Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
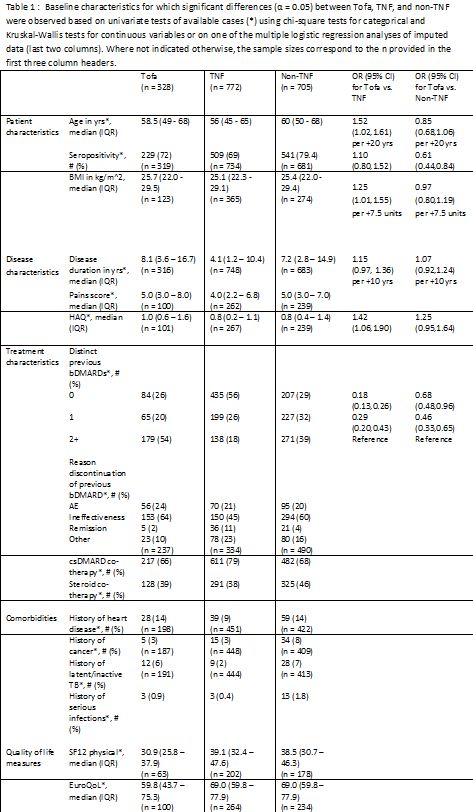
Background/Purpose: The oral Janus kinase inhibitor Tofacitinib (Tofa) has been licensed in Switzerland 2013 for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA), who have failed methotrexate. Besides Tofa, rheumatologists in Switzerland can choose from 5 TNF inhibitors (TNF) and 3 non-TNF-bDMARD (nonTNF) licensed in the same indication. We aimed at characterizing the patient population starting treatment with Tofa for the first time and at gaining insight into the factors determining the prescription of Tofa vs bMARDs in routine care.
Methods: This is an observational cohort study within the Swiss Clinical Quality Management (SCQM) registry. All therapies with Tofa, TNF, and non-TNF initiated in adult RA patients naïve to Tofa between August 1, 2013 and May 1, 2016 were considered. Exposure of interest was the initiated treatment (Tofa, TNF, non-TNF). Baseline characteristics were described and compared between treatments. Odds for the prescription of Tofa vs TNF and vs non-TNF were assessed with logistic regression after multiple imputation (MI) of missing covariate data assuming a missing at random mechanism. The following covariates at baseline of treatment were included in the model: sex, age, smoking status, seropositivity (rheumatoid factor or ACPA), disease duration, number of previous bDMARDs, BMI, HAQ, and DAS28. A sensitivity analysis with a complete case analysis revealed no concerns with respect to the chosen MI approach.
Results: A total of 1805 therapies were initiated during the study period (328 Tofa, 772 TNF, 705 non-TNF). Tofa therapy was initiated in 25% as second line therapy after conventional DMARDs, in 20% after one bDMARD and in 55% after two or more bDMARDs. Significant differences between Tofa, TNF, and non-TNF were observed for some patient, disease, and treatment characteristics, as well as comorbidities and quality of life measures (Table 1). Tofa as well as non-TNF were used more often as monotherapy than TNF. The multiple regression analysis revealed significantly increased odds for prescribing Tofa as opposed to TNF in patients with two or more previous bDMARDs and with higher age, BMI, and HAQ. Compared to non-TNF, the odds for prescribing Tofa were also significantly higher for patients who had two or more previous bDMARDs and who were seronegative. Of the observed associations, the most relevant was with number of previous bDMARDs.
Conclusion: Taken together our data suggest that in real-life, since being licensed 2013, Tofa was used predominantly as a third+ line therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kyburz D, Riek M, Herzog L, Scherer A, Gabay C, Dudler J, Zufferey P, Finckh A. Real-World Use of Tofacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Data from the Swiss Clinical Quality Management RA Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-use-of-tofacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-data-from-the-swiss-clinical-quality-management-ra-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-use-of-tofacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-data-from-the-swiss-clinical-quality-management-ra-registry/