Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The overall incidence of cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is modestly elevated compared with the general population. The extent to which cancer rates in RA populations vary across cohorts and across patient subsets defined by disease activity or treatment is less known. Available data are often difficult to compare, since background malignancy rates may vary across the world, and due to methodological differences and population differences between studied RA cohorts. We investigated malignancy rates in 5 international RA registries from 4 continents, employing a standard set of analyses and standardizing rates to a common population.
Methods: Participating RA registries were CORRONA (USA), SRR (Sweden), NOAR (UK), CORRONA International (East Europe, Latin America, India) and IORRA (Japan). Within each registry, we analyzed a primary cohort of all RA patients from January 2000 to last available data of each register (2010–2013), and several subcohorts as defined by disease activity, treatment status, calendar time, duration of follow-up and prior comorbidity for sensitivity analyses. Malignancy rates with 95% confidence intervals were estimated, and were standardized for age, sex and, in 1 sensitivity analysis, also for HAQ, using the distributions from a typical RA trial program population.
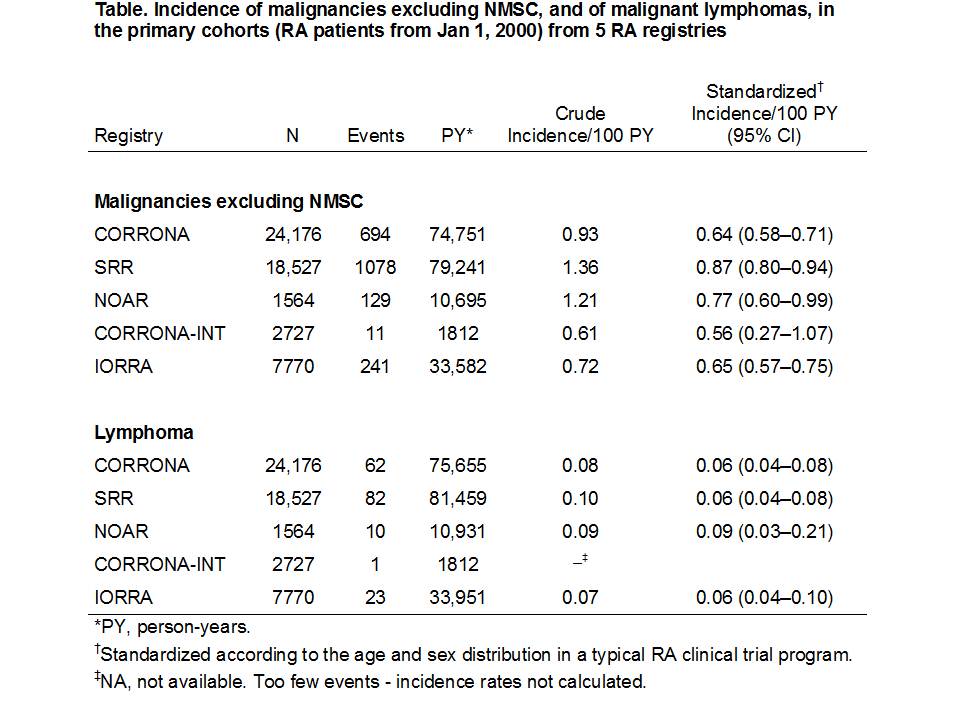
Results: There was remarkable consistency in crude malignancy rates across registries (Table). Sex and age standardization reduced heterogeneity further, with standardized rates of malignancy excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) varying from 0.56 to 0.87 per 100 person-years (Table). Within each registry, rates were generally also consistent across the sensitivity analyses, which also differed little from the main analyses based on the full cohort (data not shown).
Conclusion: A consistent methodology and analysis with standardization of rates facilitated comparison across registries and demonstrated that in real world RA populations from different countries and with variations in RA management and comorbidity, rates of overall malignancy excluding NMSC and of lymphoma were surprisingly consistent across and within the cohorts.
Disclosure:
J. Askling,
AstraZeneca,
2,
AstraZeneca,
5;
N. Berglind,
AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb,
1,
AstraZeneca,
3;
S. Franzén,
AstraZeneca,
1,
AstraZeneca,
3;
T. Frisell,
None;
C. Garwood,
None;
J. D. Greenberg,
AstraZeneca, CORRONA, Pfizer,
5,
Corrona,
1;
M. Ho,
AstraZeneca,
3;
M. Holmqvist,
None;
L. Horne,
AstraZeneca,
1,
AstraZeneca,
3;
K. Lampl,
AstraZeneca,
1,
AstraZeneca,
3;
K. Michaud,
University of Nebraska Medical Center and the National Data Bank for Rheumatic Diseases,
3;
F. Nyberg,
AstraZeneca,
3,
AstraZeneca,
1;
D. A. Pappas,
Corrona,
3,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Adjunct assistant professor at Columbia University,
6;
G. Reed,
Corrona,
3;
E. Tanaka,
None;
T. Tran,
Medimmune LLC,
3;
S. Verstappen,
None;
H. Yamanaka,
AstraZeneca, Abbott, AbbVie, Chugai, Takeda, Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Teijin, Nippon Kayaku, Taishotoyama, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Astellas, Eisai, MSD, Santen, GlaxoSmithKline, Asahikasei, Janssen,
2,
AstraZeneca, Abbott, AbbVie, Chugai, Takeda, Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Teijin, Nippon Kayaku, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Astellas, Eisai,
5,
Abbott, AbbVie, Chugai, Takeda, Pfizer, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Teijin, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Astellas, Eisai,
8;
D. Symmons,
AstraZeneca,
2,
AstraZeneca,
5.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rates-of-malignancies-in-patients-from-5-rheumatoid-arthritis-registries-across-the-world/