Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common cause of pain and is associated with depression in older adults. Pain and depression are major burdens to people suffering from OA. Being physically active has broad health benefits for people with OA, including reduced pain and depressive symptoms. Increasing physical activity within a fixed 24-hour day requires trading time with other behaviors. Applying isotemporal substitution methods to observational data, we modeled the potential benefits in relation to pain and high depressive symptoms from trading time in one type of activity for another (e.g. replacing sedentary time with moderate physical activity).
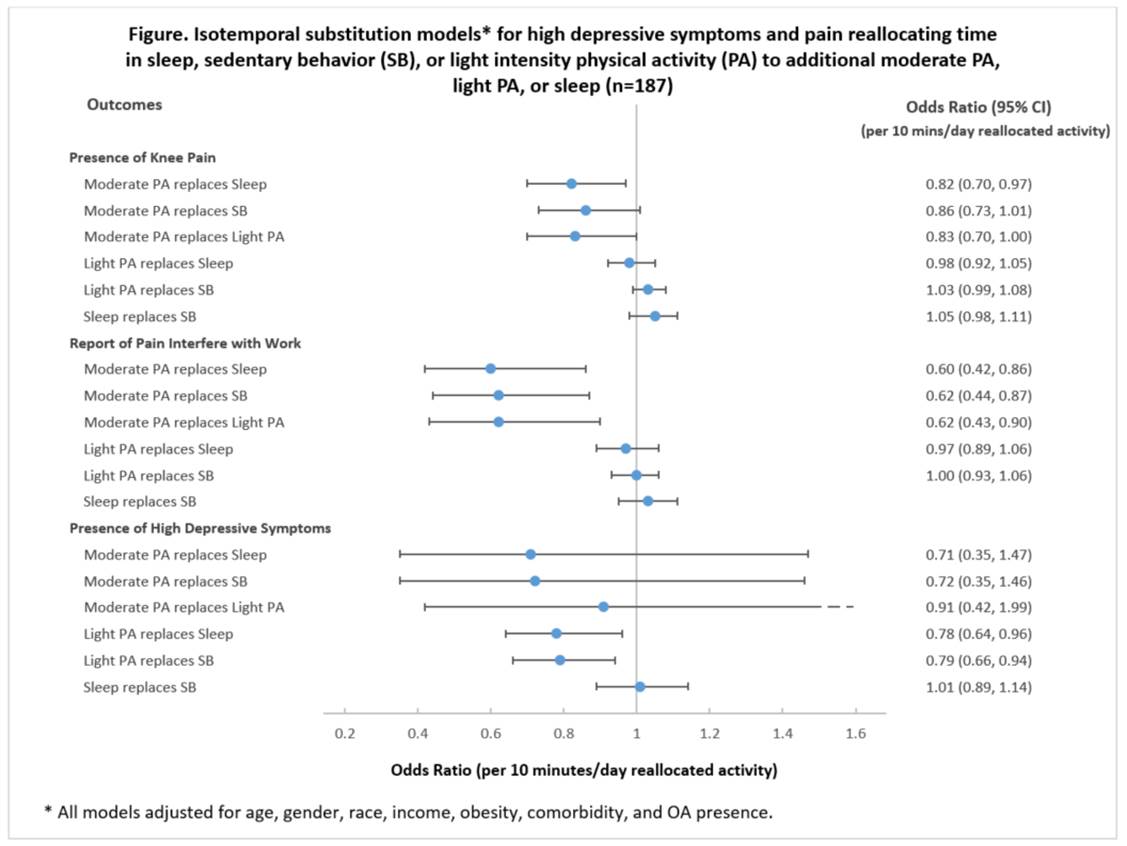
Results: These 187 men and women had mean age 67 (SD 8.5), 50% were female, 41% obese and 60% had radiographic knee OA. On a daily basis, these adults on average spent 7 hours in sleep, 10 hours in sedentary behavior, 6 hours in light PA, and 27 minutes in moderate PA. Isotemporal analyses on WOMAC pain indicated substituting 10 minutes/day of moderate PA for either sleep (OR=0.82) or light PA (OR=0.83) was significantly (P≤0.05) associated with less frequent reports of knee pain. Similarly, substituting 10 minutes/day of moderate PA for sleep (OR=0.60), sedentary behavior (OR=0.62) or light PA (OR=0.62) was significantly associated with less frequent pain interference. Isotemporal analyses on high depressive symptoms indicated substituting 10 minutes/day of light PA for either sleep (OR=0.78) or sedentary behavior (OR=0.79) was significantly associated with less frequent report of high depressive symptoms.
Conclusion: Interventions promoting moderate activities may be beneficial to address pain while substituting light activity for sedentary behavior or sleep may be beneficial to address depressive symptoms.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Song J, Dunlop DD, Semanik P, Chang AH, Jackson RD, Chang RW, Lee J. Reallocating Time Spent in Sleep, Sedentary Behavior and Physical Activity and Its Association with Pain and Depression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reallocating-time-spent-in-sleep-sedentary-behavior-and-physical-activity-and-its-association-with-pain-and-depression/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reallocating-time-spent-in-sleep-sedentary-behavior-and-physical-activity-and-its-association-with-pain-and-depression/