Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: 18F-FDG-PET/CT is a sensitive and comprehensive technique to diagnose giant cell arteritis (GCA). This technique may be also very useful to test whether vascular inflammation in GCA has disappeared or not, judging effectiveness of anti-inflammatory treatment. However, the role of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in monitoring disease activity and judging disease remission is less well-established to date.
RIGA is an observational 2-center study that addresses the resolution of vascular inflammation in patients with new-onset GCA that are treated with either glucocorticoid monotherapy (GLC), GLC/methotrexate (MTX) or GLC/tocilizumab (TOC).
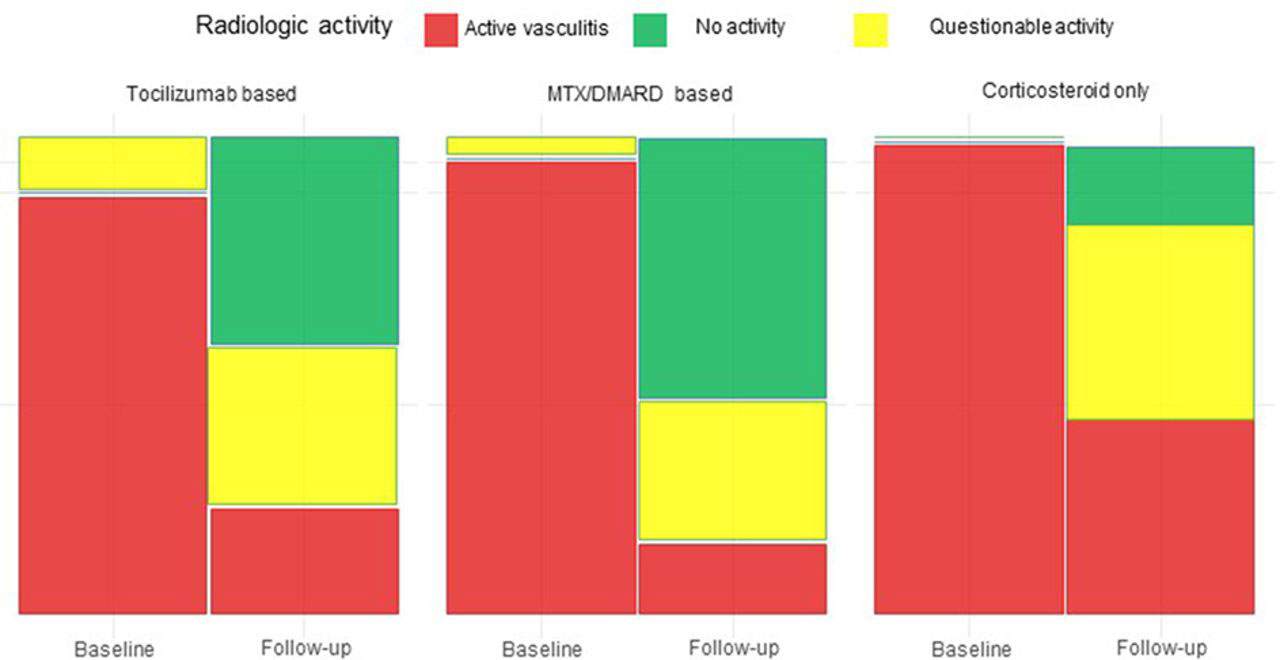
Methods: Patients with newly diagnosed GCA with large vessel involvement were clinically documented, subjected to sequential 18F-FDG-PET/CT scanning and received treatment with GLC, MTX or TOC upon physicians’ decision. Images were graded as active, questionable active and inactive according to nuclear medicine physician opinion and additionally graded by PETVAS score proposed by Grayson et al. (0-27) (1). We performed a mixed effects linear regression analysis to estimate the change in the PETVAS score adjusted by baseline CRP level and tested for treatment group interactions. We compared the proportion of radiologic activity states according to the activity tracer uptake in the follow up 18F-FDG-PET/CT scan in three treatment groups with a chi-squared test.
Results: We included 48 patients (n=20 from Germany, n=28 from Italy) with a mean age of 66 years. At baseline, 18F-FDG-PET/CT scan was graded as active in 46 patients while it was graded as questionable active in the remaining 2 patients. The mean CRP level was 66,8 mg/L (min 1,2; max 233,2 mg/l) and the mean PETVAS score was 21,1 (min=10 max=27). 12 patients received GLC, 27 MTX and 9 TOC as primary treatment. Follow-up PET/CT scans were graded as active in 11, questionable active in 16 and inactive in 21 patients. The mean CRP level at follow up was 12,4 mg/l (min 0,2; max 76,0) and the mean PETVAS score was 9,1 (min 0, max 27) with significant decreases in all 3 groups. The mean adjusted improvement in the PETVAS score (95%CI) was 13.0 (8.7 – 17.3) in GLC, 11.7 (8.9 – 14.6) in MTX and 11.8 (6.8 – 16.7) in TOC groups and interaction terms for treatment effect were not significant. However, only 17% of patients who received GLC showed no vasculitis activity in their follow up PET-CT compared to 53% of patients who received MTX or TOC (figure 1).
Conclusion: GLC, MTX and TOC significantly reduced vascular inflammation in GCA, but no significant differences between the three treatment strategies was found in this yet small population. However, when looking at complete resolution of vascular inflammation, MTX and TOC appear as being superior to GLC monotherapy, suggesting that addition of these agents right from the beginning of treatment of GCA may be beneficial to achieve complete control of vascular inflammation.
1. Grayson, P. C. et al, 18F‐Fluorodeoxyglucose–Positron Emission Tomography As an Imaging Biomarker in a Prospective, Longitudinal Cohort of Patients With Large Vessel Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol, 70: 439-449 doi:10.1002/art.40379
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schönau V, Roth J, Tascilar K, Rech J, Schmidt D, Kuwert T, Crescentini F, Boiardi L, Casali M, Versari A, Pazzola G, Schett G, Salvarani C, Muratore F. Resolution of Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis Receiving Glucocorticoids, Methotrexate or Tocilizumab Treatment: Data from the Italian/German RIGA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/resolution-of-vascular-inflammation-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-receiving-glucocorticoids-methotrexate-or-tocilizumab-treatment-data-from-the-italian-german-riga-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/resolution-of-vascular-inflammation-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-receiving-glucocorticoids-methotrexate-or-tocilizumab-treatment-data-from-the-italian-german-riga-study/