Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Cystoid macular edema (CME) represents the leading cause of blindness in uveitis of different immune mediated diseases (IMD). Our aim was to evaluate the efficacy of Tocilizumab (TCZ) in different IMD with refractory CME to other immunosuppressive drug.
Methods: Multicentre study of 24 patients with CME due to uveitis of different IMD refractory to traditional treatment with systemic corticosteroids and at least one conventional immunosuppressive drug including in most cases biological therapy (n=21). CME was defined by (OCT >300 μm). We studied CME with TCZ in 4 different IMD: juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JiA), Behçet’s disease (BD), Birdshot retinochoroidopathy (BR) and idiopathic.
The main outcome was the improvement of macular thickness. Other variables assessed were inflammation of the anterior chamber and vitreous and best corrected visual acuity (BCVA).
Results: We studied 16 ♀/8 ♂, mean age 35.2±19.3 years. The associated diseases were: JiA (n=9), BD (n=7), BR (n=4) and idiopathic (n=4). The ocular patterns were: panuveitis (9), anterior uveitis (6), posterior uveitis (5) and intermediate uveitis (4). Most patients had bilateral involvement (22). The biological therapy used before the administration of TCZ were infliximab (8), adalimumab (18), etanercept (2), golimumab (2), rituximab (2), abatacept (3), anakinra (1) and daclizumab (1).
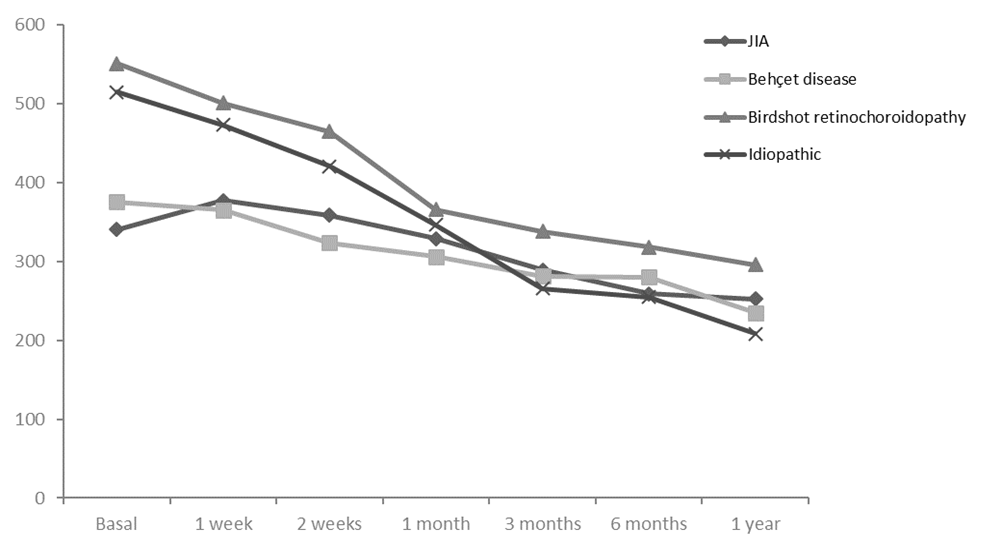
TCZ administration schedule was 8 mg/kg/4 weeks iv. (n=23) or every 2 weeks (n=1). TCZ was used in monotherapy (12) or combined with conventional immunosuppressive drugs (12). OCT values improved considerably in 12 months: in JiA from 340.6 ± 134.1 μm to 252.5 ± 30 μm, in BD from 375.1 ± 117 μm to 235 ± 7.1 μm, in BR from 550.7 ± 214.4 μm to 295.5 ± 43.2 μm and in idiopathic from 515 ± 219.6 μm to 208.3 ± 46.7 μm (FIGURE). Inflammation in anterior chamber and vitritis and BCVA also improved in the 4 subtypes. No major side effects were observed, so no patient had to stop treatment.
Conclusion: TCZ seems a rapid effective treatment in severe and refractory uveitic CME, regardless of the underlying IMD.
FIGURE
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vegas-Revenga N, Calvo-Río V, Mesquida M, Adan A, Hernández MV, Beltrán E, Valls Pascual E, Diaz-Valle D, Díaz-Cordovés G, Hernandez Grafella M, Martínez-Costa L, Calvo I, Atanes A, Linares LF, Modesto C, Aurrecoechea E, Cordero-Coma M, Demetrio-Pablo R, Domínguez-Casas LC, Hernández JL, González-Gay MA, Blanco R. Refractory and Severe Uveitic Cystoid Macular Edema Improves with Tocilizumab in Different Immune Mediated Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/refractory-and-severe-uveitic-cystoid-macular-edema-improves-with-tocilizumab-in-different-immune-mediated-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/refractory-and-severe-uveitic-cystoid-macular-edema-improves-with-tocilizumab-in-different-immune-mediated-diseases/