Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Here we hypothesized that (i) IL-23/IL-23R system more specifically the specific IL-23p19 subunit mediated signaling system regulates expansion/maintenance and functional maturation in respect to production of the signature cytokines of Th17 cells (IL-17 and IL-22) in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and that (ii) a high affinity humanized IgG1/j monoclonal antibody that binds to the p19 subunit of IL-23 such as tildrakizumab will block IL-23 induced JAK/STAT signaling system and inhibit expansion/maintenance and functional maturation of the effector Th17 cells in PsA and AS.
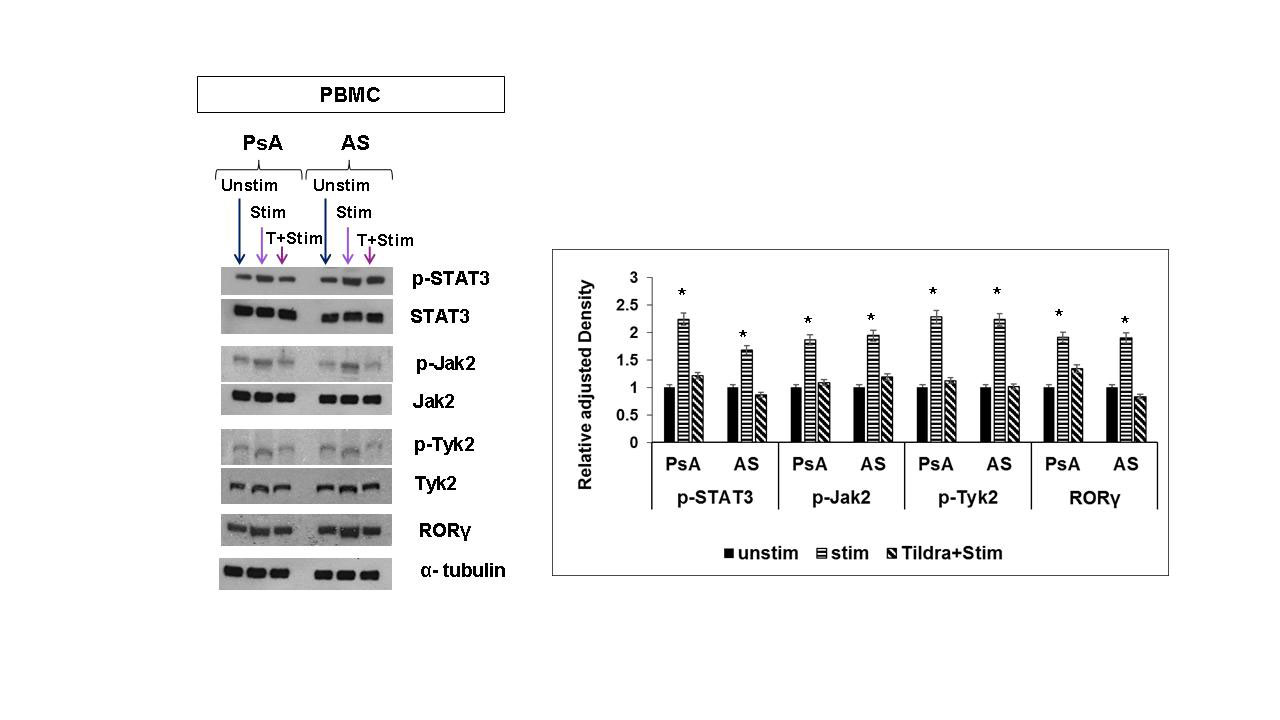
Methods: PsA and AS patients with an active disease not on DMARDS/biologics were recruited in this study. Mononuclear cells from peripheral blood (PBMC) and synovial fluid (SFMC) of age/sex matched PsA patients (n=10), PBMCs from AS patients (n=10) and normal individuals (n=10) were isolated. Magnetically selected CD3+ T cells (106 cells/ml) were activated with anti-human CD3/CD28 cocktail+rIL-23. Activated CD3+ T cells were cultured with and without tildrakizumab (120 pM). To identify the activated memory CD4+CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells and CD4+CD11a+CD45RO+IL-22+ T cells Hi-D FACS studies were performed (FACSFusion Aria); the % of cell population and the MFI were analyzed by using Flow Jo software. Anti-proliferative effect of tildrakizumab on PBMCs and SFMCs was assessed by MTT and CFSE dilution assays. Immunoblot assays were done on lysates of the cultured CD3+T cells to identify Jak2/p-Jak2, Tyk2/p-Tyk2, stat3/p-stat3, and RORγt.
