Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Vasculitic neuropathy (VN) is a major complication of systemic vasculitis and contributes to morbidity, functional limitation, and health care utilization in affected patients. Patient reported outcomes (PRO) in patients with VN is limited. Our aim was to compare long term PRO for neuropathic symptoms in patients with VN undergoing induction treatment with rituximab (RTX) or cyclophosphamide (CYC).
Methods: The medical record was screened by keywords for patient charts that included vasculitis and neuropathy. Diagnosis of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, microscopic polyangiitis, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, or isolated VN was confirmed per ACR classification criteria or 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Nomenclature. VN diagnosis was confirmed independently by a neurologist reviewing clinical presentation, EMG findings, and nerve biopsy. Patient with neuropathy secondary to other etiologies were excluded. Data including treatment regimen, affected limb, Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS), and duration of follow up was collected. Patients were invited to participate in a survey utilizing validated, neuropathy-specific PRO. Outcomes of interest were Chronic Acquired Polyneuropathy-Patient Reported Index score (CAP-PRI), a visual analog scale of self-perceived improvement in symptoms (VAS), and Overall Disability Sum Score (ODSS). Comparisons between treatment groups were performed with ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test, Pearson’s chi-square test, or Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Multiple regressions were performed to control for disease duration, BVAS, and affected limb.
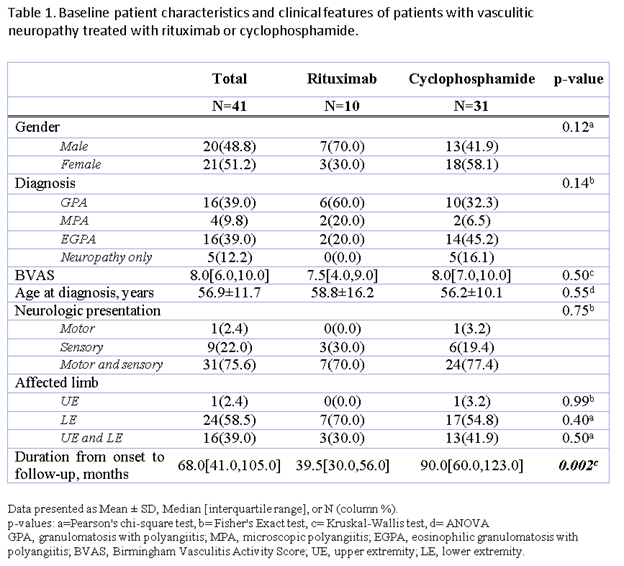
Results: Sixty-four patients with VN were sent PRO surveys. Survey response rate was 64% (n=41, 25% RTX, 75% CYC). Baseline patient characteristics, clinical features, and specific vasculitis diagnoses are listed in Table 1. No significant differences between treatment groups were seen in CAP-PRI (p=0.16) or VAS (p=0.13) (Table 2). There was no difference between treatment groups for ODSS (p=0.17) in patients with only lower extremity involvement. In patients with both upper and lower extremity involvement, patients treated with RTX had higher disability by ODSS at follow up (p=0.039), though small sample size limits interpretability. Multivariable analyses did not reveal significant differences in CAP-PRI, VAS, or ODSS in the two treatment groups after adjustment.
Conclusion: Overall, no significant differences in PRO were found in patients with VN treated with RTX compared to CYC. Prospective studies could help validate these findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel A, Byram K, Jin Y, Wu A, Li Y, Calabrese LH, Hajj-Ali RA. Rituximab Versus Cyclophosphamide for Vasculitic Neuropathy: A Patient Reported Outcomes Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-versus-cyclophosphamide-for-vasculitic-neuropathy-a-patient-reported-outcomes-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-versus-cyclophosphamide-for-vasculitic-neuropathy-a-patient-reported-outcomes-study/