Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Anxiety and depression are highly prevalent in patients (pts) with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA)/PsA.1,2 We report mental health data in pts with axSpA/PsA from trials of bimekizumab (BKZ; monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A).
All trials coincided at least partially with COVID-19 pandemic; local lockdown measures/health issues had varying impacts on mental health.
Methods: Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) reported for pooled phase 2/3 axSpA/PsA trial populations (BE AGILE 1 & 2, BE MOBILE 1 & 2, BE MOVING, AS0013; BE ACTIVE 1 & 2, BE OPTIMAL, BE COMPLETE, BE VITAL). An independent Neuropsychiatric Adjudication Committee evaluated potential suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB) TEAEs, including abnormal electronic Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (eC-SSRS) and Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ)-9 scores.
BE MOBILE 1 & 2 (axSpA: NCT03928704; NCT03928743), BE OPTIMAL and BE COMPLETE (PsA: NCT03895203; NCT03896581) were phase 3 trials of subcutaneous (sc) BKZ 160 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W);3–6 all double‑blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled to Week (Wk) 16. BE OPTIMAL included an active reference arm (sc adalimumab 40 mg Q2W) to provide a reference for BKZ benefit/risk profile. Pts with active suicidal ideation or PHQ-9 ≥15 were excluded at screening.
eC-SSRS questionnaire assessed SIB of increasing severity; responses pooled within phase 3 axSpA/PsA trials to Wk 16 (PBO-controlled period); reported to Wk 52 of BE OPTIMAL (active treatment-blind period with reference arm).
We report depression severity scores to 1 year (yr) using PHQ-9 (0–27; higher scores indicate worse depression). Data reported as observed case or using multiple imputation.
Results: In pooled analyses of phase 2/3 trials (2,804.0 patient-yrs [PY] of BKZ exposure in axSpA [N=928]; 3,949.0 PY in PsA [N=1,415]), exposure-adjusted incidence rate/100 PY (95% CI) of adjudicated SIB TEAEs was 0.11 (0.02, 0.31) for axSpA; 0.05 (0.01, 0.18) for PsA. Rates were low for anxiety disorders (axSpA 0.04 [0.00, 0.20]; PsA 0.03 [0.00, 0.14]) and depressive disorders (axSpA 0.32 [0.15, 0.61]; PsA 0.41 [0.23, 0.66]); there were no completed suicides across trials.
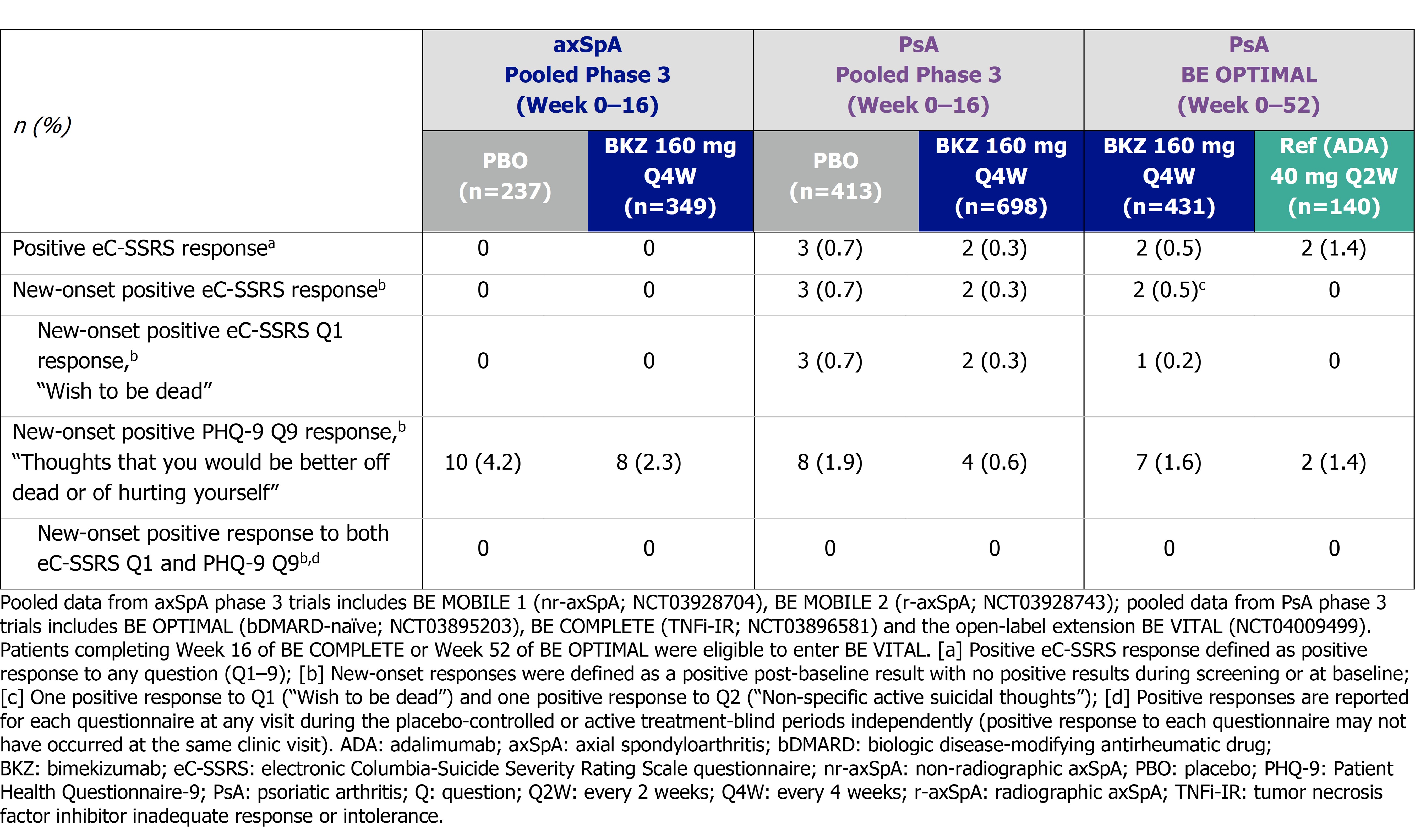
To Wk 16, proportions of BKZ pts with overall and new-onset positive eC-SSRS responses (to any question) were low and generally similar to PBO in axSpA/PsA trials (Table). Most new‑onset responses were to Q1 (passive suicidal ideation).
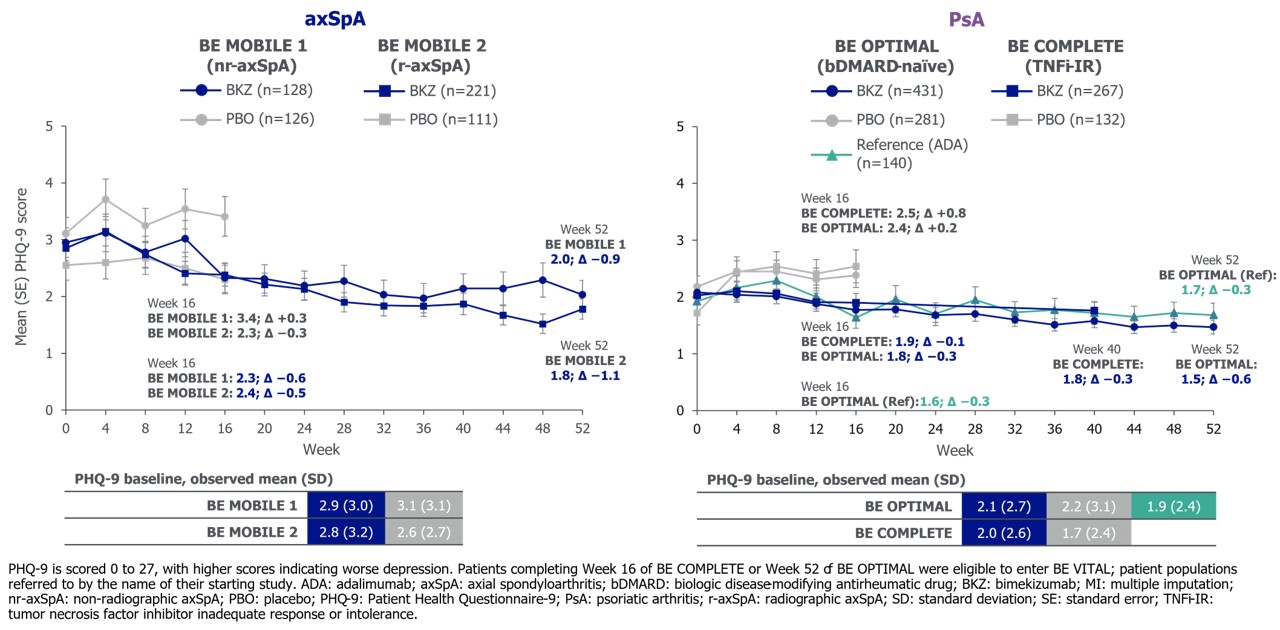
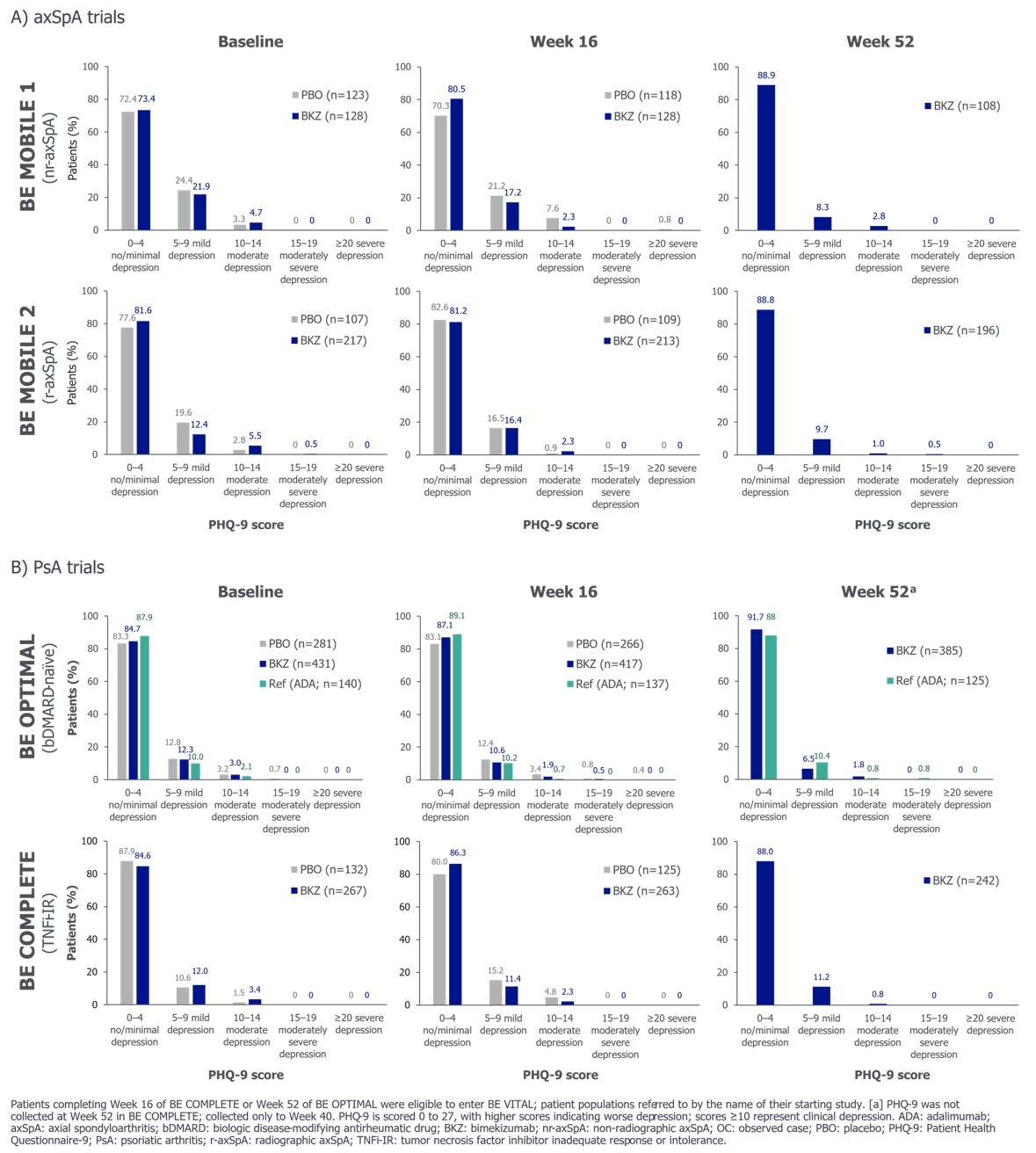
