Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia (FM) is a nociplastic syndrome of chronic widespread pain, nonrestorative sleep, fatigue, cognitive dysfunction and mood symptoms. RESILIENT was a confirmatory Phase 3 trial of daily bedtime TNX-102 SL (TNX, sublingual cyclobenzaprine [CBP] HCl) 5.6 mg for FM.
Methods: Across 33 US sites, 457 patients meeting 2016 Revised FM criteria were randomized 1:1 to 2 weeks TNX 2.8 mg followed by 12 weeks 5.6 mg, or to matching placebo (PBO). The primary endpoint was Week 14 change from baseline in weekly average of daily diary numeric rating scale (NRS) pain intensity. Six key secondary endpoints were: Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC)-responders; Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire – Revised (FIQR) Symptoms (S) and Function (F) domains; PROMIS Sleep Disturbance (SD) and Fatigue; and Sleep Quality by daily diary NRS. The primary and continuous key secondary efficacy endpoints were analyzed by mixed model repeated measures with multiple imputation; and dichotomous endpoints by Pearson Chi-Squared; with multiplicity adjustment and type 1 error control by prespecified sequential testing waterfall. Exploratory secondary endpoints were the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II), Changes in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire short form (CSFQ-14) and individual FIQR items. All patients received e-learning training on placebo response reduction and accurate pain reporting at every visit.
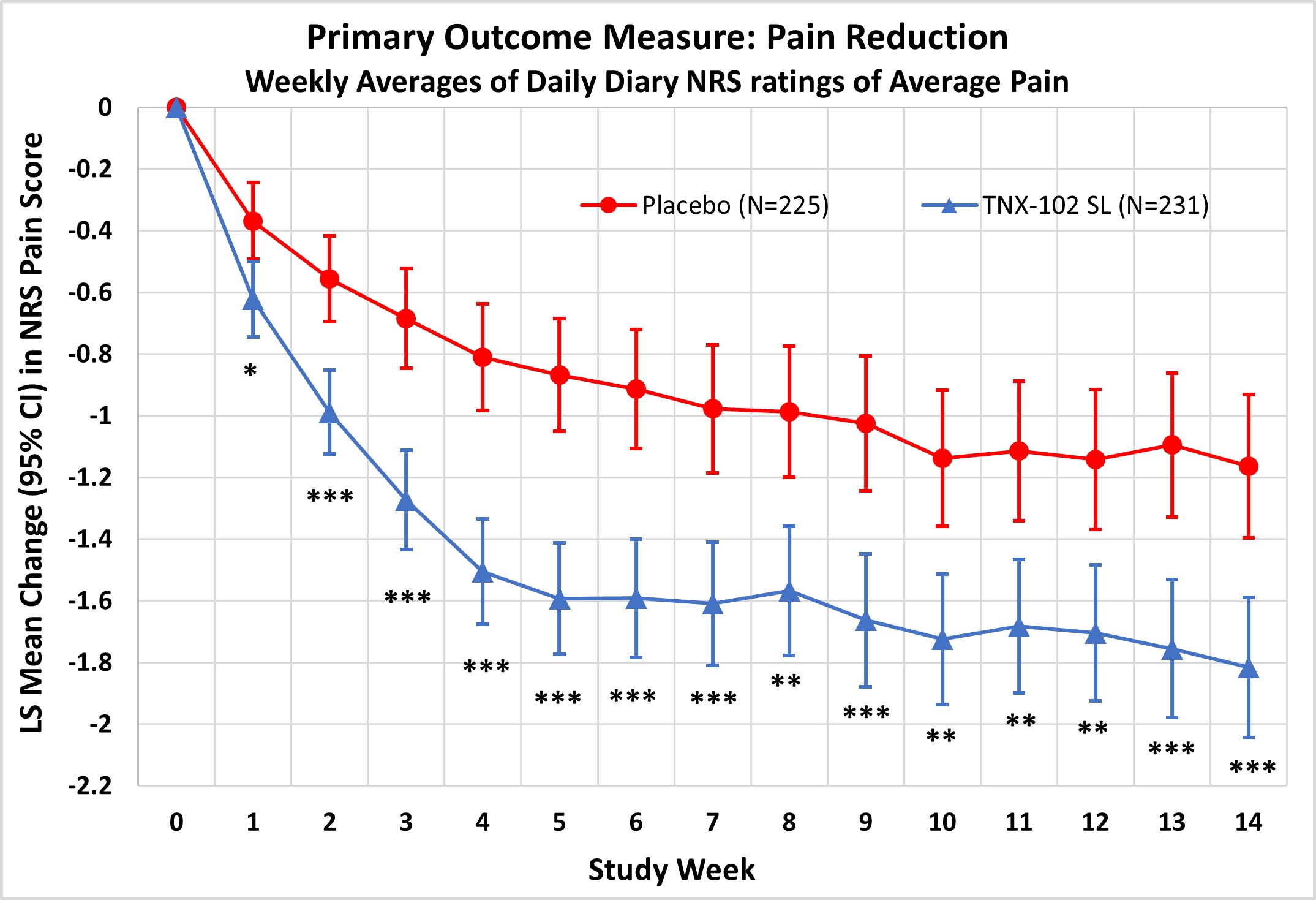
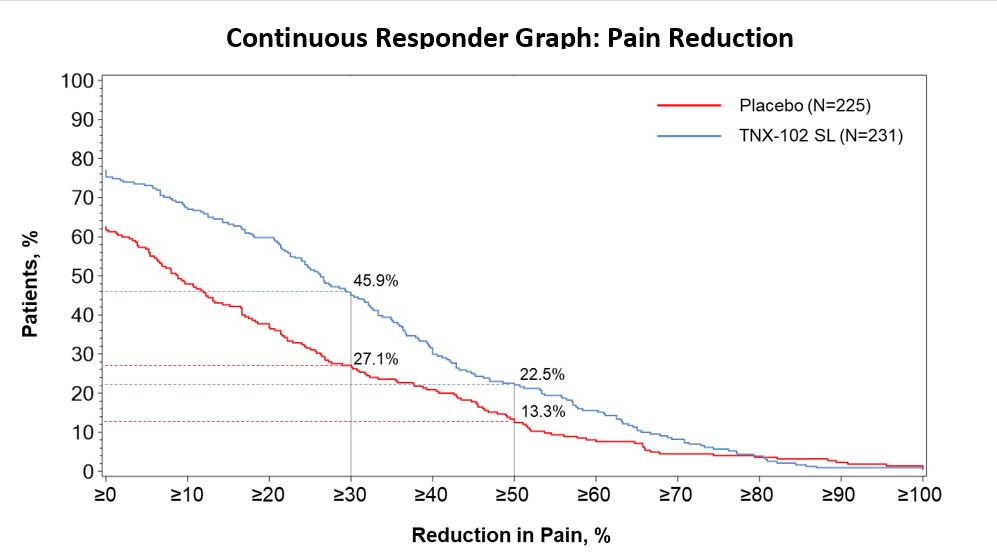
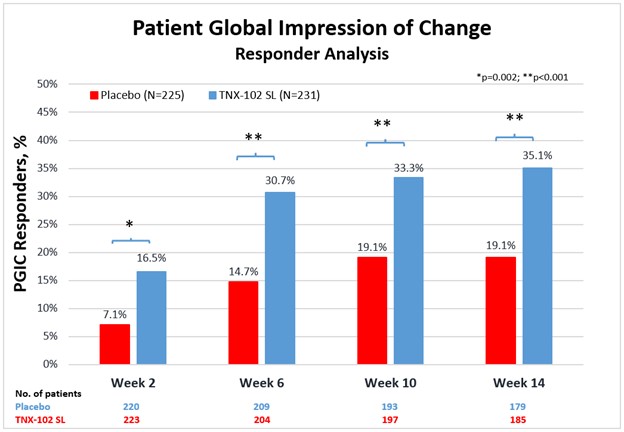
