Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I: Biomarkers and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Neuropsychiatric involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with SLE but not well understood. The aim of this study was to identify risk factors for NPSLE and its recurrence.
Methods: We enrolled consecutive patients with SLE who had visited Keio University Hospital between 2013 and 2015. The patients were divided according to the presence or absence of NPSLE, and their clinical characteristics, manifestations, findings of cerebrospinal, electroencephalographic and neuroimaging examination, treatment and prognosis were compared. Patients with NPSLE were further divided by the recurrence of NPSLE, and its risk factors were examined.
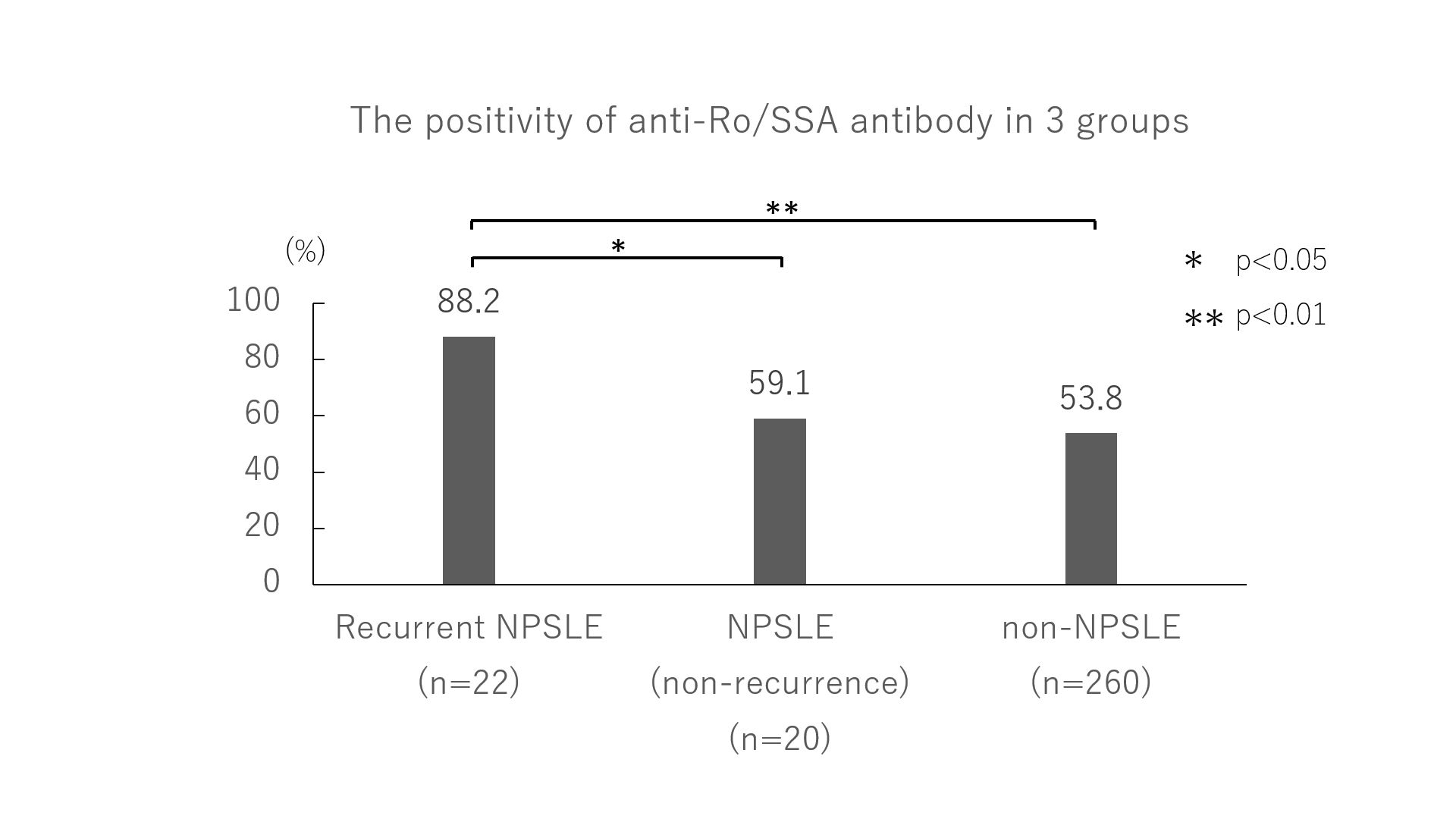
Results: A total of 302 patients with SLE were enrolled. Two hundred seventy (89%) were female, and the mean age was 49.2 years. Forty-two (14%) patients were diagnosed with NPSLE during the course of SLE according to the ACR case definitions. The patients with NPSLE had a history of serositis more frequently than those without (37% vs 20%, p=0.03). Anti-Ro/SSA antibody (76% vs 54%, p=0.02) and anti-phospholipid antibody (55% vs 35%, p=0.03) were more frequently detected in patients with NPSLE while no difference was found in other autoantibodies including anti-DNA, anti-Sm, anti-RNP, and lupus anticoagulant. Among NPSLE patients, 22 (52%) had recurrent central nervous involvement. Serologically, the recurrent group had higher positivity of anti-Ro/SSA antibody than the non-recurrent group (88% vs 59%, p=0.02). Patients with focal hypoperfusion in single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) at the first NPSLE had significantly higher relapse rate than those with diffuse hypoperfusion (86% vs 36%, p=0.02). Patients treated with intravenous cyclophosphamide at the first NPSLE were at a lower risk of recurrence (12% vs 46%, p=0.01).
Conclusion: Anti-Ro/SSA antibody was a risk for recurrent NPSLE. Patients with focal hypoperfusion of SPECT at the first NPSLE had significantly higher risk for NPSLE recurrence. Cyclophosphamide is important for preventing the recurrence of NPSLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Anan R, Kaneko Y, Kikuchi J, Takeuchi T. Risk Factors for Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Its Recurrence [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-for-neuropsychiatric-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-its-recurrence/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-for-neuropsychiatric-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-its-recurrence/