Mean PHQ-9 scores were low at baseline (BL). To Wk 16, mean PHQ-9 scores on BKZ remained low and generally lower than PBO. Low mean PHQ-9 scores were sustained to 1 yr on BKZ and were similar to reference arm in BE OPTIMAL (Figure 1). Most pts had no/minimal depression (PHQ-9 0–4) at BL, Wk 16 and Wk 52 (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Across trials of BKZ in pts with axSpA and PsA, eC-SSRS and PHQ-9 scores were low and similar to PBO to Wk 16. Adjudicated SIB, anxiety, and depression rates remained low to 1 yr, despite impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic.
References: 1. Zhao SS. Clin Rheumatol 2020;39:217–25; 2. Reddy KN. Eur J Rheumatol 2021;9:8–13; 3. Baraliakos X. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;83:199–213; 4. Ritchlin CT. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82:1404–14 ; 5. Coates LC. RMD Open 2024;10:e003855; 6. BE VITAL: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04009499.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Magrey M, Poddubnyy D, Lebwohl M, Bajracharya R, de Cuyper D, Marten A, Peterson L, Stark J, Merola J. Reporting Mental Health and Associated Disorders from Trials of Bimekizumab in Patients with Active Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reporting-mental-health-and-associated-disorders-from-trials-of-bimekizumab-in-patients-with-active-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reporting-mental-health-and-associated-disorders-from-trials-of-bimekizumab-in-patients-with-active-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/