Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Certolizumab pegol (CZP) is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker first approved in the U.S. in 2008. CZP is approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease in the U.S. and elsewhere. Data suggest that there is limited to no placental transfer of CZP to the fetus. However, there are few controlled studies published on the effect of CZP during human pregnancy. Data from the CZP pregnancy registry in the U.S. and Canada have been collected by MotherToBaby Pregnancy Studies conducted by the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS).
Methods: Pregnant women treated with CZP for an approved indication who had received at least one dose in the first trimester with or without continued use in pregnancy were enrolled in an observational prospective cohort study. Pregnant women with no exposure to CZP in pregnancy but with the same underlying diseases were enrolled in a disease-matched (DM) comparison group. Pregnant women with no chronic diseases were enrolled in a healthy comparison (HC) group. Pregnancy exposure and outcome data were collected from telephone interviews and medical records. Follow-up of live born children included a dysmorphological exam, review of pediatric records to 5 years of age, and developmental screening at 15-17 months of age. Crude Hazard Ratios (HR) and Relative Risks (RR) with 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) were calculated comparing the exposed group to the comparison groups, and adjusted HR (aHR) and RR (aRR) were calculated where appropriate using inverse probability of treatment weighting with propensity scores for selected confounders.
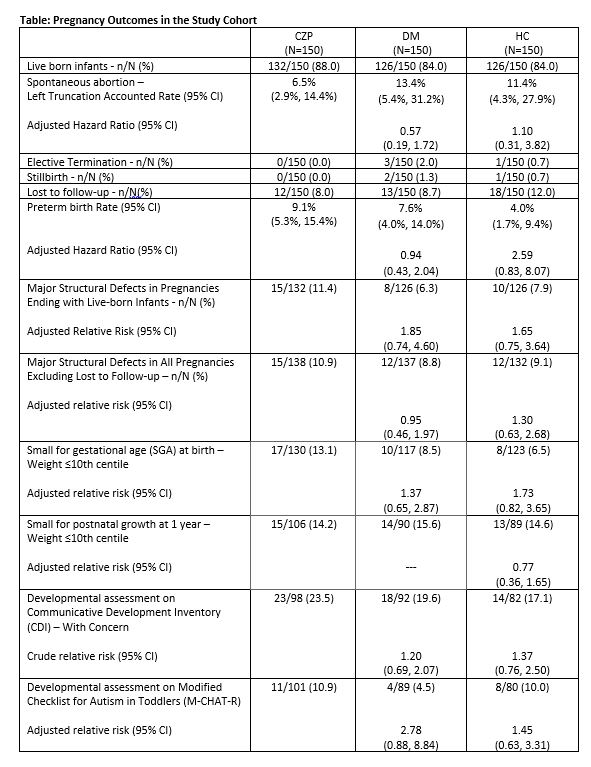
Results: Between March 2012 and May 2022, data were collected for 450 participants, consisting of 150 CZP exposed, 150 DM comparison and 150 HC pregnancies. In the CZP group, 12 (8.0%) took CZP only in the 1st trimester and 119 (86.9%) used CZP in all trimesters. Pregnancy outcomes are shown in the table. Major birth defects among live born infants were reported in 15/132 (11.4%) in the CZP group, compared to 8/126 (6.3%) in the DM group (aRR 1.85, 95% CI 0.74, 4.60), and 10/126 (7.9%) in the HC group (aRR 1.65, 95% CI 0.75, 3.64). Among all pregnancies excluding lost-to -follow-up, the aRR for major birth defects in CZP exposed compared to the DM group was 0.95 (95% CI 0.46, 1.97); compared to the HC group the aRR was 1.30 (95% CI 0.63, 2.68). There was no evidence of a pattern of major or minor structural defects in the CZP group, and no increased risks associated with CZP exposure for spontaneous abortion, preterm delivery, pre or postnatal growth deficiency, serious or opportunistic infections, malignancies, adverse vaccine reactions, or neurodevelopmental concerns.
Conclusion: Results from the analysis did not suggest a risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes following exposure to CZP. Although the sample size was relatively small, these results provide reassuring data to pregnant women who require treatment with CZP. Completion of data collection and analysis for an additional 326 pregnancies, including neurodevelopmental testing for a subset of children in the preschool to school-age range in each cohort, is anticipated in 2026.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chambers C, Adams J, Xu R, Johnson D, Luo Y, Jones K. Results from the Certolizumab-pegol Pregnancy Exposure Registry: An OTIS Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/results-from-the-certolizumab-pegol-pregnancy-exposure-registry-an-otis-autoimmune-diseases-in-pregnancy-project/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/results-from-the-certolizumab-pegol-pregnancy-exposure-registry-an-otis-autoimmune-diseases-in-pregnancy-project/