Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Fibroblast like synoviocytes (FLS) and T lymphocytes are considered as major effector cells in the pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis (AA) such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), due to their significant contribution in formation of pathognomonic “pannus”1,2. Several studies suggest deficiency of Vitamin D in RA and its correlation with disease severity1,3. 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 (Vit D) is an active metabolite of Vitamin D3 and induces immuomodulatory effect through Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) which is expressed on antigen presenting cells, lymphocytes, FLS. Here we are reporting the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic potential of Vit D in FLS and T lymphocytes of AA patients.
Methods: PBMC and FLS were isolated respectively from blood and synovial tissues of RA (n=5) and PsA (n=5) patients. CD3+ T cells were magnetically sorted from PBMC. FLS were cultured in presence or absence of growth factor (PDGF), pro-inflammatory cytokine (IL-17) and Vit D (10-6M) for 5 days. T cells were stimulated with CD3/CD28 cocktail and treated with Vit D (10-6M) for 5 days. MTT and flow cytometric (CFSE) based proliferation assays were performed. T cell apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry using Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI). Staurosporine was used as a positive control for apoptosis assay.
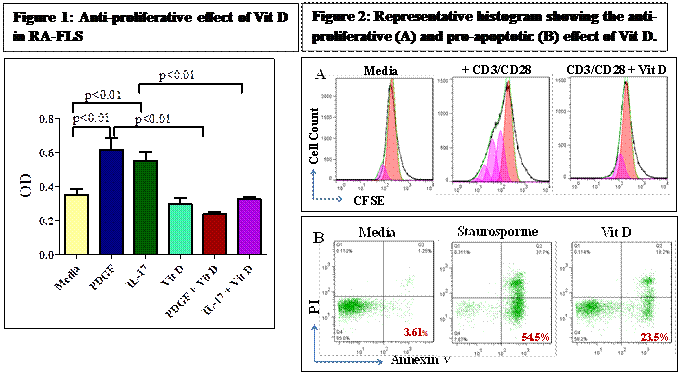
Results: In MTT assay (n=5), Vit D significantly inhibited the PDGF (OD: 0.61 ± 0.06 vs. 0.23 ± 0.01, p<0.01) and IL-17 (0.55 ± 0.05 vs. 0.32 ± 0.01, p<0.01) induced proliferation of RA-FLS (Figure 1). Similar results were observed with PsA-FLS. CD3/CD28 stimulation induced significant proliferation of CD3+ T lymphocytes (17.54 ± 2.48% vs. 6.06 ± 1.13%, p<0.01) and Vit D significantly inhibited activated T lymphocytes proliferation (11.21 ± 2.28 vs. 17.54 ± 2.48%, p<0.01) (Figure 2A). We also observed that Vit D significantly induced apoptosis (Annexin V+ PI–) of T lymphocytes (26.1 ± 2.05% vs. 3.28 ± 0.17%, p<0.001) (Figure 2B).
Conclusion: This demonstrates showed that Vit D has a regulatory role in pannus formation by exerting anti-proliferative effect on two major effector cells of AA such as FLS and T lymphocytes. Moreover the pro-apoptotic effect of Vit D on activated T lymphocytes further suggests its immunomodulatory effect in AA.
Disclosure:
S. P. Raychaudhuri,
None;
A. Datta Mitra,
None;
A. Mitra,
None;
C. Abria,
None;
S. K. Raychaudhuri,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/regulatory-role-of-1-25-dihydroxyvitamin-d3-in-the-pathogenesis-of-autoimmune-arthritis/