Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1442–1487) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that increases the risk of severe clinical outcomes and mortality. However, the association between SLE and the risk of diabetes mellitus (DM) is unclear. Our study aimed to investigate the risk of DM and to evaluate the impact of SLE therapies on the risk of developing DM in patients with SLE.
Methods: Electronic database searches of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, together with hand search, were performed from inception to February 2023. Studies analyzing the relationships between risk factors for DM in SLE patients in cohort or case-control were included. Data were pooled utilizing fixed- or random-effects metanalysis to estimate pooled relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The study was registered with PROSPERO, CRD42023402774.
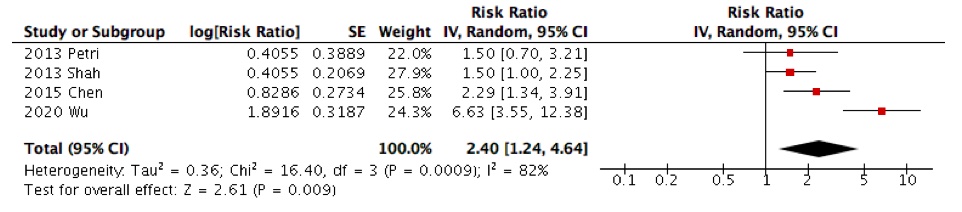
Results: A total of 36 studies (23 case-control and 13 cohort studies) involving 265,822 patients with SLE were included. In the pooled analysis from case-control studies, we found a greater risk (OR = 1.05, 95% CI 0.87-1.27; P = 0.63) of diabetes in patients with SLE compared with non-SLE controls. However, the pooled risk estimate of cohort studies did not show a significant risk of DM (RR= 1.32, 95% CI 0.93-1.87; P = 0.12). In a subgroup analysis, reduced risk of diabetes was reported with antimalarials (RR= 0.56, 95% CI 0.42-0.75; P < 0.001), while glucocorticoids use was associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes (RR= 1.45, 95% CI 1.20-1.76; P = 0.0002). Age, sex, hypertension, and immunosuppressants were not associated with DM in SLE patients.
Conclusion: Although there was not an increased risk of DM in overall SLE patients compared to controls, antimalarials users or adherents had a decreased risk, while GCT users had an increased risk.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MENDOZA PINTO C, Munguía-Realpozo P, Etchegaray-Morales I, García-Carrasco M, Méndez Martínez S. Risk of Diabetes Mellitus in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-diabetes-mellitus-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-diabetes-mellitus-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/