Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tildrakizumab (TIL), a high-affinity anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody, is approved for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis treatment and is under investigation for PsA. This study evaluated the 24-week efficacy and safety results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose, phase 2b TIL study in patients with active PsA (NCT02980692).
Methods: Patients with active PsA were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to receive TIL (200 mg once every 4 weeks [Q4W] [n = 78], 200 mg every 12 weeks [Q12W] [n = 79], 100 mg Q12W [n = 77], 20 mg Q12W [n = 78] to week 24), or placebo (PBO) Q4W to week 24 (n = 79). Stable concomitant methotrexate or leflunomide use was permitted but not mandated. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved a 20% reduction from baseline in ACR response criteria (ACR20) at week 24. Other outcome measurements included proportion of patients achieving ACR50/70 response and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75, PASI 90, and changes in swollen and tender joint count at week 24. Safety assessments included monitoring of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
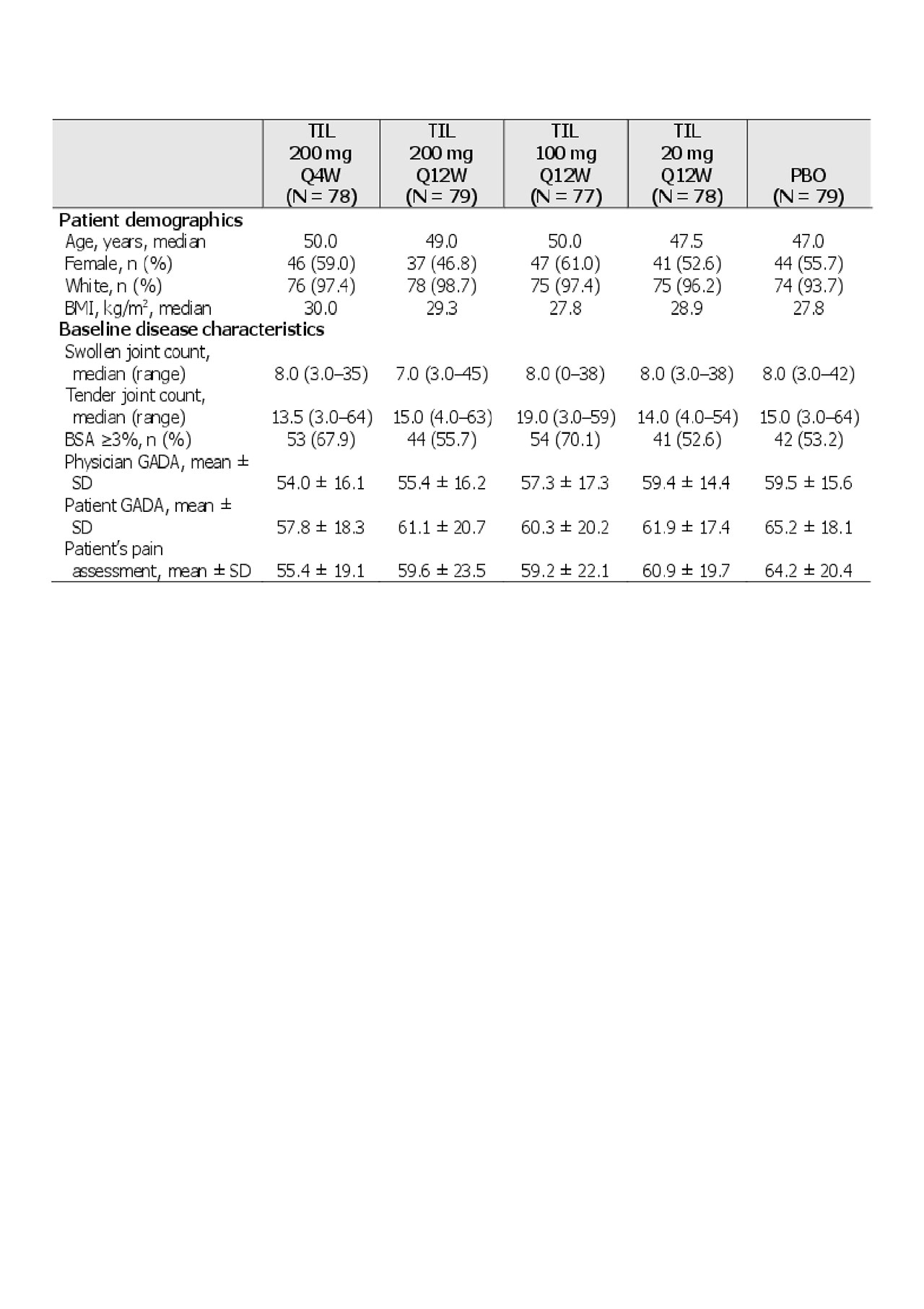
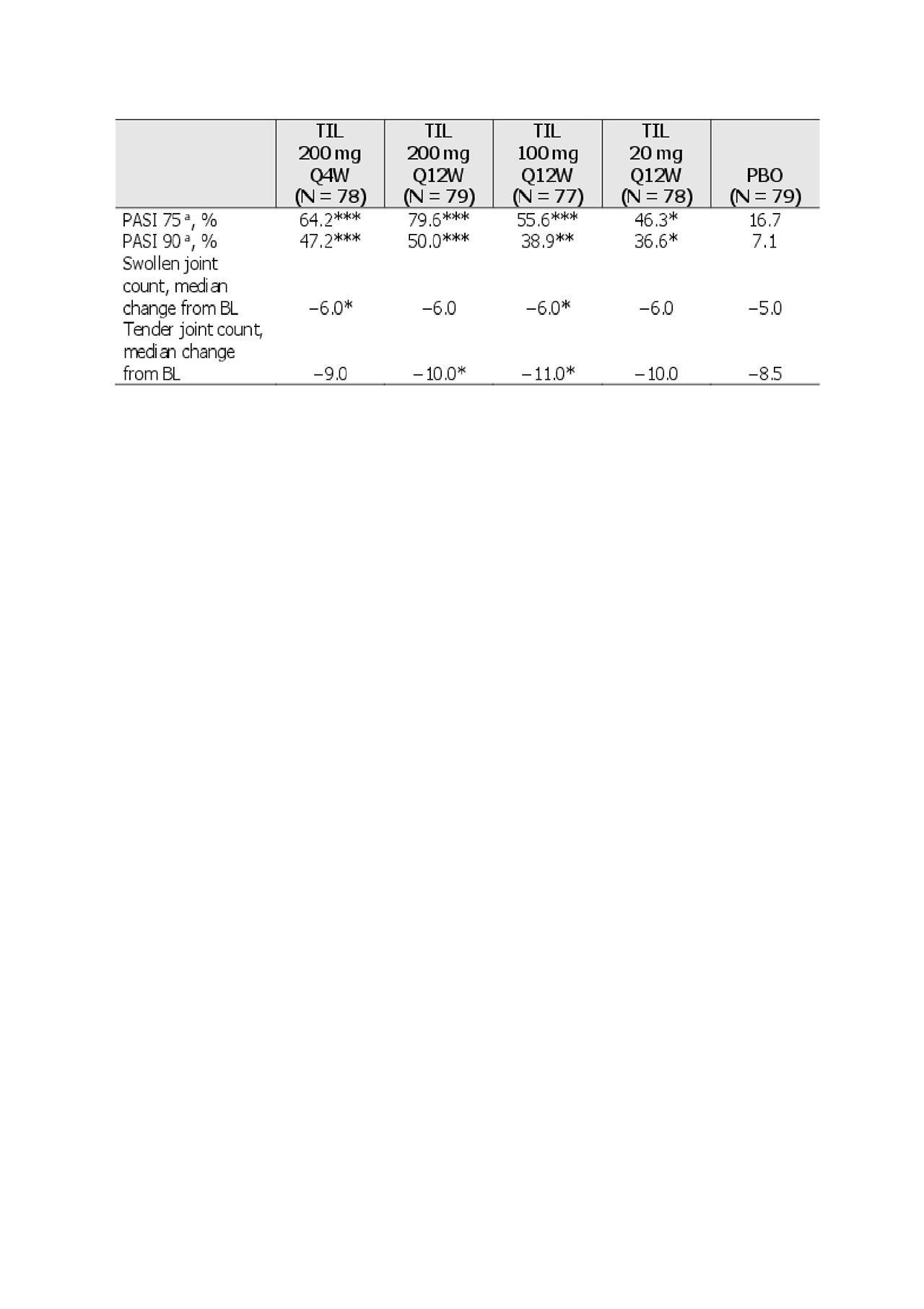
