Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Depression is highly prevalent in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) is a simple screening tool widely used in medical settings and validated in multiple ethnic and linguistic groups. However, its measurement properties have not been assessed among low socioeconomic status (SES) Spanish-speaking Latinos with RA. We investigated factor structure, reliability and validity of the Spanish-language PHQ-9 in low SES Latinos with RA living in the US.
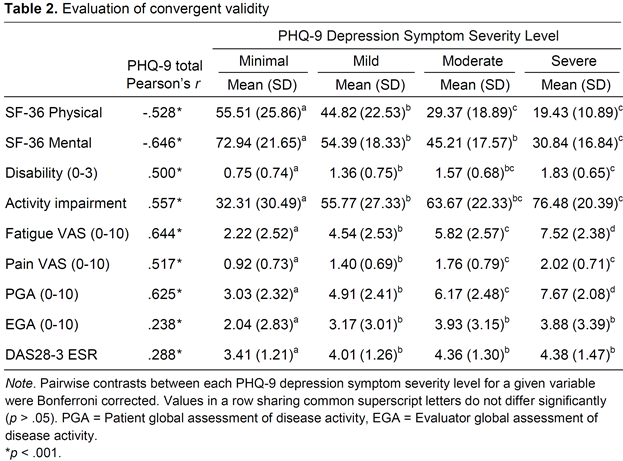
Methods: We evaluated 447 patients from a single center. On the PHQ-9, participants rated from 0 (none) to 3 (almost daily) their feelings of depressed mood and 8 other symptoms of depression (see Table 1). Total scores (0-27) correspond to depression severity levels: minimal (0-4), mild (5-9), moderate (10-14), and moderately severe to severe (>=15). Internal consistency and reliability were examined with Cronbach’s alpha and corrected item-total correlations. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) assessed the hypothesized unidimensional factor structure. Multi-group CFA examined the generalizability of the factor structure across distinct patient subgroups. Convergent validity was explored via correlations among PHQ-9 scores and measures of health-related quality of life (Physical and Mental Components of the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey), disability (Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index), activity impairment (Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire), fatigue VAS, pain VAS, patient and evaluator global assessments of disease activity, and Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28-3 ESR).
Results: Patients were 89% female with a mean age of 52.6 years and mean RA duration of 10.7 years. The internal consistency of the PHQ-9 was good (a =.91) and all corrected item-total correlations reached an acceptable level (Table 1). CFA showed the one-factor solution provided a good fit to the data: S-Bx2(27) = 67.85, p <.05, CFI =.971, TLI =.961, RMSEA =.058 with all significant factor loadings (Table 1). Multi-group CFA demonstrated the factor structure can be generalized across age groups, RA disease duration and levels of disease activity. Convergent validity was supported by significant associations of PHQ-9 scores and severity levels in the expected directions with related measures (Table 2).
Conclusion: Findings support use of the PHQ-9 as a brief, low-burden screen for depression in low SES Spanish-speaking Latinos with RA. 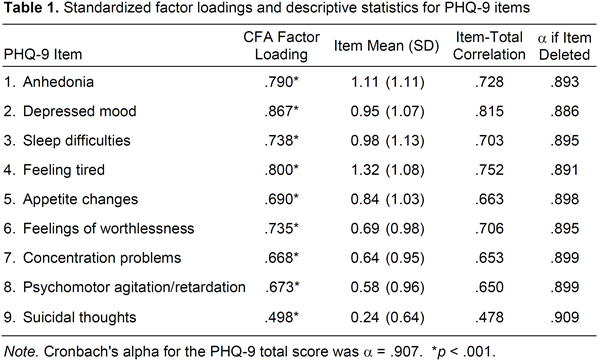
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ormseth S, Draper T, Hernandez E, Karpouzas GA. Reliability and Validity of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for Assessment of Depression in Socioeconomically Disadvantaged Latinos with Rheumatoid Arthritis Living in the United States [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-and-validity-of-the-patient-health-questionnaire-9-for-assessment-of-depression-in-socioeconomically-disadvantaged-latinos-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-living-in-the-united-states/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-and-validity-of-the-patient-health-questionnaire-9-for-assessment-of-depression-in-socioeconomically-disadvantaged-latinos-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-living-in-the-united-states/