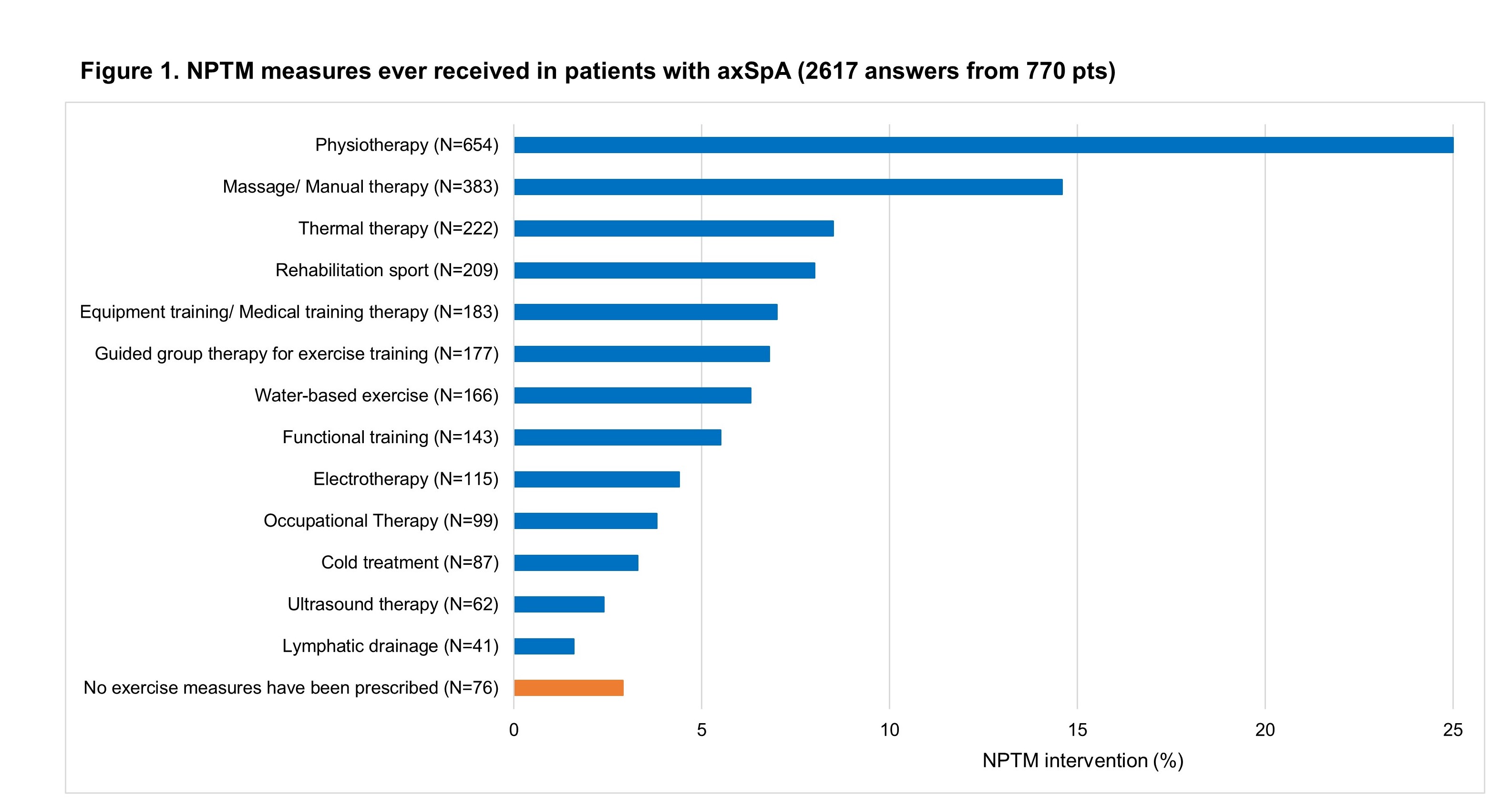 Multiple answers were permitted. A total of 2617 answers were submitted from 770 patients. N, total number of pts. NPTM, non-pharmacological treatment modalities.
Multiple answers were permitted. A total of 2617 answers were submitted from 770 patients. N, total number of pts. NPTM, non-pharmacological treatment modalities.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Meyer-Olson D, Hoeper K, Hammel L, Lieb S, Haehle A, Kiltz U. Role of Patient Organizations in Implementation of Recommended Non-pharmacological Treatment Modalities in Spondyloarthritis: Evidence for the Effectiveness of Self-management Strategies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-patient-organizations-in-implementation-of-recommended-non-pharmacological-treatment-modalities-in-spondyloarthritis-evidence-for-the-effectiveness-of-self-management-strategies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-patient-organizations-in-implementation-of-recommended-non-pharmacological-treatment-modalities-in-spondyloarthritis-evidence-for-the-effectiveness-of-self-management-strategies/
