Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The efficacy of biologics and targeted synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic agents approved for treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is well documented, but cardiovascular safety profile of these agents is still a matter of debate. We examined risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) associated with use of biologics and targeted synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic agents in PsA.
Methods: Medline, PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Central, and clinicaltrials.gov were searched to identify phase 3 and 4 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) reporting safety data of biologics and targeted synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic agents used in PsA. Outcome of interest was MACE within on-treatment or placebo-controlled duration. Mantel–Haenszel approach was used to pool data after continuity correction of zero events. Mixed treatment comparisons were computed using a fixed-effect NMA within frequentist framework. Effect estimates were expressed as odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). P-scores were calculated to establish relative rankings of different treatment options. A sensitivity analysis was conducted using non-central hypergeometric (NCH) approach with Breslow approximation. All statistical analyses were conducted in R (v4.0.2).
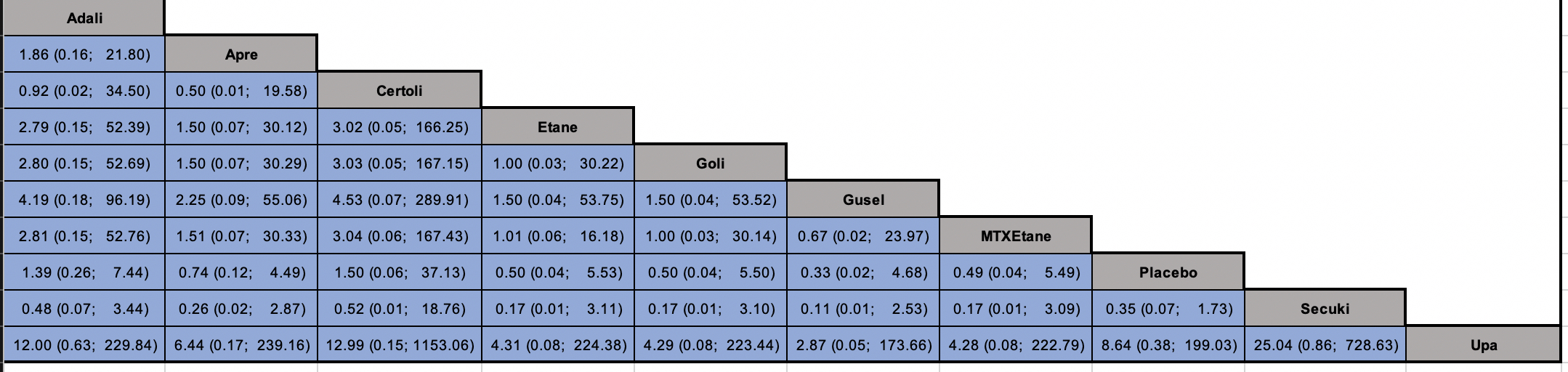
Results: 33 trials met inclusion criteria; 12 RCTs [n=8501] with10 unique treatments and event(s) in at least one arm were included in network meta-analysis (Figure 1). Ten trials were excluded based on lack of reported data on MACE and 11 trials were excluded based on zero reported events in both or all arms (in case of multi-arm trials). A total of 27 (0.3%) MACE outcomes were observed among different treatments. Mixed treatment comparisons showed no statistically significant differences with upadacitinib (OR 0.12; 95% CI 0.01-2.66), guselkumab (OR 0.33; 95% CI 0.02-4.68,) methotrexate-etanercept (OR 0.49; 95% CI 0.04-5.49), golimumab (OR 0.50; 95% CI 0.04-5.50), etanercept (OR 0.50; 95% CI 0.04-5.53), apremilast (OR 0.74; 95% CI 0.12-4.49), adalimumab (OR 1.39, 95% CI 0.26-7.44), certolizumab (OR 1.50; 95% CI 0.06-37.13), and secukinumab (OR 2.85 95% CI 0.58-14.48) when compared to placebo. Similarly, no significant differences were observed among different biologics and targeted synthetic agents (Figure 2). Certainty of evidence was low due to very serious imprecision. The results were consistent with sensitivity analysis with NCH approach.
Limitations included study-level data with a relatively small number of studies and events of interest, sparse direct evidence, and open network.
Conclusion: During limited follow-up period in controlled clinical trials, composite MACE outcomes were not different among PsA patients treated with biologics and targeted synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic agents.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ajmal M, Bilal J, Naqvi S, Riaz I, Shahid Z, Khakwani K, Liu Y, Bhattacharjee S, Bogucka R, Asghar N, Kwoh K. Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE) with Biologic and Targeted Synthetic Antirheumatic Agents in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-mace-with-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-antirheumatic-agents-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-network-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-mace-with-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-antirheumatic-agents-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-network-meta-analysis/