Results: TNX significantly reduced FM pain at Week 14 (LS mean [SE] difference v PBO of −0.7 [0.16]; P = 0.00005; effect size = 0.38). Significant improvement was also observed in: PGIC (TNX-response 35.1% v 19.1% PBO, P = 0.0001); FIQR-S (P = 0.000002); FIQR-F (P = 0.001); PROMIS SD (P = 0.0000001) and Fatigue (P = 0.00009); and Sleep Quality (P = 0.0007). Among exploratory endpoints, BDI-II total score (P = 0.001, uncorrected) and the FIQR Memory item (P = 0.001, uncorrected) were more improved on TNX. CSFQ-14 in females suggested TNX improved sexual function over PBO based on total score, and orgasm/completion and desire/frequency domains (all P < 0.05, uncorrected). TNX was well tolerated without clinically meaningful changes in blood pressure or weight. The only systemic adverse events (AEs) at >3.0% rate were COVID-19, headache and somnolence. Administration site reactions of oral hypoaesthesia were the most frequent (TNX 23.8%, PBO 0.4%), and were transient, self-limited, and rated as mild (22.1%), occasionally moderate (1.7%), and never severe. Comparing TNX-treated patients with or without oral sensory AEs showed no significant difference in the treatment effect on pain.
Conclusion: This confirmatory Phase 3 study demonstrates TNX significantly improves a broad spectrum of core FM symptoms including widespread pain, and nonrestorative sleep, fatigue, as well as global function. TNX improved depressive symptoms, cognitive function and female sexual function in exploratory analyses. TNX had a favorable tolerability profile. These results suggest TNX has potential to treat fibromyalgia at a syndromal level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lederman S, Arnold L, Kelley M, Vaughn B, Engels J, Sullivan G. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Confirmatory Phase 3 Trial of Bedtime Sublingual Cyclobenzaprine (TNX-102 SL) in Fibromyalgia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-confirmatory-phase-3-trial-of-bedtime-sublingual-cyclobenzaprine-tnx-102-sl-in-fibromyalgia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-confirmatory-phase-3-trial-of-bedtime-sublingual-cyclobenzaprine-tnx-102-sl-in-fibromyalgia/