Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: A third COVID-19 vaccination is currently recommended for patients under immunosuppression. However, a fast decline of antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein has been reported. Currently it remains unclear whether immunosuppressive therapy affects stability of a humoral and cellular immune response.
Methods: 51 patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID) under immunosuppression and 45 healthy controls (HCs) received a 3rd dose of an mRNA-based vaccination and were monitored over a 12-weeks period. Humoral immune response was assessed 4 and 12 weeks after 3rd dose. Antibodies were quantified using the Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S immunoassay against the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell responses were analyzed 1 and 12 weeks after 3rd dose and were quantified by IFN-γ ELISpot assays. Adverse events, including SARS-CoV-2 infections, were monitored over a 12-week period.
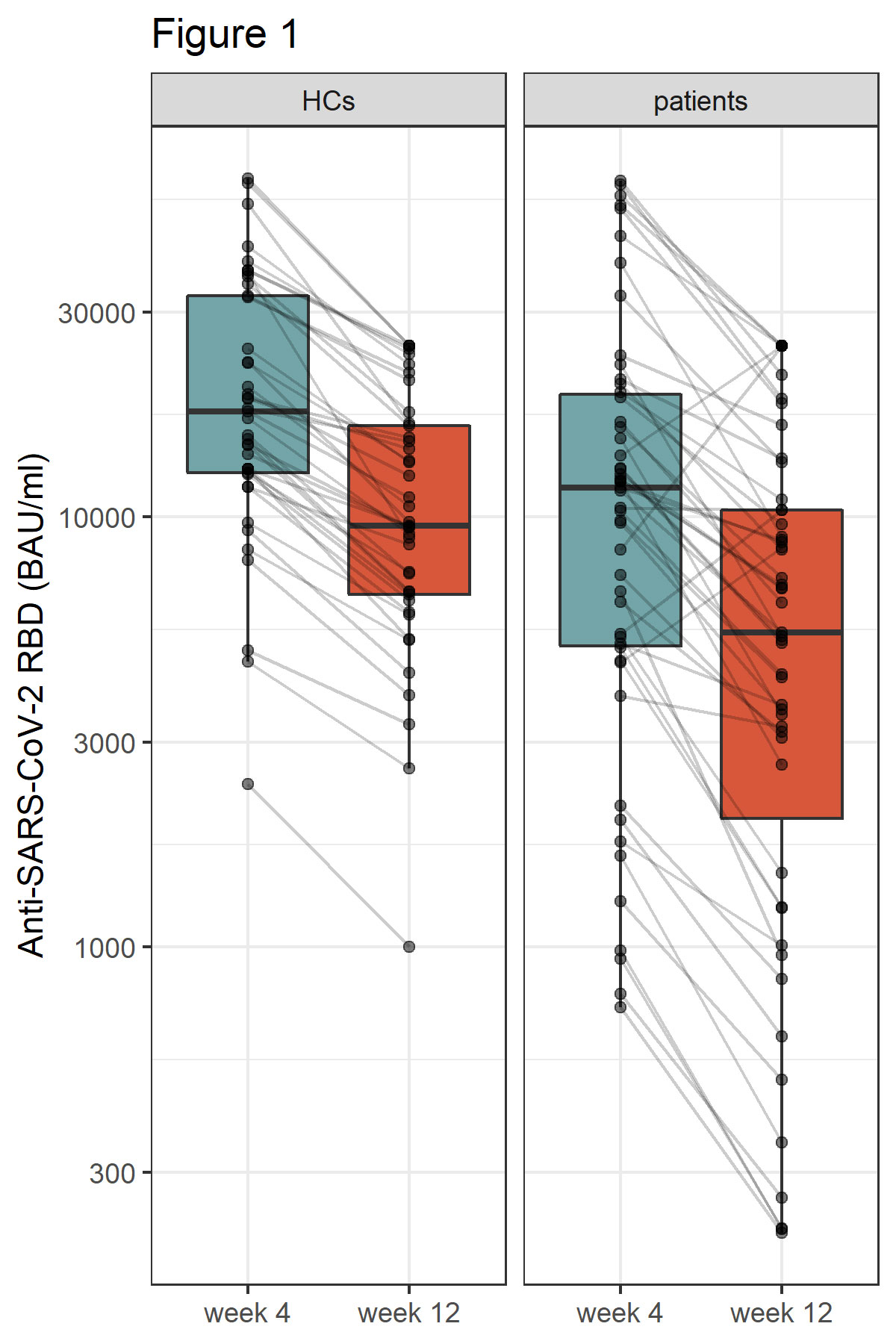
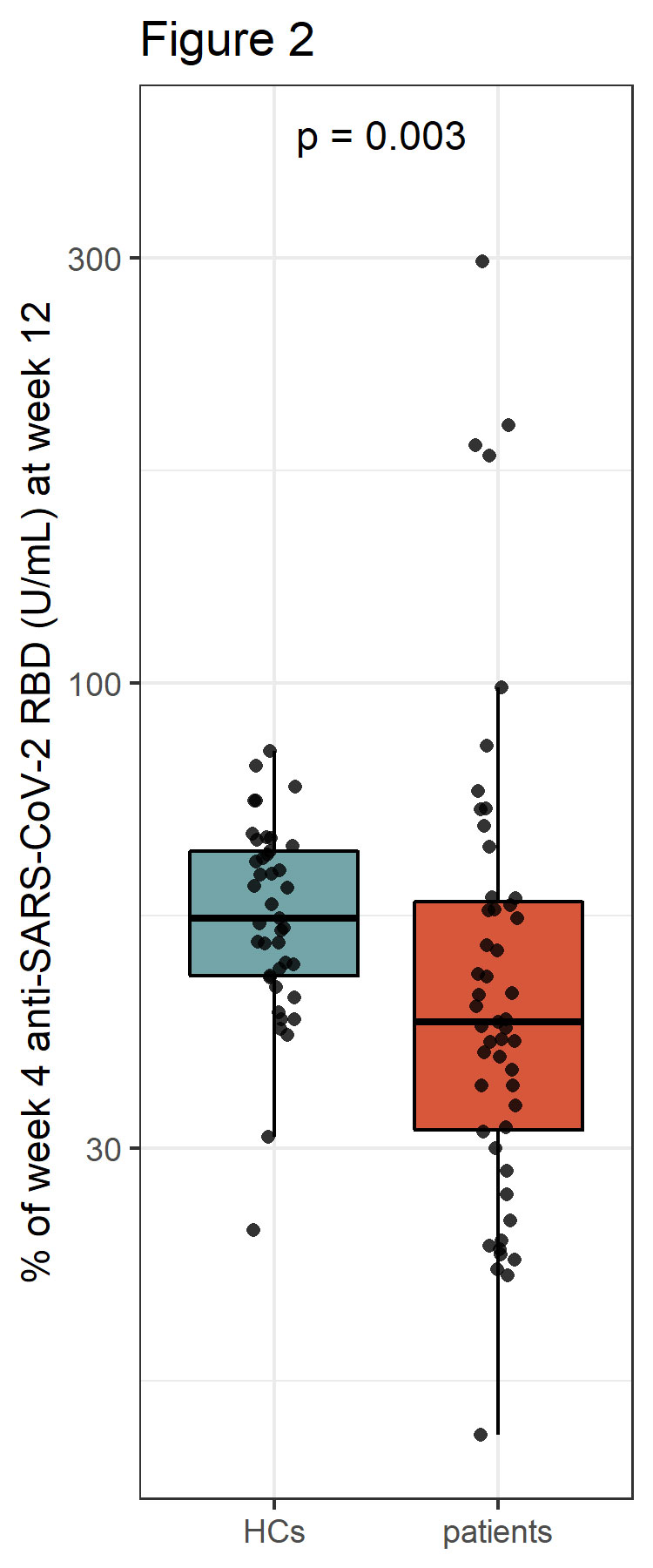
Results: At week 12 reduced anti-RBD antibody levels were observed in IMID patients as compared HCs (median antibody level 5400 BAU/ml [2074, 10400] versus 9500 BAU/ml [6610, 16300], p=0.003). Relative reduction in antibody levels was significantly higher in IMID patients as compared to HCs at week 12 (p=0.003). Lowest levels of anti-RBD antibody levels were detected in IMID patients who received a combination therapy with conventional synthetic and biological diseases modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Number of SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells remained stable over 12 weeks in IMID patients and HCs. No serious adverse events were reported. Two IMID patients and two HCs were tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 between week 4 and 12.
Conclusion: A fast decline in anti-RBD antibodies was observed in IMID patients under immunosuppression. A 4th vaccination should therefore be considered in this vulnerable group of patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mrak D, Kartnig F, Sieghart D, Simader E, Radner H, mandl P, Göschl L, Hofer P, Hummel T, Deimel T, Gessl I, Kain R, Winkler S, Smolen J, Perkmann T, Haslacher H, Aletaha D, Heinz L, Bonelli M. Reduced Humoral but Maintained Cellular Immune Response to a 3rd COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases as Compared to Healthy Controls over a 3-months Observational Period [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduced-humoral-but-maintained-cellular-immune-response-to-a-3rd-covid-19-vaccination-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-as-compared-to-healthy-controls-over-a-3-months-observation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduced-humoral-but-maintained-cellular-immune-response-to-a-3rd-covid-19-vaccination-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-as-compared-to-healthy-controls-over-a-3-months-observation/