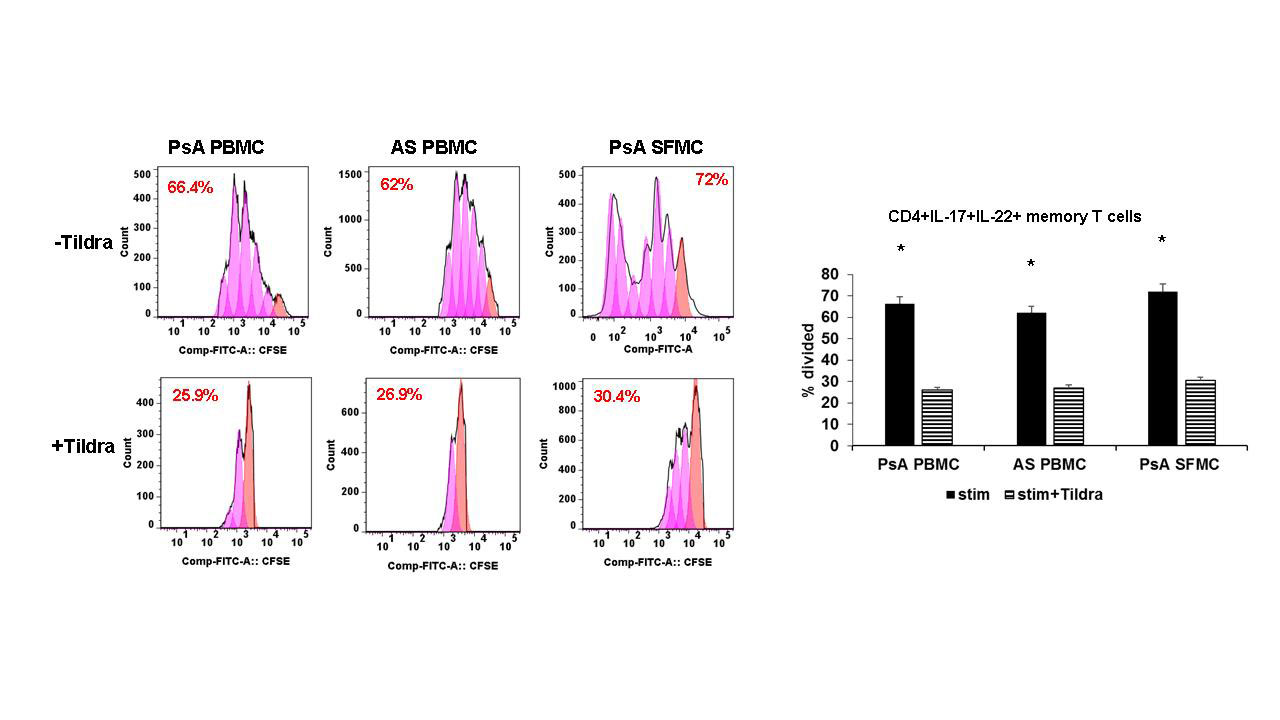
Results: (i). In PBMCs/SFMCs of PsA and AS patients rIL-23 induced marked upregulation of IL-17A and IL-22 in the memory T cells (CD11a+CD45RO+); tildrakizumab inhibited rIL-23 induced IL-17 and IL-22 expression in CD4+ memory T cells, more specifically we noticed with tildrakizumab there was marked reduction of CD4+CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells and CD4+CD11a+CD45RO+IL-22+ T cells (p< .01)) (ii) tildrakizumab significantly inhibited proliferation of these CD4+IL-17+ memory T cells and CD4+IL-22+ (Fig 1) (iii) Immunoblot assays demonstrated PsA/AS activated CD3+ T cells treated with tildrakizumab had decreased expression of phospho-STAT3/Jak2/Tyk2/RORgt by two-folds (p< 0.001) compared to CD3+ T cells not treated with tildrakizumab (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Marked upregulation of IL-23 at the disease sites of PsA and AS is well established. rIL-23 activated sorted pathological CD3+ T cells in PsA and AS induced proliferation of CD4+IL-17+IL-22+ memory T cells and upregulations of IL-17A and IL-22 (by ELISA) and tildrakizumab inhibited all these outcomes significantly. We noticed in secukinumab treated PsA patients (n=10) those who had pretreatment higher levels of IL-22 did not respond to secukinumab. This suggests that by blocking the IL-23R an additional therapeutic advantage can happen because of its inhibition of both IL-17 and Il-22. Putting together here we have provided the (i) proof of concept about IL-23p19 induced immune dysregulations in PsA and AS (ii) the potentials of p19 targeted therapy for PsA and AS (iii) a prospect for a choice of anti-IL23p19 therapy in anti-IL-17 resistant patients.
PBMCs of PsA -n=10-, AS -n=10-, OA -n=10- and SFMCs of PsA -n=5-, OA -n=5- were stained with 5μM CFSE and then incubated in the presence or absence of tildrakizumab prior to stimulation with CD3/CD28+rIL-23. HI-D FACS studies were performed to identify live CD3+CD4+CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+IL-22+ T cells. Cells pre-treated with tildrakizumab had significant reduction of proliferation of IL-17+IL-22+ memory T cells -p<.01-.
Unstim= Unstimulated; Stim= Stimulated, T+ Stim= tildrakizumab + Stimulated
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raychaudhuri S, Raychaudhuri S. Regulatory Role of IL-23 and Its Receptor System in Spondyloarthritis and Its Therapeutic Relevance in anti-IL-17 Failure Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/regulatory-role-of-il-23-and-its-receptor-system-in-spondyloarthritis-and-its-therapeutic-relevance-in-anti-il-17-failure-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/regulatory-role-of-il-23-and-its-receptor-system-in-spondyloarthritis-and-its-therapeutic-relevance-in-anti-il-17-failure-patients/