Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The national prevalence of PsA among patients (pts) with psoriasis (PsO) in Japan is estimated to be 14.3%. Risankizumab (RZB) was approved for the treatment of PsO and PsA in Japan in March 2019. Real-world data on treatment persistence for PsA does not fully include recently approved biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs). This analysis quantified real-world treatment switching and discontinuation rates for pts with PsA in Japan initiating bDMARDs over 24 months, accounting for recent advancements in treatment.
Methods: A retrospective database study conducted using administrative claims from the Japan Medical Data Center Payer-Based Database from January 2005 through August 2022 included pts who had ≥ 1 medical claim for PsA preceding a claim for an approved bDMARD. Pts had ≥ 6 months of continuous eligibility prior to the first claim for a bDMARD (index date) and were evaluated for all treatments for which they had a qualifying index date. Treatment switch, defined as a claim for another bDMARD approved for PsA after the index date, and treatment discontinuation, defined as a gap in treatment without refill equal to 150% of the assumed days supply of the last prescription fill, were assessed up to 24 months past treatment initiation and rates were evaluated using Kaplan-Meier time-to-event analyses censored for loss of follow-up. bDMARD-specific adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using multivariate Cox proportional hazards models. HRs were adjusted for pt demographics, treatment history, and baseline comorbidities and healthcare charges.
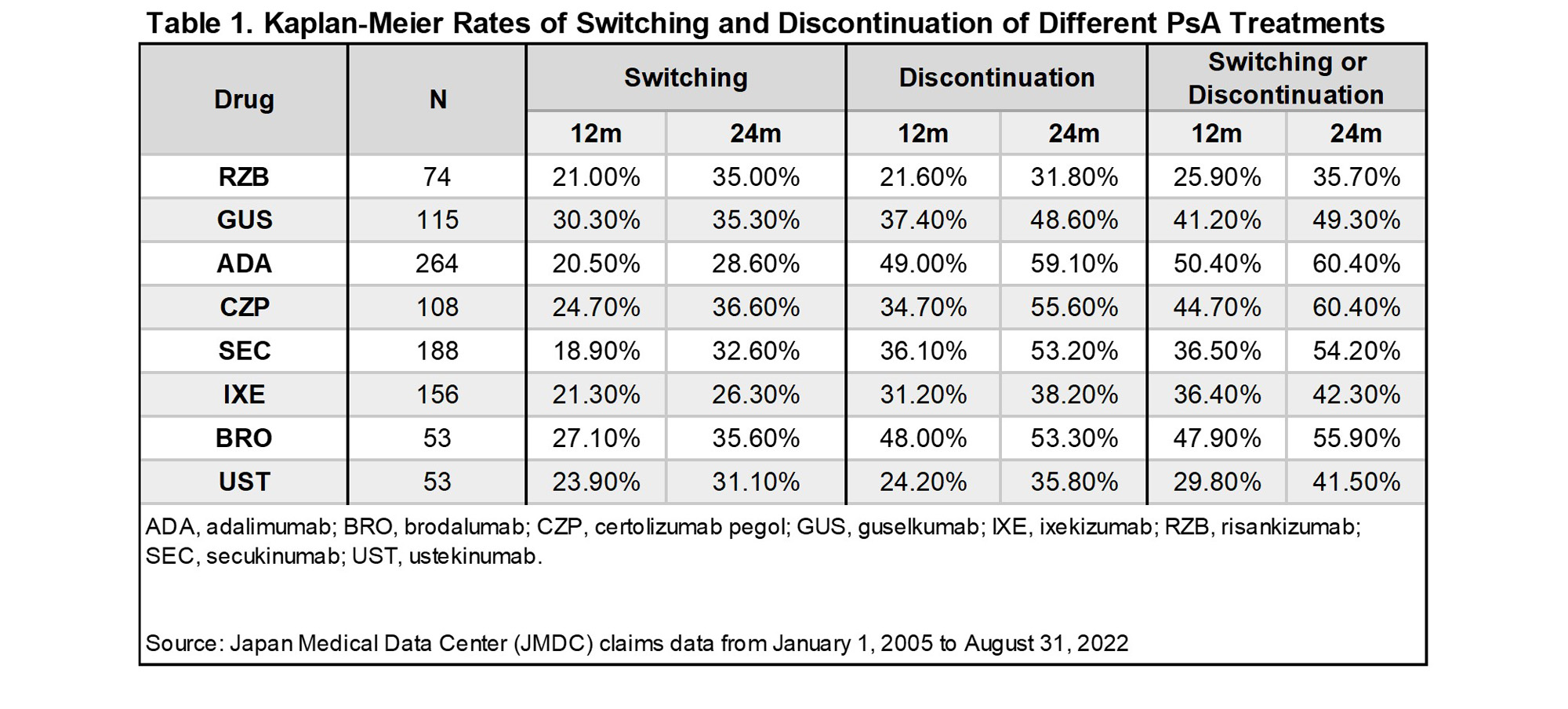
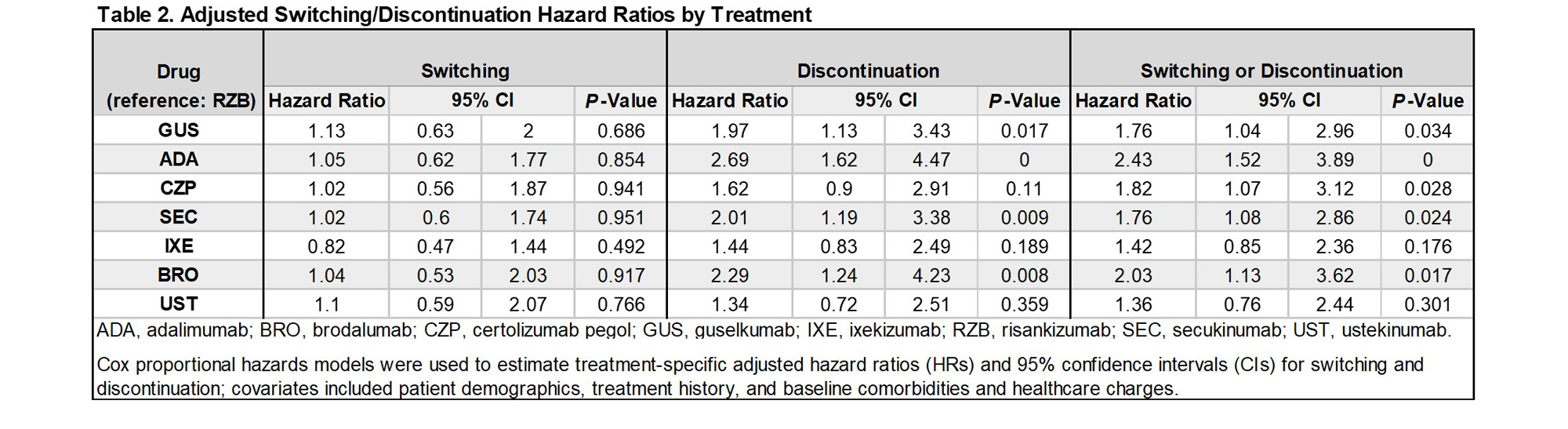
