Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: It has been proposed that the fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) phenotype is determined by genetic factors, lack of physical exercise, mood disorders, maladaptive pain responses, and both current and past stressors, including a history of abuse. In this study we examined the predictive role of a history of abuse on FMS severity measures, and the association between self-reported abuse and socioeconomic status, symptoms, psychiatric comorbidities, and disability.
Methods: All consecutive patients clinically diagnosed with FMS who answered the question ‘Do you have a history of abuse?” were enrolled. Patients’ characteristics were compared between those who reported a history of abuse and those how did not. Linear regression analysis was performed to determine the predictive effect of a history of abuse on fibromyalgia impact questionnaire and fibromyalgianess scale, used as FMS severity measures.
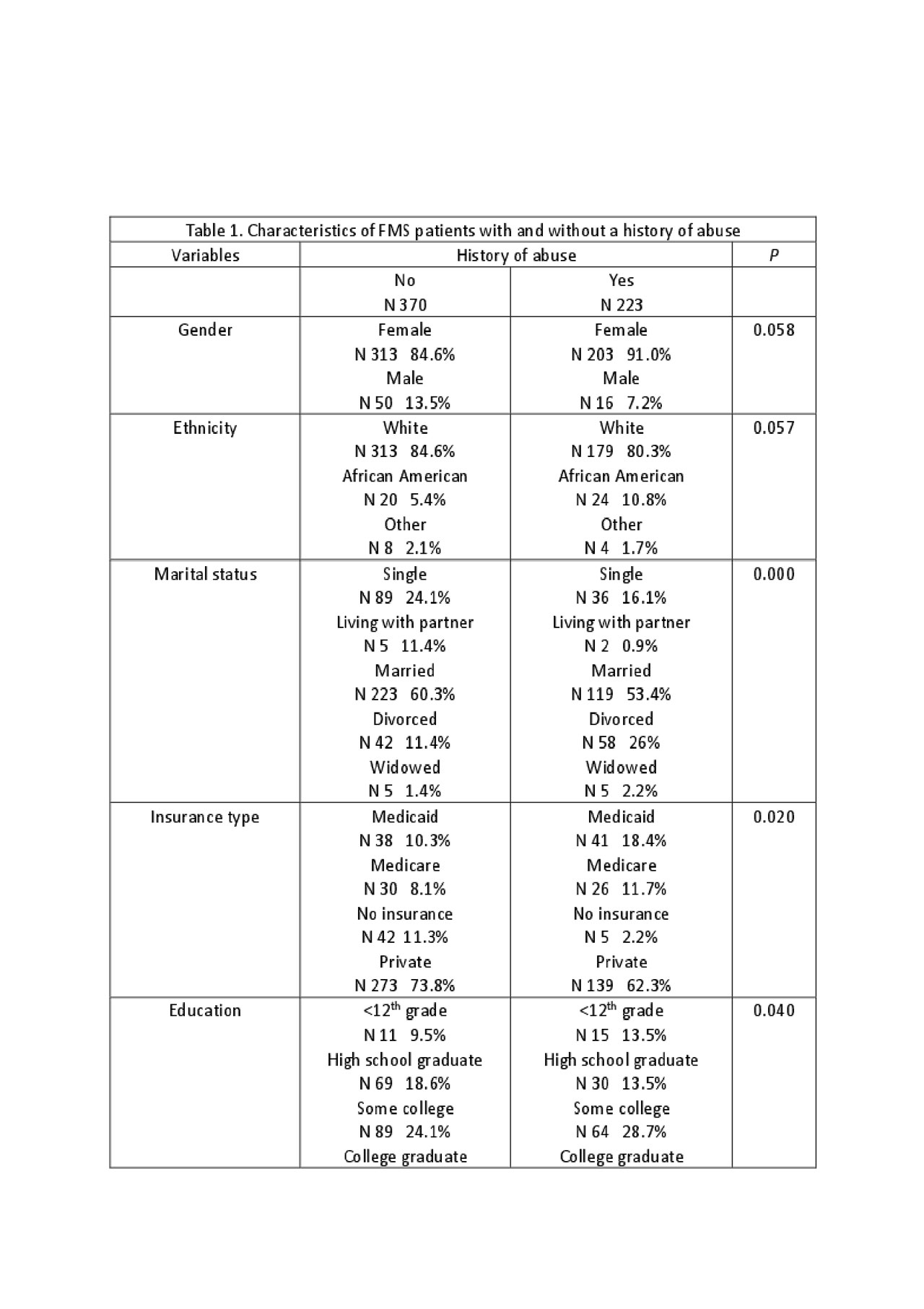
Results: We enrolled 593 consecutive patients with FMS, mean age 43.8 (12.3), 87% female, of which 85.2% met the ACR 2010 criteria. A history of abuse was reported by 223 patients, sexual abuse by 125 (56.5%), physical abuse by 155 (69.5%) and both by 78 (34.9%). Fibromyalgia patients with a history of abuse had worse socioeconomical status as measured by higher percentages of single and divorced patients, lower education level, lack of private insurance and greater reliance on Medicare and Medicaid, lower employment rates, and higher disability compared with those without abuse. A higher prevalence of personal and family history of psychiatric comorbidity was found in patients with a history of abuse. Fibromyalgia severity scores, including fibromyalgianess scale, pain disability index, fibromyalgia impact questionnaire and the health assessment disability index were all higher in patients with FMS and a history abuse compare to those without abuse (Table 1). A linear regression model predictied 46% of FMS severity measured by fibromyalgia impact questionnaire variability, p< 0.0005, from abuse, exercise, non-refreshing sleep, current stressors, depression and anxiety (Table 2). A similar model, p< 0.0005, predicted 32% of fibromyalgianess scale variability (Table 3).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that stressors such as abuse have a wide range of detrimental effects on FMS. We recommend that abuse should be inquired about in all patients evaluated for FMS as this may give more clarity to the nature and severity of the FMS presentation and prompt the need for psychological interventions.
