Session Information
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Clinical Aspects and Treatment: Psoriatic Arthritis
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: It is well established that methotrexate (MTX) co-medication improves efficacy of TNF-inhibitors (TNFi) in rheumatoid arthritis, while in ankylosing spondylitis it is widely accepted that it does not. The role of MTX co-medication in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is still unclear. Our objective was to investigate if patients receiving concomitant MTX have better responses and drug survival to their 1st TNFi.
Methods: Data are from NOR-DMARD, an observational study of adult patients with inflammatory arthropathies starting DMARD-treatment. Patients with PsA receiving their 1st TNFi, either combined with MTX or in monotherapy, were selected. Due to heterogeneity in clinical presentation, the selected outcome measures were patient and physician global assessments, MHAQ and SF-6D. Baseline characteristics and state and change at 3, 6 and 12 months were compared by two-sample t-test and Chi2 test, as appropriate. Drug survival at 1, 2 and 3 years was compared using Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank test, and sub-analyses were done for patients receiving Infliximab (IFX), Etanercept (ETN) and Adalimumab (ADA).
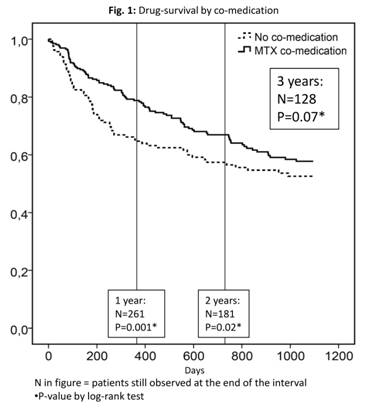
Results: 440 patients were included. We found significant baseline group differences in no. of swollen joints, physician global and SF6D scores (table 1). Three-month states and responses were similar between the groups, with significant differences only for physician global (table 1). Similar results were seen at 6 and 12 months. We did, however, find improved drug survival in the combination group (fig. 1) reaching statistical significance at 1 and 2 years. This was most prominent for IFX (p=0.01) and negligible for ETN (p= 0.79), with a trend for ADA (p=0.12).
Conclusion: We found similar responses at 3 months in PsA patients receiving their first TNFi with and without MTX co-medication. However, drug survival was better in patients receiving concomitant MTX, and this was most prominent in patients receiving IFX.
Table 1
|
Overall |
No co-medication |
MTX co-medication |
P-value |
|
|
Baseline characteristics
|
||||
|
N=440
|
N=170
|
N=270
|
||
|
Age (years) |
46.5 (11.6) |
47.0 (11.4) |
46.1 (11.7) |
0.46 |
|
Females (%) |
46.4 |
47.6 |
45.6 |
0.70 |
|
Disease duration (yrs) * |
5.2 (1.5-12.5) |
5.1 (1.1-11.7) |
5.5 (1.6-12.7) |
0.44 |
|
No of prev. DMARDs |
1.49 (1.09) |
1.49 (1.20) |
1.48 (1.02) |
0.30 |
|
Swollen joints * |
3 (1-6) |
2 (0-5) |
3 (1-7) |
0.004 |
|
CRP mg/l * |
9 (5–20) |
7 (5-22) |
9 (5-20) |
0.44 |
|
Physician global (0-100) |
37.4 (17.9) |
39.6 (19.2) |
36.0 (16.9) |
0.04 |
|
Patient global (0-100) |
54.6 (23.7) |
56.5 (22.8) |
53.4 (22.5) |
0.17 |
|
MHAQ score (0-3) |
0.70 (0.46) |
0.72 (0.47) |
0.69 (0.46) |
0.41 |
|
SF6D score (0-1) |
0.59 (0.12) |
0.57 (0.12) |
0.60 (0.12) |
0.01 |
|
3-month responses
|
||||
|
N=328 |
N=123 |
N=205 |
||
|
Physician global (0-100) |
15.9 (15.0) |
18.5 (17.1) |
14.4 (13.5) |
0.02 |
|
Δ Physician global |
-21.7 (22.1) |
-20.0 (23.0) |
-22.6 (21.7) |
0.32 |
|
Patient global (0-100) |
29.2 (23.9) |
32.4 (26.1) |
27.3 (22.3) |
0.07 |
|
Δ Patient global |
-24.8 (26.4) |
-22.0 (29.1) |
-26.3 (24.7) |
0.17 |
|
MHAQ score (0-3) |
0.39 (0.41) |
0.42 (0.43) |
0.37 (0.40) |
0.30 |
|
Δ MHAQ score |
–0.31 (0.44)
|
–0.30 (0.50)
|
–0.32 (0.39)
|
0.67 |
|
SF-6D (0-1) |
0.70 (0.15) |
0.68 (0.15) |
0.70 (0.14) |
0.15 |
|
Δ SF-6D |
0.10 (0.13) |
0.10 (0.14) |
0.10 (0.13) |
0.92 |
Values are expressed as mean (SD) unless otherwise stated
MHAQ = Modified health assessment questionnaire
SF-6D = Short form – 6 dimensions
*Median(IQR)
Disclosure:
K. M. Fagerli,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
8,
Pfizer Inc,
8,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
8,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
8;
E. Lie,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
8;
D. van der Heijde,
Abbott Laboratories; Amgen; AstraZeneca; BMS; Centocor: Chugai; Eli-Lilly; GSK; Merck; Novartis; Pfizer; Roche; Sanofi-Aventis; Schering-Plough; UCB; Wyeth,
5,
Imaging Rheumatology,
4;
M. S. Heiberg,
None;
E. Rødevand,
None;
S. Lexberg,
Pfizer Inc,
8,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
8,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
8,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
8;
S. Kalstad,
None;
K. Mikkelsen,
None;
T. K. Kvien,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
8,
AstraZeneca,
8,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
8,
NiCox, S.A.,
8,
Pfizer Inc,
8,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
8,
UCB,
8,
BMS,
5,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
5,
NiCox, S.A.,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
UCB,
5.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-and-drug-survival-of-1st-tnf-inhibitor-in-440-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-what-is-the-role-of-co-medication-with-methotrexate/