Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Given that tocilizumab (TCZ) directly inhibits IL-6 signaling and strongly suppresses the inflammatory reaction, there is concern that the signs and symptoms associated with infection are not easily detected in the early phase of infection during TCZ treatment. The aim of this study was to identify initial symptoms before serious infection (SI) developed in TCZ-treated patients using clinical narratives from a postmarketing adverse events (AE) reporting database.
Methods: A postmarketing AE reporting database maintained by Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. was used to obtain individual case safety reports including structured (age, sex, drugs, AE term, laboratory test values) and unstructured (clinical narratives) data. Reports had to meet 4 criteria: (1) obtained between April 16, 2008, and April 10, 2015; (2) originated from Japanese patients with RA who received TCZ; (3) included SIs; (4) causality between TCZ and SIs reported by medical professionals. Patient characteristics were summarized by descriptive statistics, and clinical narratives were analyzed by automated text mining to explore symptoms. AEs and symptoms were coded using MedDRA/Japanese version 17.1.
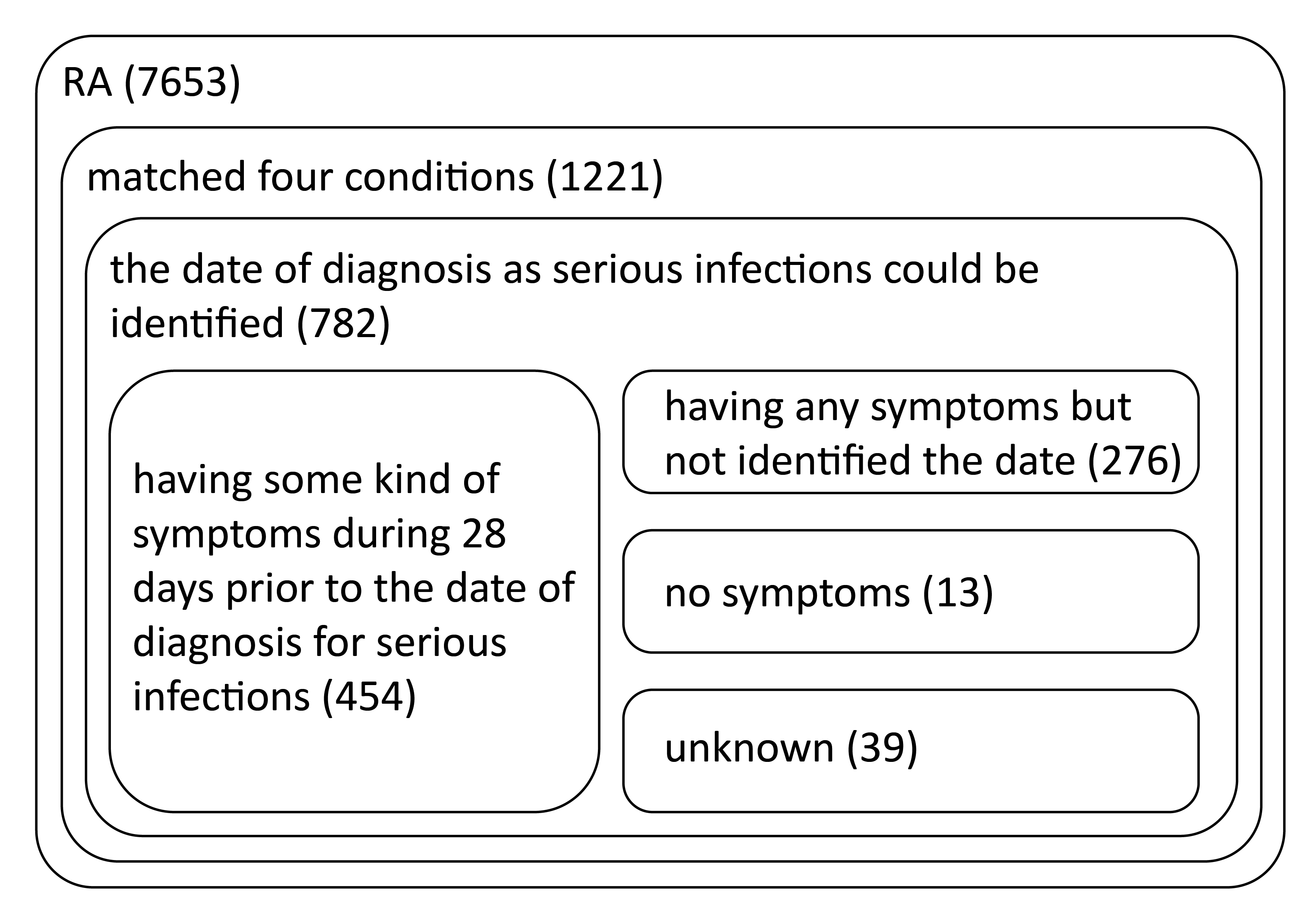
Results: The database included 7653 RA patients with a mean ± SD age of 60.0 ± 12.7 years (<65, 45.8%; ≥65-<75, 22.1%; ≥75, 8.3%; missing, 23.8%). Of these, 1221 patients had reports meeting the 4 criteria (mean ± SD age, 63.4 ± 11.7 years) (<65, 35.5%; ≥65-<75, 25.9%; ≥75, 11.8%; missing, 26.8%) encompassing 1591 reported SIs. The most frequently reported SIs were pneumonia (n = 253, 15.9%), cellulitis (n = 158, 9.9%), and sepsis (n = 80, 5.0%). The date of diagnosis of SI was available for 782 patients: 454 (58.1%) had symptoms during the 28 days before diagnosis of SI, 13 (1.7%) had no symptoms, 276 (35.3%) had symptoms but the date of prodromal symptoms was not identified, and 39 (5.0%) were unknown (Figure). The most common prodromal symptoms among patients who had symptoms during the 28 days before diagnosis of SI were cough (n = 104, 22.9%), pain (n = 103, 22.7%), pyrexia (n = 100, 22.0%), swelling (n = 80, 17.6%), productive cough (n = 49, 10.8%), abdominal pain (n = 49, 10.8%), erythema (n = 47, 10.4%), dyspnea (n = 38, 8.4%), rash (n = 37, 8.1%), and malaise (n = 31, 6.8%).
Conclusion: The presence of prodromal symptoms in patients who developed SIs after TCZ administration was described in most cases. Therefore, data mining of clinical narratives may have additional value in characterizing SIs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Atsumi T, Ando Y, Hayashi Y, Matsuda S, Tanaka R, Takagi N, Nakasone A. Retrospective Analysis for Determining the Signs and Symptoms of Infections before They Become Serious in Tocilizumab-Treated RA Patients Using a Postmarketing Adverse Events Reporting Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/retrospective-analysis-for-determining-the-signs-and-symptoms-of-infections-before-they-become-serious-in-tocilizumab-treated-ra-patients-using-a-postmarketing-adverse-events-reporting-database/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/retrospective-analysis-for-determining-the-signs-and-symptoms-of-infections-before-they-become-serious-in-tocilizumab-treated-ra-patients-using-a-postmarketing-adverse-events-reporting-database/