Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Plenary Session III
Session Type: ACR Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose:
Monogenic autoinflammatory interferonopathies, including chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatosis with lipodystrophy and elevated temperatures (CANDLE) and STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI), present with a prominent interferon (IFN)-response gene signature (IRS) in the blood, systemic inflammation, and organ-specific damage often associated with increased morbidity and mortality in childhood. An Expanded Access Program with baricitinib, a JAK kinase inhibitor with ex vivo IFN blocking capacity, was developed to provide baricitinib to patients (pt.) with no comparable or satisfactory treatment options.
Methods:
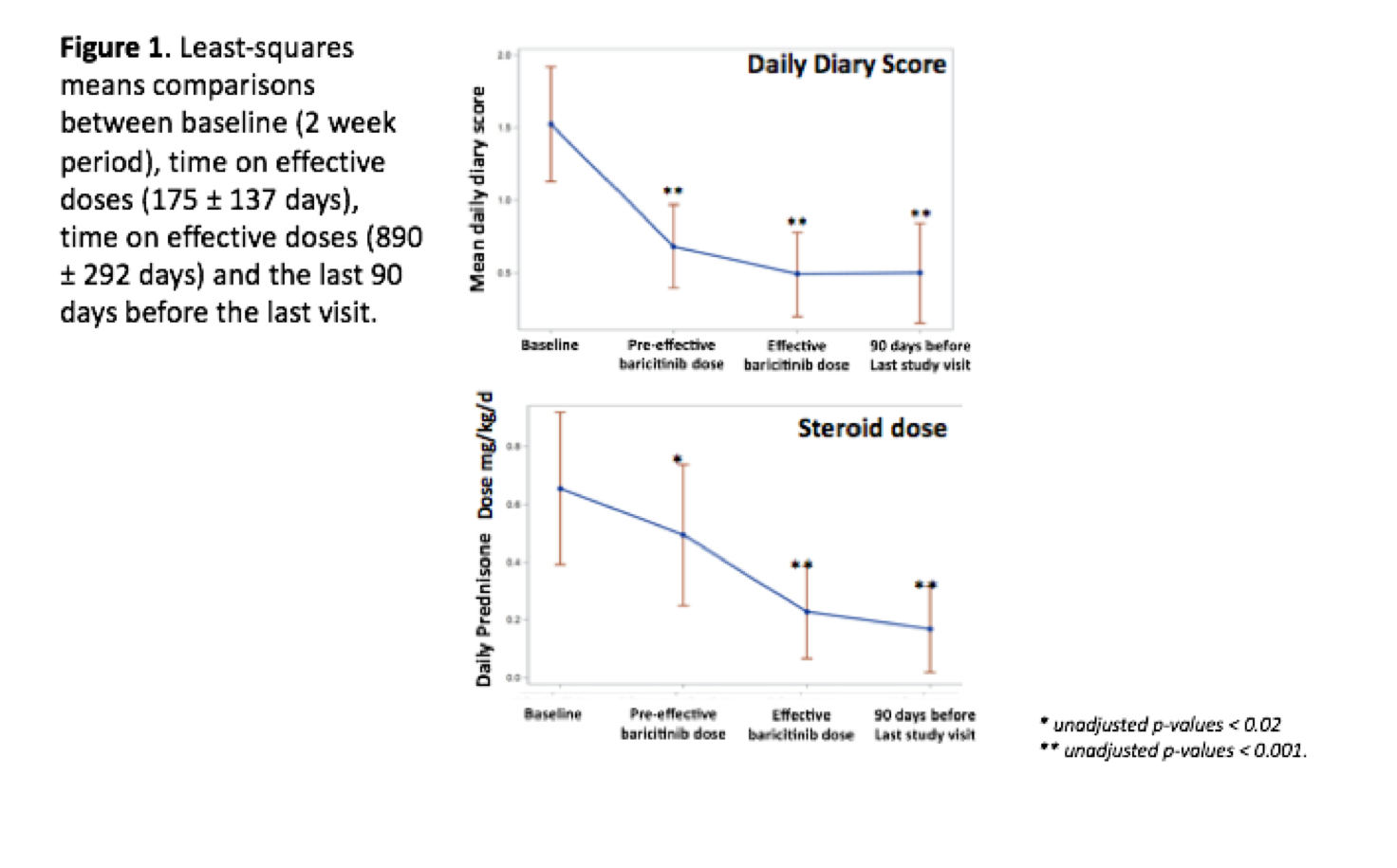
Potential benefit was assessed by reductions in daily symptom diary to <0.5 (CANDLE and CANDLE-like pt.) and to <1.0 (SAVI pt.) and reductions of steroid doses to <0.15mg/kg/day or by at least 50% from baseline. Quality of life assessments, linear growth, and changes in IRS and IFN-induced biomarkers are also reported. Drug safety was longitudinally followed. Paired t-tests were used to compare daily mean daily symptom diary and prednisone doses at the last clinic visit to baseline data.
Results:
Between October 2011 and October 2016, 18 pt. were enrolled and treated,10 CANDLE pt., 4 SAVI pt., and 4 CANDLE-like pt. Mean follow-up duration 3.0 years. The median daily symptom diary score decreased from 1.3 (IQR 0.93-1.78) to 0.25 (IQR 0.1-0.63) (p<0.001) with responses most significant in CANDLE patients. In 14 patients receiving steroids at baseline, daily prednisone doses decreased from 0.44 mg/kg/day (IQR 0.31-1.9) to 0.11 mg/kg/day (IQR 0.02-0.24) (P< 0.005); 5 of 10 CANDLE patients achieved lasting clinical remission. All active patients (n=16), except two, reported improvement in quality of life. 9 of the 13 patients with growth potential improved their Z-scores from -4.34 to -2.83 (p=0.02). DEXA Z-scores also improved from -4.0 to -3.1 (p=0.006). IFN scores significantly dropped and durably normalized in 5 CANDLE patients. Treatment-related serious adverse events included infections; 2 patients with genetically undefined interferonopathies discontinued due lack of efficacy, one also had avascular necrosis. One CANDLE patient developed BK viremia and azotemia and was discontinued from the program. The most common adverse events included upper respiratory infections and BK viruria (baseline screening for BK virus in blood and urine was not performed).
Conclusion:
Daily doses of baricitinib significantly improved clinical disease manifestations, laboratory parameters, linear growth, and bone mineral density, and decreased IFN signaling in patients with CANDLE, SAVI and 2 other autoinflammatory interferonopathies. Monitoring safety and efficacy is important in benefit-risk assessment.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the NIH IRP of NIAID and NIAMS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Montealegre Sanchez GA, Reinhardt A, Ramsey S, Wittkowski H, Hashkes PJ, Murias S, Berkun Y, Schalm S, Dare JA, Brown D, Stone DL, Gao L, Klausmeier TL, Carter JD, Colbert R, Chapelle DC, Kim H, Dill S, Almeida de Jesus A, Wakim P, Zlotogorski A, Ozen S, Brogan P, Goldbach-Mansky R. Response to JAK1/2 Inhibition with Baricitinib in “Candle”, “Savi” and “Candle-like” Diseases. a New Therapeutic Approach for Type I IFN-Mediated Autoinflammatory Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-jak12-inhibition-with-baricitinib-in-candle-savi-and-candle-like-diseases-a-new-therapeutic-approach-for-type-i-ifn-mediated-autoin/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-jak12-inhibition-with-baricitinib-in-candle-savi-and-candle-like-diseases-a-new-therapeutic-approach-for-type-i-ifn-mediated-autoin/