Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with work disability
and lower employment rates (evidence shows 20–30% of
pts are work disabled in the first 3 yrs and up to 40–50% in
the first 10 yrs of RA). Improvements in workplace/household productivity with
certolizumab pegol (CZP)+MTX have been reported in established RA.1
Here we estimate the RA burden on work disability in DMARD-naïve early RA vs
established RA and assess the CZP+MTX effect on workplace/household
productivity in DMARD-naïve early RA pts over 52 wks.
Methods:
C-EARLY (NCT01519791) is a phase 3 study assessing efficacy and safety of CZP
in DMARD-naïve pts with severe, active and progressive RA (≤1 yr since
diagnosis) and poor prognostic factors.2 RAPID1 (NCT00152386) and
RAPID2 (NCT00160602) reported efficacy and safety of CZP in pts with active RA
of ≥6 months’ duration on MTX for ≥6 months prior to baseline (BL).1
The burden of early/established RA on workplace and household productivity was
assessed at study BL in C-EARLY (full analysis set [FAS]) and pooled RAPID1/2
studies (intent-to-treat [ITT] population), using the validated arthritis
specific Work Productivity Survey (WPS).3 WPS responses (LOCF
imputation) in C-EARLY were compared between groups using a non-parametric
bootstrap-t method.
Results:
At BL, mean age, disease activity and functioning were similar between early
and established RA pts (early/established RA: age 50.6/52 yrs; DAS28(ESR)
6.7/6.9; HAQ-DI 1.6/1.6) with differences in mean disease duration since
diagnosis (early/established RA: 2.9 months/6.1 yrs) and mean prior synthetic
DMARD use (early/established RA: 0/1.3). More early RA pts were employed vs
established RA; (52.2% vs 40.9%); more established RA pts were RA work disabled
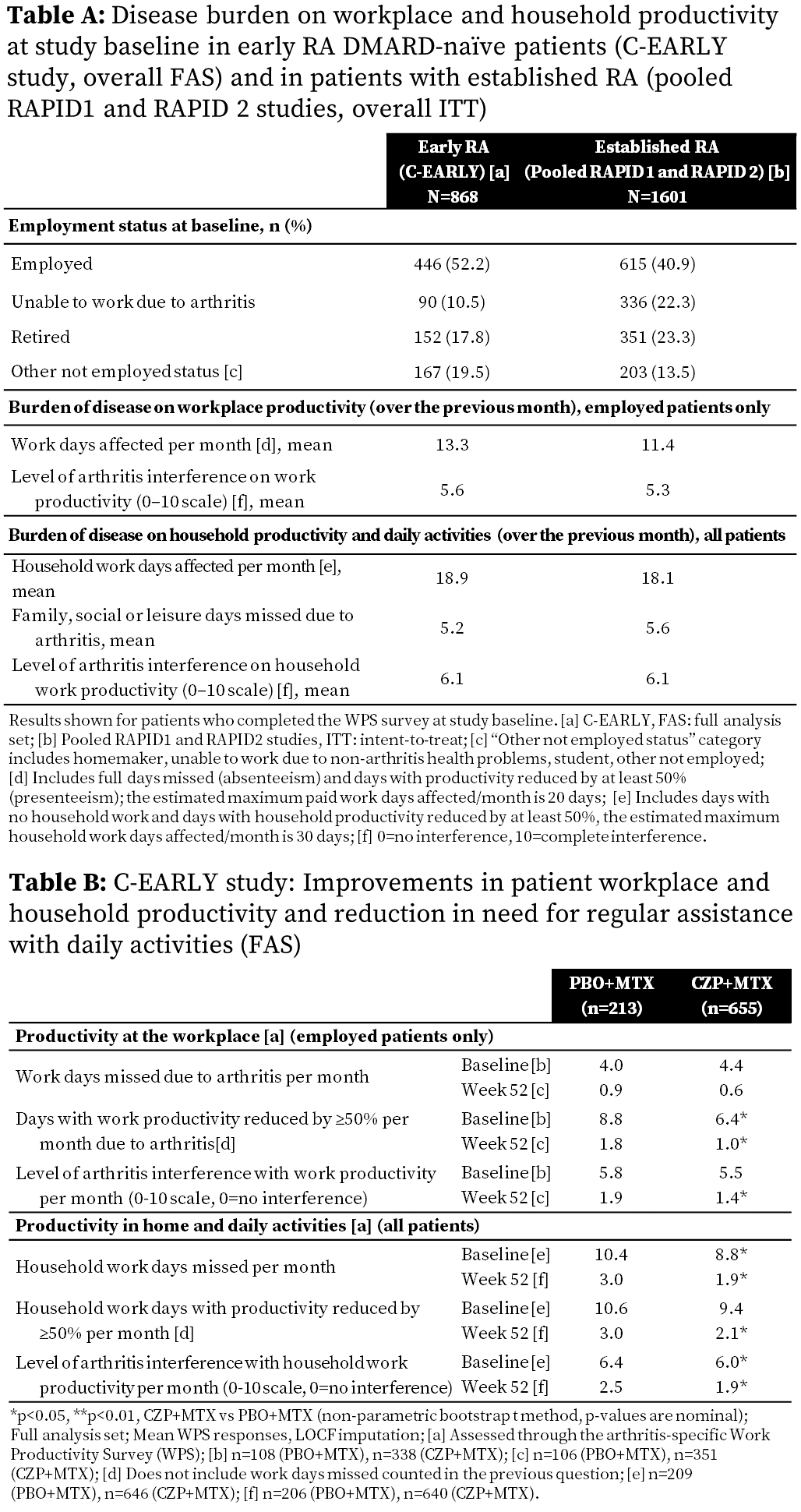
vs early RA (22.3% vs 10.5%) (Table A). High RA burden was reported at BL in
both early and established RA pts with >2 wks of paid work (mean 13.3 vs
11.4 days), >2 wks of household duties (mean 18.9 vs 18.1 days), and mean
5.2 vs 5.6 days of social activities affected over previous month, respectively
(Table A). At Wk52 in DMARD-naïve pts, greater improvements were reported in
CZP+MTX arm vs PBO+MTX in household productivity, and in absenteeism and
presenteeism (employed pts only) (Table B).
Conclusion:
DMARD-naïve pts with early severe RA and poor prognostic factors have a similar
high burden on workplace and household productivity to that reported in
established RA, which could lead to large financial burden for pts and society.
CZP+MTX showed greater improvements at 1 yr in workplace and household
productivity in DMARD-naïve pts with severe, active, progressive RA (≤1 yr
since diagnosis), which could reduce the economic burden of this disease.
References:
1. Kavanaugh A.
Arthritis Rheum 2009;61(11):1592–1600
2. Emery P. Ann Rheum
Dis 2015;74(S2):712
3. Osterhaus J.
Arthritis Res Ther 2009;11:R7
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bykerk V, Bingham C, Burmester G, Furst DE, Mariette X, Purcaru O, VanLunen B, Weinblatt M, Emery P. Reduction of Disease Burden on Workplace and Household Productivity Following 52 Weeks of Treatment with Certolizumab Pegol in Combination with Methotrexate in DMARD-Naïve Patients with Active, Severe, Progressive Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduction-of-disease-burden-on-workplace-and-household-productivity-following-52-weeks-of-treatment-with-certolizumab-pegol-in-combination-with-methotrexate-in-dmard-naive-patients-with-active-severe/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduction-of-disease-burden-on-workplace-and-household-productivity-following-52-weeks-of-treatment-with-certolizumab-pegol-in-combination-with-methotrexate-in-dmard-naive-patients-with-active-severe/