Results: A total of 779 unique pts met the inclusion criteria for the study, and were treated with adalimumab (ADA; n = 264), bimekizumab (BIM; n = 5), brodalumab (BRO; n = 53), certolizumab pegol (CZP; n = 108), guselkumab (GUS; n = 115), ixekizumab (IXE; n =156), risankizumab (RZB; n = 74), secukinumab (SEC; n = 188), tildrakizumab (TIL; n = 5), and ustekinumab (UST; n = 53). Owing to small sample sizes, results are not shown for BIM and TIL. At 12/24 months following treatment initiation, 37.5%/49.0% of pts had discontinued their index bDMARD, while 22.2%/31.2% of pts had switched treatment. Switch rates varied across bDMARDs from 18.9-30.3% at 12 months, and 26.3%-36.6% at 24 months (Table 1). Discontinuation rates at 12/24 months were lowest for RZB (21.6%/31.8%), followed by UST (24.2%/35.8%), IXE (31.2%/38.2%), GUS (37.4%/48.6%), SEC (36.1%/53.2%), BRO (48.0%/53.3%), CZP (34.7%/55.6%), and ADA (49.0%/59.1%) [Table 1]. Adjusting for baseline pt characteristics, HRs of switching or discontinuation over 24 months were higher among CZP, SEC, ADA, BRO, and GUS, relative to RZB (p< 0.05) [Table 2].
Conclusion: Treatment switching and discontinuation were common in the first 24 months of treatment with bDMARDs for PsA in Japan. While treatment switch rates varied across bDMARDs, discontinuation rates were lowest for RZB at each timepoint that was examined. Hazards of switching or discontinuation relative to RZB were generally higher across most bDMARDs, indicating higher treatment persistence rates for RZB.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Erik L, Soliman A, Nunag D, Lippe R, Davis M, Kishimoto M. Real-World Switching and Discontinuation Patterns for Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis in Japan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-switching-and-discontinuation-patterns-for-biologic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-in-japan/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-switching-and-discontinuation-patterns-for-biologic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-in-japan/