Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Axial involvement is a clinically relevant manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) that can influence management strategies. Evidence on the real-world effectiveness of advanced therapies, in particular, interleukin-23’s (IL-23), on axial symptoms in PsA is scarce. This study aimed to evaluate the real-world effectiveness of risankizumab (RZB) on axial symptoms in routine clinical practice among biologic-naïve (bDMARD) patients with PsA across the United States (US) and Europe.
Methods: In this retrospective analysis (June 2023 to June 2024) using data from the Adelphi Spondyloarthritis VI Disease Specific Programme™, biologic-naïve patients with PsA receiving RZB 150 mg were included from the US and Europe (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom). The analysis was based on cross-sectional questionnaires completed by physicians and their consulting patients during their most recent visits. Effectiveness assessments of axial symptoms at treatment initiation and the most recent patient visit included change in the proportion of patients with physician-reported inflammatory back pain (IBP) or spinal pain, morning stiffness, pain on movement, pain at rest, nocturnal pain, persistent lower back pain, pain associated with morning stiffness, sleep disturbance, and sacroiliitis (either by X-ray or MRI). These outcome assessments were compared using McNemar tests (P < .05). Outcomes were evaluated in bDMARD-naïve ± conventional synthetic (cs)DMARD patients with PsA (overall patient population) and in bDMARD-naïve patients with an inadequate response (IR) to ≥ 1 csDMARD (csDMARD-IR/bDMARD-naïve).
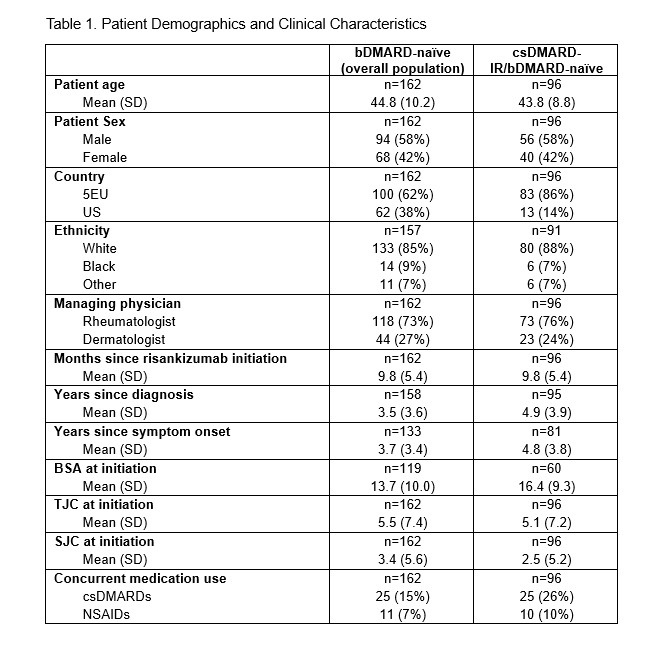
Results: A total of 162 patients who initiated treatment with RZB were included in the analysis, with 62 (38%) from the US and 100 (62%) from Europe (Table 1). Patients were on average 44.8 years old at the time of data collection, 42% were female, 73% managed by rheumatologists, and body surface area (BSA) affected by psoriasis was 13.7% at treatment initiation. The mean duration of RZB treatment was 9.8 months, and the mean TJC68 and SJC66 at treatment initiation were 5.5 and 3.4, respectively. The csDMARD-IR/bDMARD-naïve subgroup comprised 96 patients with a mean age of 43.8, BSA of 16.4%, and mean TJC68 and SJC66 at treatment initiation of 5.1 and 2.5, respectively. The prevalence of IBP at treatment initiation was 28% in the overall group and 34% in the csDMARD-IR/bDMARD-naïve subgroup. Overall, the presence of all axial symptoms significantly decreased from treatment initiation to the most recent visit (all comparisons, P < .001) (Figure 1). Significant improvements in axial symptoms were observed in the overall population and the csDMARD-IR/bDMARD-naïve subgroup (Figure 1).
Conclusion: In real-world clinical settings, biologic-naïve patients with PsA who initiated RZB treatment demonstrated significant improvements in axial symptoms, highlighting effectiveness of RZB in managing a key manifestation of PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Ostor A, Saffore C, Ye X, Patel M, Biljan A, Lippe R, Edwards M, Armstrong I, Baraliakos X. Real-World Effectiveness of Risankizumab on Axial Symptoms in Biologic-Naïve Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis in the United States and Europe [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-effectiveness-of-risankizumab-on-axial-symptoms-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-in-the-united-states-and-europe/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-effectiveness-of-risankizumab-on-axial-symptoms-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-in-the-united-states-and-europe/

.jpg)