Results: Of 500 patients screened, 391 patients met the inclusion criteria (including ≥18 years old, PsA diagnosis with symptoms for 6 months, and ≥3 tender and ≥3 swollen joints). Demographics and baseline disease characteristics are shown in Table 1. There were significantly greater proportions of ACR20/50/70 and PASI 75/90 responders with TIL vs PBO at week 24, and in some cases differences in parameters were noted as early as week 8 (Figure 1 and Table 2).
The most frequent TEAEs through week 24 included nasopharyngitis (pooled TIL arms: 5.4% [17/312]; PBO: 6.3% [5/79]); and diarrhoea (TIL: 1.3% [4/312]; PBO: 0). There were no reports of candidiasis, inflammatory bowel disease, major adverse cardiac events, or malignancy. No patients discontinued treatment due to TEAEs and no deaths were reported. Serious TEAEs occurred in 2.2% (7/312) of TIL-treated patients vs 2.5% (2/79) in PBO-treated patients.
Conclusion: By week 24, TIL was significantly more efficacious than PBO in the treatment of joint and skin manifestations of PsA. Furthermore, there was a clear separation between TIL and PBO as early as 8 weeks for ACR20 (TIL 200 mg Q4W and 100 mg Q12W) and 12 weeks for both ACR20 (TIL 200 mg doses) and ACR50 (all TIL groups). Shortening the dosing interval from Q12W to Q4W for the 200-mg dose did not result in a measurable increase in skin or joint response scores. There was a low rate of TEAEs in the TIL-treated group.
Editorial support was provided by Claire Daniele, PhD, CMPP; and Marie-Louise Ricketts, PhD, of AlphaBioCom, LLC, and funded by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
BMI, body mass index; BSA, body surface area; GADA, global assessment of disease activity; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q12W, every 12 weeks; PBO, placebo; SD, standard deviation; TIL, tildrakizumab.
*P <0.05; **P <0.001; ***P <0.0001 vs PBO.
PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q12W, every 12 weeks; TIL, tildrakizumab.
aResponse rates only calculated in patients with BSA ≥3% at baseline, missing responses were imputed as nonresponses. *P <0.05; **P <0.001; ***P <0.0001 vs PBO.
BL, baseline; BSA, Body Surface Area; PASI, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q12W, every 12 weeks; TIL, tildrakizumab.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Chohan S, García Fructuoso F, Gottlieb A, Chou R, Mendelsohn A, Ballerini R, Luggen M. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multiple-Dose, Phase 2b Study to Demonstrate the Safety and Efficacy of Tildrakizumab, a High-Affinity Anti–Interleukin-23P19 Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-multiple-dose-phase-2b-study-to-demonstrate-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-tildrakizumab-a-high-affinity-anti-interleukin-23p19-monoclonal-antibody/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-multiple-dose-phase-2b-study-to-demonstrate-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-tildrakizumab-a-high-affinity-anti-interleukin-23p19-monoclonal-antibody/