Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis-Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy IV: Safety of Targeted Therapies
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose:
XmAb®5871 is a humanized Fc engineered monoclonal antibody that binds to the B cell restricted surface antigen CD19 and has enhanced Fc binding to the inhibitory Fcγ receptor IIb (FcγRIIb). Co-ligation of CD19 and FcγRIIb by XmAb5871 has been demonstrated to reversibly down-regulate B cell activity. XmAb5871 is in development for the treatment of B cell mediated autoimmune disorders. The primary objective of this study was to determine the safety, tolerability, PK, PD and immunogenicity profile of XmAb5871 in patients with active RA on stable non-biologic DMARD therapy. A secondary objective (Part B) was to evaluate the effect of XmAb5871 on RA disease response at Day 85 as measured by changes in DAS28-CRP.
Methods:
This multi-center, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, clinical study was conducted in patients with active RA despite DMARD therapy. All patients fulfilled ACR criteria for RA. Patients received 6 IV infusions of XmAb5871 or placebo (Pbo) on an every 14 day schedule. In Part A, 30 RA patients were randomized to Pbo or XmAb5871 in 4 consecutive dose cohorts of 0.3, 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg. After completion of Part A, 27 patients with active disease were enrolled in an extension cohort, Part B, to receive either 10 mg/kg XmAb5871 or Pbo in a 2:1 ratio. Disease efficacy assessments occurred 2 weeks after the 6thinfusion on Day 85.
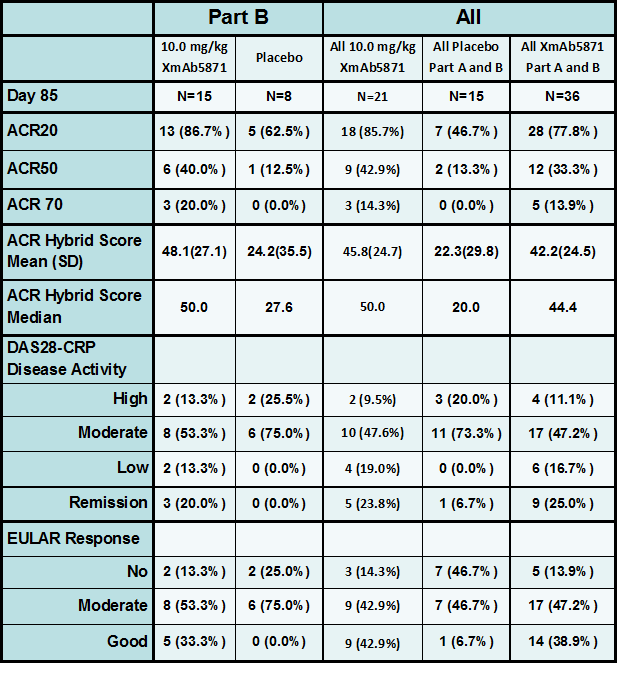
Results: A total of 57 patients were randomized; 40 patients received at least 1 dose of XmAb5871. Peripheral B cell count decreased ~40% from baseline after the 1stdose in all XmAb5871 cohorts and did not decrease further with subsequent doses. XmAb5871 was generally well tolerated, with 2 SAEs in the XmAb5871 group (infusion-related reaction, venous thrombosis). The most common treatment-related adverse events in the XmAb5871 group were nausea, vomiting or diarrhea that occurred only during the 1st infusion in 25% of patients. Two subjects experienced infusion reactions with hypotension (both at 10 mg/kg) and were discontinued. The nature and severity of these infusion reactions were consistent with those reported for other monoclonal antibody therapies. In Part B, 15 XmAb5871-treated and 8 Pbo-treated patients were evaluable for disease activity assessment at Day 85. More subjects treated with XmAb5871 (10 mg/kg) achieved DAS28-CRP low disease or remission at Day 85 than did the Pbo treated subjects. Similar trends were seen with other disease assessments. Median ACR Hybrid scores over time were consistently greater in XmAb5871-treated patients than in Pbo-treated patients.
Conclusion:
XmAb5871 administered over 12 weeks was found to be generally well tolerated. Although the trial was not powered to show a significant difference in efficacy results between XmAb5871 and Pbo, sufficient efficacy trends were seen to warrant continued clinical development of XmAb5871 in autoimmune diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zack D, Jaraczewska Baumann M, Korkosz M, Suljok G, Sramek P, Rojkovich B, Daniluk S, Bartalos J, Foster P. Results of a Phase 1b/2a Study of the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of XmAb®5871 in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/results-of-a-phase-1b2a-study-of-the-safety-tolerability-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-xmab5871-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/results-of-a-phase-1b2a-study-of-the-safety-tolerability-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-xmab5871-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/