Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Calprotectin is a member of S100 leukocyte. Serum calprotectin is a sensitive biomarker of disease activity in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). While various CV risk score only shown modest correlation with augmented CV risk in patient with PsA, whether calprotectin could play an addition role remains uncertain. Therefore, the aim of this study is to elucidate the association between serum calprotectin and subclinical atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness in patient with PsA
Methods: Seventy-eight PsA patient (age: 53±11 years, 47(54%) male) without CV event was recruited into this cross-sectional study. High resolution carotid ultrasound was performed to assess the presence of carotid plaque and intima-media thickness (IMT). Arterial stiffness was measured by branchial-ankle pulse wave velocity (PWV) and augmentation index (AIx). Serum calprotectin level was measured by QUANTA Lite Calprotectin Extended Range ELISA kit from (INOVA Diagnostics, San Diego, CA, USA).
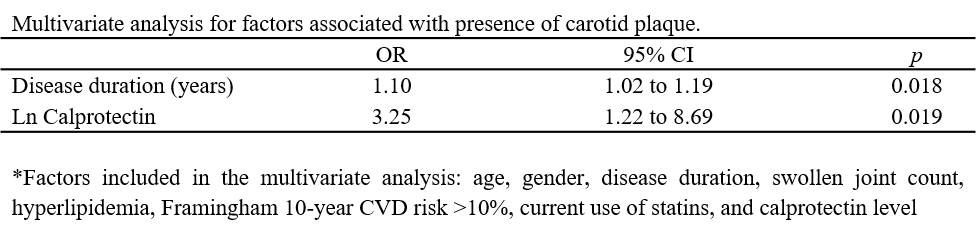
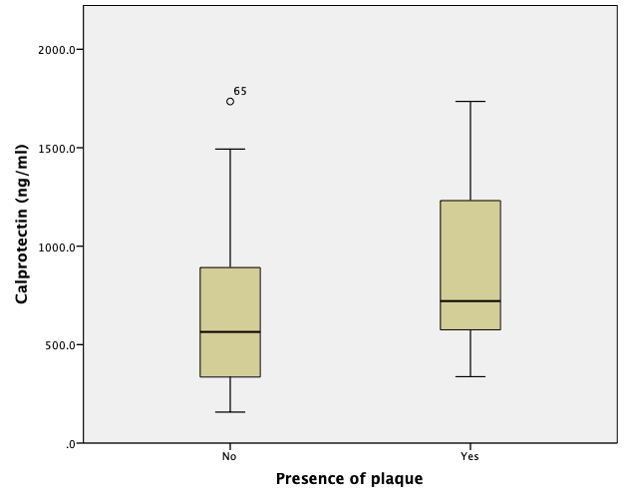
Results: 29/78 (38%) of patient had carotid plaque (CP+). Subjects in the CP+ group were older, had higher inflammatory burden in terms of higher number of swollen joint and longer disease duration. The prevalence of statins use was also higher in the CP+ group. Serum calprotectin level were significantly higher in the CP+ group (CP- group: 639.2 ±378.2 ng/ml,vs CP+ group: 911.8ng/ml ±429.4, p=0.005) (Figure 1). Using multivariate logistic regression analysis, higher level of ln calprotectin was an independent explanatory variable associated with the presence of carotid plaque (OR: 3.25, 95%CI: 1.22 to 8.69, p=0.019) after adjusting for baseline covariates. There was also significant correlation between calprotectin level and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) (r=0.237, p=0.037), mean IMT (r=0.301, p=0.021) and maximum IMT (r=0.265, p=0.043). However, no significant association were observed between calprotectin level and PWV or AIx.
Conclusion: Increased calprotectin level were associated with presence of plaque and increased IMT. Serum calprotectin may be a novel biomarker for assessing CV risk in patient with PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheng I, Li M, Li E, Lee A, Tam L. Relationship Between Serum Calprotectin Level and Presence of Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Arterial Stiffness in Patient with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-serum-calprotectin-level-and-presence-of-subclinical-atherosclerosis-and-arterial-stiffness-in-patient-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-serum-calprotectin-level-and-presence-of-subclinical-atherosclerosis-and-arterial-stiffness-in-patient-with-psoriatic-arthritis/