Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: It has been suggested that the velocity of resolution of tophi in chronic tophaceous gout is related to serum uric acid (sUA) levels.1 However, few subjects with a persistent sUA <4.0 mg/dL have been studied. Pegloticase is a recombinant uricase conjugated to polyethylene glycol approved in the U.S. for chronic refractory gout that profoundly decreases sUA in responders to <1 mg/dL.2 The results from the pegloticase randomized clinical trials (RCTs) permitted determination of the impact of persistent, very low sUA levels on the velocity of tophus resolution.
Methods: This analysis used results from two RCTs of 6-months duration.2,3 Photographs were taken of hands, feet and up to 2 other locations. Serial standardized digital images of tophi were analyzed by a blinded reader using computer-assisted quantitative measurement software. Subjects were defined as responders and non-responders (NRs) based upon persistent sUA lowering.2
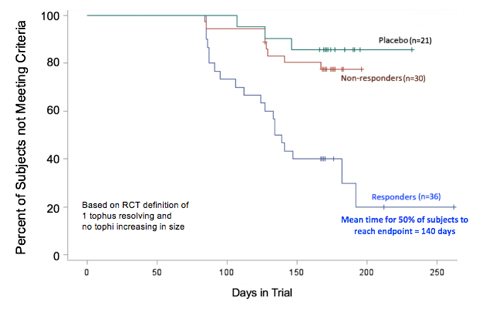
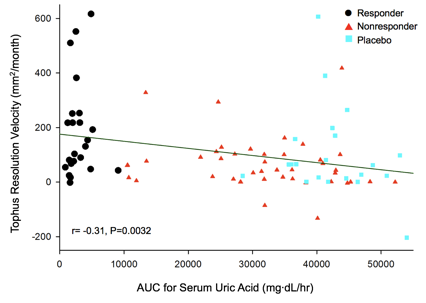
Results: A total of 952 tophi were analyzed in 87 subjects; 341 in 30 responders; 361 in 36 NRs receiving pegloticase infusions; and 250 in 21 subjects receiving placebo infusions. At baseline, the mean tophus areas were 644.7 ± 789.2 mm2 (mean ± SD) in responders, 820.0 ± 1349 mm2 in NRs, and 777.2 ± 1056.0 mm2 in placebo-treated subjects (3 group comparison, not significantly different). Achievement of tophus resolution in the three groups is summarized in Figure 1. By regression analysis, the velocity of tophus reduction over 6 months of treatment was 66.4 mm2/mo in responders (P<0.0001 comparing all visits). The mean time for complete resolution of tophi in responders was 9.7 mo (range 5.2 Ð 23.1 mo). By contrast, in NRs, the velocity of resolution was -74.9 mm2/mo from dose 1 to dose 7 (P<0.0001) and +23.5 mm2/mo from dose 7 to the final dose (P>0.05), reflecting the loss of urate lowing effect in the NRs during the latter 3 months. The sUA AUC during the 6 months of the RCT was calculated for all subjects. There was a significant negative correlation between the velocity of tophus resolution and sUA AUC (r= -0.31, P=0.0032) Figure 2. Baseline age, BMI, gender, race, total tophus area and tophus location did not significantly influence velocity of tophus resolution.
Conclusion: Pegloticase treatment causes a rapid resolution of tophi in responders. However, there is considerable heterogeneity in the velocity of tophus reduction.
- Perez-Ruiz F, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;47:356.
- Sundy JS, et al. JAMA. 2011;306:711.
- Becker MA, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:146
Figure 1. Tophus resolution in responders, NRs, and placebo- treated subjects
Figure 2. sUA vs velocity of tophus reduction in responders, NRs, and placebo subjects
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mandell BF, Baraf HSB, Yeo A, Lipsky PE. Rapid Tophus Resolution in Chronic Refractory Gout Patients Treated with Pegloticase [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-tophus-resolution-in-chronic-refractory-gout-patients-treated-with-pegloticase/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-tophus-resolution-in-chronic-refractory-gout-patients-treated-with-pegloticase/