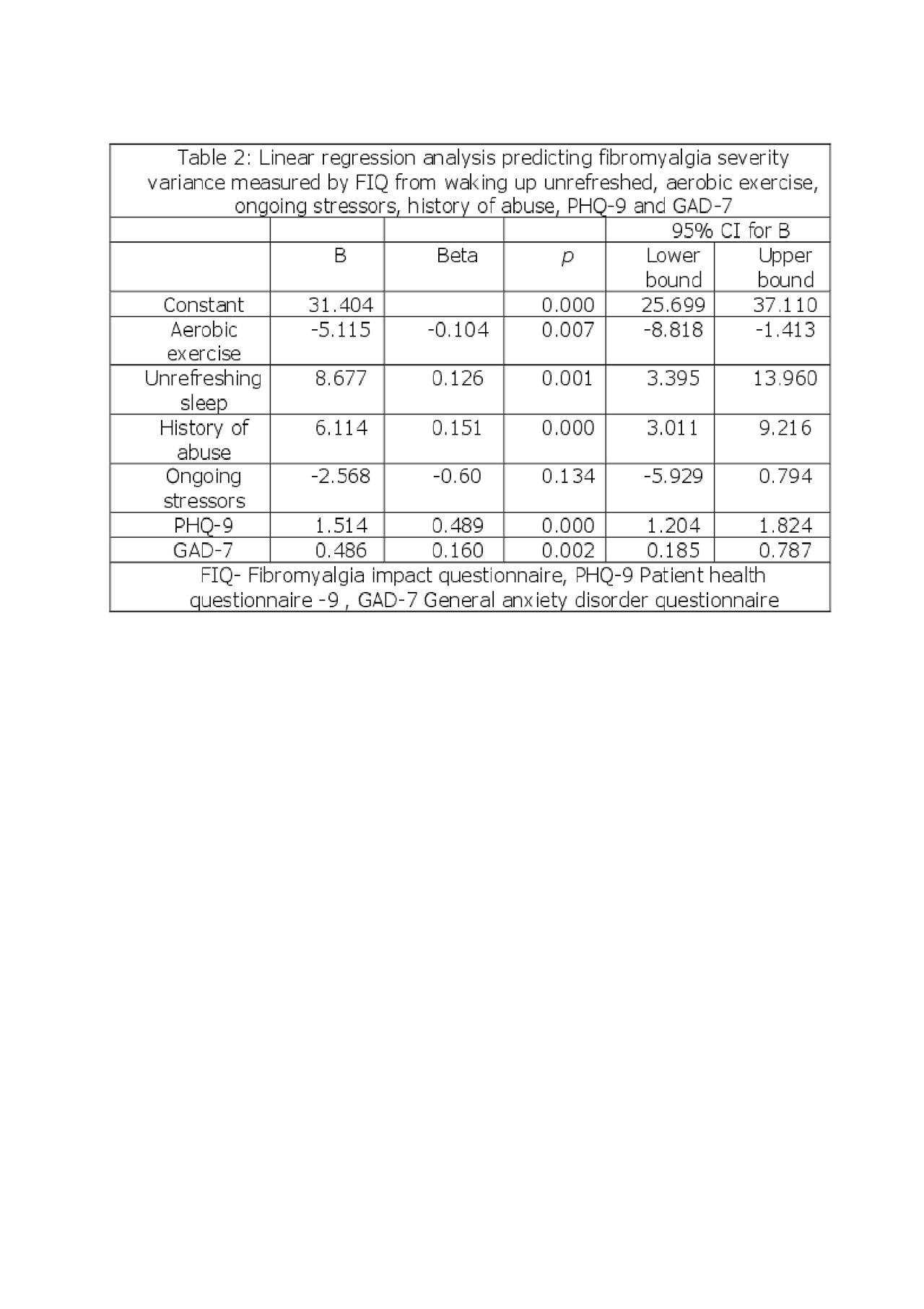
Table 2 for ACR abuse abstract
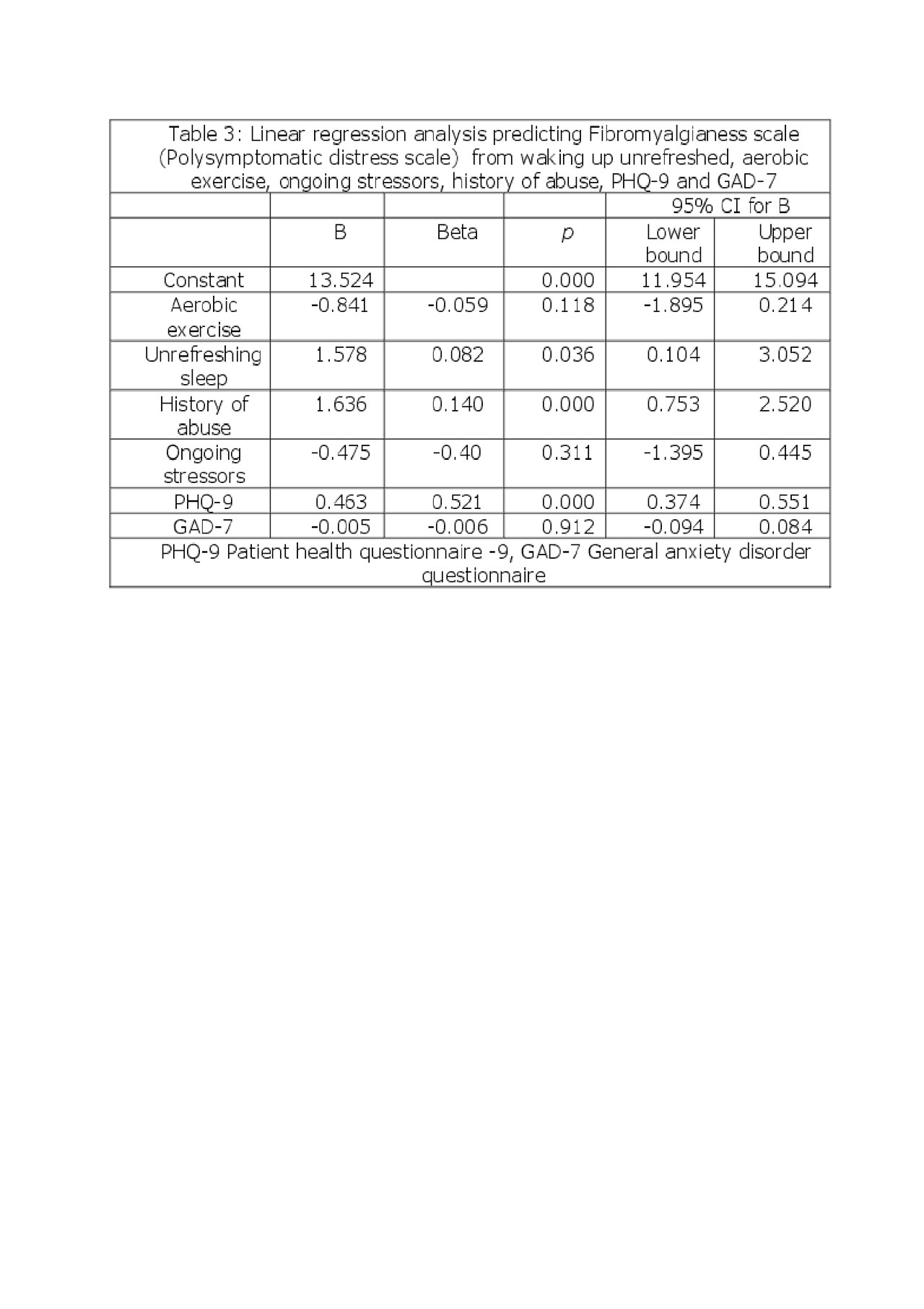
Table 3 for ACR abuse abstract
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gota C, Kaouk S, Yaseen K, Jhala N, Wilke W. Relationship Between a History of Abuse and Fibromyalgia Symptoms and Severity: Data from the Cleveland Clinic Fibromyalgia Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-a-history-of-abuse-and-fibromyalgia-symptoms-and-severity-data-from-the-cleveland-clinic-fibromyalgia-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-a-history-of-abuse-and-fibromyalgia-symptoms-and-severity-data-from-the-cleveland-clinic-fibromyalgia-registry/