Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: AWARE (Comparative and Pragmatic Study of Golimumab IV Versus Infliximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis) is an ongoing prospective Phase 4 comparator study designed to provide a real-world assessment of intravenous golimumab (GLM) and infliximab (IFX) in patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The primary endpoint compares the proportion of GLM and IFX pts with an infusion reaction (52wks). Here we report on IFX dose escalation (DE, defined as at least 1 increase in prescribed dose above baseline) patterns from an interim analysis (IA) of the ongoing AWARE study. The baseline dose was chosen to judiciously evaluate DE by not focusing on pts at 3mg/kg that may be “routinely” moved to 5 mg/kg, but rather to report on the DE pattern of what may be considered more significant IFX DEs.
Methods: AWARE is a noninterventional 3-year study at 100 US sites. All treatment decisions including prescribed dose are made at the discretion of the treating rheumatologist. We report on DE patterns of IFX pts with a starting dose (infusion 1) of ≥5mg/kg. Data shown are mean ± standard deviation.
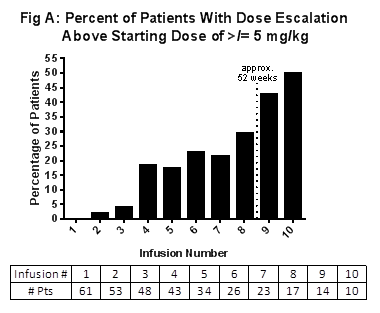
Results: Here we report on IFX pts, who’s first prescribed dose was ≥5mg/kg, age = 53.7±13.46 yrs, body weight = 85.1 ± 24.38kg, BMI = 31.6 ± 10.8 kg/m2 and 75.4% were female. Baseline CDAI of DE pts = 32.0 ± 16.17. Among pts with initial prescribed dose ≥5mg/kg, 26.4% were DE after the first infusion, and 38.2% of pts had two or more consecutive infusion intervals < 7 weeks duration (37.7% had both a DE and contraction of dosing interval). Among this cohort of pts who had ≥3 infusions, 16.7% had at least one dose ≥8mg/kg. The pattern of DE is shown in the figure below, and in the table the % of pts prescribed ≥8mg/kg at each infusion visit is shown.
|
Infusion # |
# Pts Treated |
# of Pts with Prescribed Initial Dose ≥8mg/kg IFX |
% of Pts with Prescribed Initial Dose of ≥8mg/kg IFX |
|
1 |
61 |
9 |
14.80 |
|
2 |
53 |
7 |
13.20 |
|
3 |
48 |
5 |
10.40 |
|
4 |
43 |
6 |
14.00 |
|
5 |
34 |
5 |
14.70 |
|
6 |
26 |
3 |
11.50 |
|
7 |
23 |
2 |
8.70 |
|
8 |
17 |
2 |
11.80 |
|
9 |
14 |
1 |
7.10 |
|
10 |
10 |
2 |
20.00 |
Conclusion: Of this subset of IFX pts, close to 20% were DE by infusion 4, with 10-14% dosed ≥8mg/kg. Dose interval shortening could further affect the impact of DE. The AWARE study will utilize these data to assess the impact on IFX utilization in a real-world rheumatology practice setting.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schwartzman S, Parenti D, Black S, Xu S, Langholff W, Kafka S. Real World Evidence Describing Infliximab Utilization Patterns in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Community Rheumatology Practices in the United States: Implications for Cost Efficiencies? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-evidence-describing-infliximab-utilization-patterns-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-community-rheumatology-practices-in-the-united-states-implications-for-cost-efficiencies/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-evidence-describing-infliximab-utilization-patterns-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-community-rheumatology-practices-in-the-united-states-implications-for-cost-efficiencies/