Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster III: Biosimilars and New Compounds
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA), an oral JAK inhibitor selective for JAK1, demonstrated efficacy in patients (pts) with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with an inadequate response (IR) to csDMARDs or bDMARDs in the SELECT-NEXT1 and SELECT-BEYOND2 trials, respectively. The purpose of the analysis was to investigate the speed of response to UPA across disease measures in csDMARD- and bDMARD-IR pts.
Methods: 661 pts in NEXT and 498 in BEYOND received UPA 15mg or UPA 30mg once daily (QD) or placebo (PBO) for 12 weeks (wks)1,2. Time to first achievement of clinically meaningful outcomes, including ACR20/50, DAS28-CRP≤3.2 and Low Disease Activity (LDA) measures of CDAI (≤10) and SDAI (≤11) was evaluated. The cumulative incidences of ACR20/50, DAS28-CRP ≤3.2 and LDA by CDAI and SDAI over 12 wks were estimated. Hazard ratios between UPA and PBO were obtained using Cox proportional hazards model with treatment group, corresponding baseline values and main stratification factors, without control for multiple comparisons. All analyses were based on observed data without imputation.
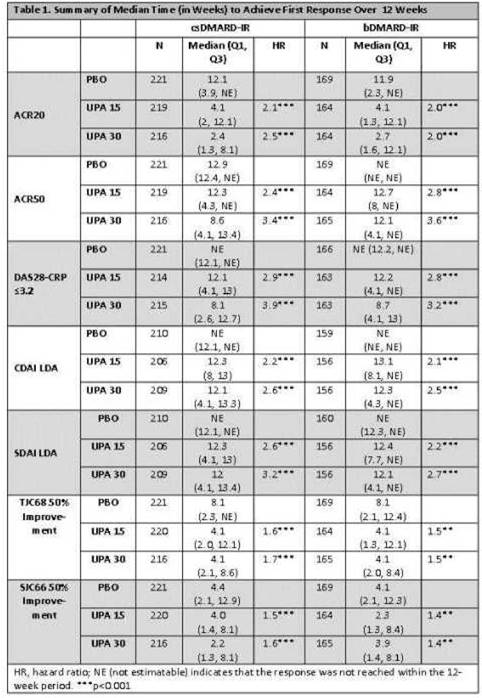
Results: Pts had a disease duration of 7 and 13 years in NEXT and BEYOND respectively.1,2 In BEYOND, pts were treatment-refractory as evidenced by 53% having received ≥2 prior bDMARDs2. Median times to achieve ACR20 were similar, irrespective of pt population, being 4 wks for UPA 15mg QD and 2-3 wks for UPA 30mg QD vs 12 wks on PBO (p<.001). In general, the median times to achieve ACR50 and DAS28-CRP≤3.2 for UPA 15mg and 30mg QD were -12 wks and -8 wks for both csDMARD-IR and bDMARD-IR pts, whereas the median was not reached for pts on PBO during the first 12 wks (p< 0.001, Table 1). The median time to LDA by CDAI and SDAI was -12 wks across UPA doses and populations, but was not reached for pts receiving PBO within that time. Pts receiving UPA were 2-4 times more likely to achieve clinical responses vs pts receiving PBO. In general, both UPA doses performed similarly across pt populations, with numerically quicker responses observed in pts receiving UPA 30mg vs UPA 15mg QD. Median times to achieve 20% and 50% improvements in tender and swollen joint counts were 1-2 wks and 2-4 wks respectively, for both UPA doses, irrespective of pt population. Median times to achieve 20% improvements in morning stiffness duration and severity were approximately 2 wks in each of the UPA arms vs 4 wks on PBO (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: Pts receiving UPA at either 15mg or 30mg QD were more likely to achieve clinical responses at significantly earlier time points when compared with pts receiving PBO. Irrespective of being csDMARD-IR or bDMARD-IR, times to achieve various clinical responses were consistent between pt populations.
References: 1. Burmester et al; Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69 S10
2. Genovese et al; Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69 S1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
FitzGerald O, Rubbert-Roth A, Chen K, Meerwein S, Enejosa JJ, Shaw T, Wells AF. Rapid Response with Upadacitinib Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Csdmards or Bdmards [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-response-with-upadacitinib-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-an-inadequate-response-to-csdmards-or-bdmards/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-response-with-upadacitinib-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-an-inadequate-response-to-csdmards-or-bdmards/