Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
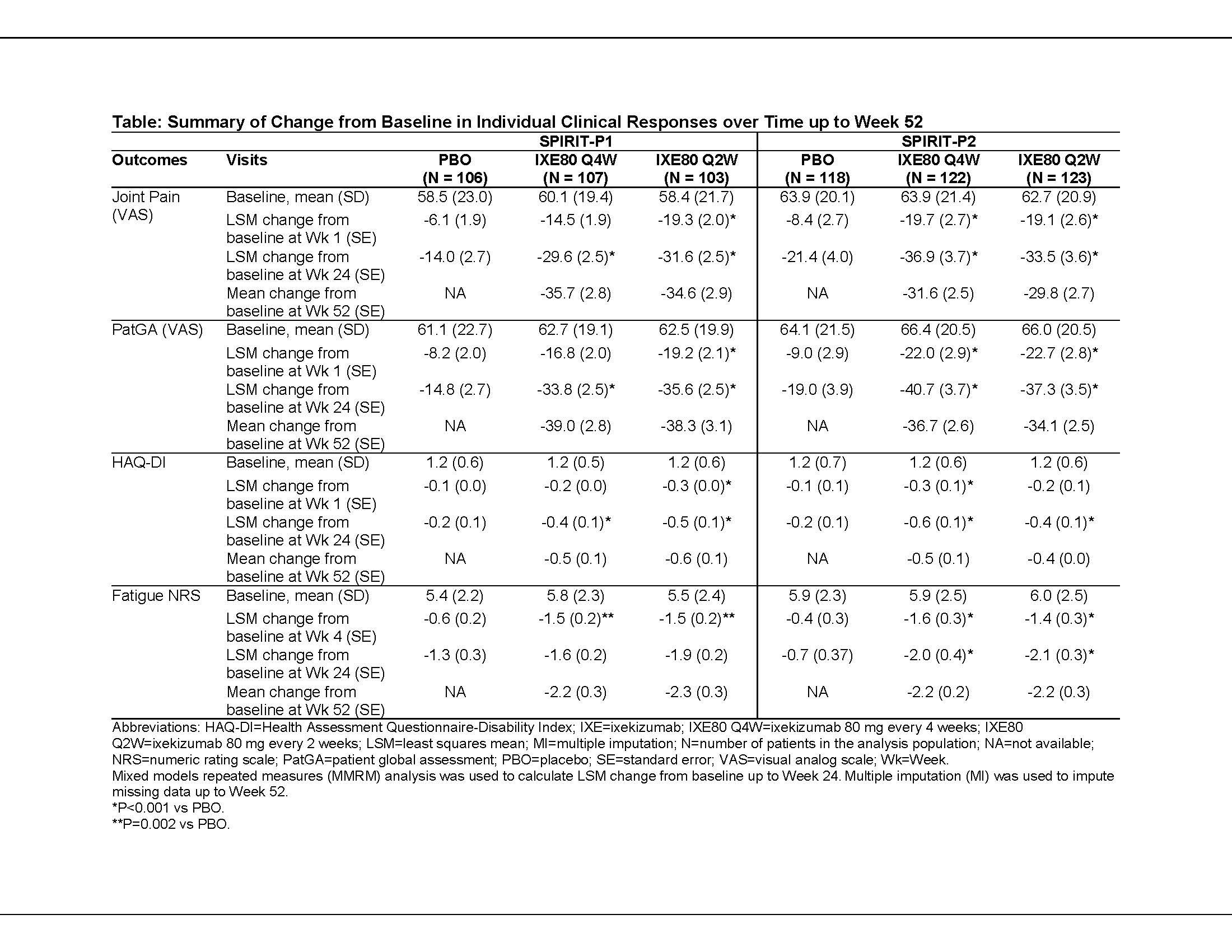
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a high-affinity mAb that selectively targets IL-17A, has shown improvements up to Week (Wk) 24 across several domains of PsA (including ACR20) compared to placebo in 2 Phase 3 trials in PsA patients (SPIRIT-P1 and SPIRIT-P2).1,2 We analyzed the onset and duration of patient-reported improvements in symptoms of PsA, including patient-reported pain and fatigue, following treatment with IXE up to Wk 52.
Methods: The SPIRIT-P1 and -P2 study designs have been reported previously.1,2 Patients with active PsA either naive to biologic DMARDs (bDMARD-naive; SPIRIT-P1) or with inadequate response to or intolerance to prior TNF-inhibitors (TNFi-IR; SPIRIT-P2) were randomized to placebo (PBO; Wk 0-24 only) or 80 mg IXE every 4 (IXE Q4W) or 2 wks (IXE Q2W) after a 160-mg starting dose. We analyzed change from baseline for the joint pain visual analog scale (VAS; 0-100 scale), patient global assessment (PatGA VAS; 0-100 scale), fatigue Numerical Rating Scale (NRS; 0 [no fatigue] to 10 [worst imaginable]), and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) up to Wk 52 (double-blind treatment period, Wk 0-24; and extension period, Wk 24-52). Continuous data were analyzed using a mixed-effects model for repeated measures (MMRM) from baseline to Wk 24. From Wk 24 onward, all missing data were imputed using the multiple imputation (MI) method.
Results: Patients treated with both IXE doses reported rapid and statistically significant reductions compared to PBO in pain VAS, PatGA, and HAQ-DI scores as early as Wk 1, which persisted or improved through Wk 52. Improvements were consistent in bDMARD-naive (SPIRIT-P1) and TNFi-IR (SPIRIT-P2) patients (Table). Fatigue scores improved in the IXE dose groups compared to PBO in both the studies at the earliest time point measured (Wk 4 in SPIRIT-P1; Wk 2 in SPIRIT-P2); results were statistically significant at Wk 24 in SPIRIT-P2, but not SPIRIT-P1 (Table).
Conclusion: Patients treated with IXE achieved significantly greater improvements compared to PBO as early as Wk 1 in joint pain, HAQ-DI, and PatGA. Fatigue also improved significantly, at the earliest time point measured (Wk 4). Improvements for pain, PatGA, and physical function persisted up to Wk 52, and were generally consistent in the bDMARD-naive (SPIRIT-P1) and TNFi-IR (SPIRIT-P2) populations.
References:
1. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1):79-87.
2. Nash P, et al. Lancet. 2017;389(10086):2317-2327.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Orbai AM, Gladman DD, Birt J, Gellett AM, Lin CY, Kvien T. Rapid and Sustained Improvements in Patient-Reported Signs and Symptoms with Ixekizumab in Biologic-Naive and TNF-Inadequate Responder Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-and-sustained-improvements-in-patient-reported-signs-and-symptoms-with-ixekizumab-in-biologic-naive-and-tnf-inadequate-responder-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-and-sustained-improvements-in-patient-reported-signs-and-symptoms-with-ixekizumab-in-biologic-naive-and-tnf-inadequate-responder-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/