Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Disease progression and therapy response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is currently evaluated using clinical and functional assessments that include subjective measurements such as DAS28, HAQ, and the Michigan Hand Outcome Questionnaire (MHQ). Studies have been conducted to determine potential associations between radiological imaging, DAS28, and HAQ. There are limited studies that investigate the connection with MHQ. Our study aims to explore if radiological studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) demonstrate any association with the more hand-focused MHQ score.
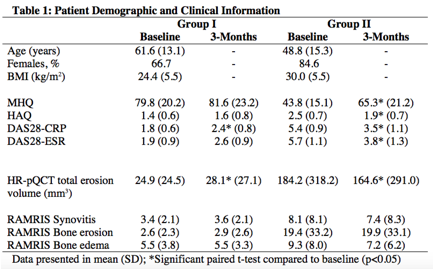
Methods: Patients were screened and separated into two groups based on their disease activity determined by DAS28: Group I: low disease activity (DAS28 ²3.2) and Group II: high disease activity (DAS28 >3.2). Following current guidelines set by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR); group I continued their current treatment using methotrexate, while group II were initiated on an anti-TNFα. At baseline (immediately before anti-TNFα initiation for group II) and 3-months, each patient underwent clinical (DAS28), functional (MHQ and HAQ), and structural (imaging of dominant hands/wrists via 3 Tesla MRI and HR-pQCT) assessments. Bone marrow edema pattern, synovitis, and erosion were graded using the RA MRI score (RAMRIS) system. Bone erosion volumes were calculated using HR-pQCT images. Measures at baseline and 3-months were compared using paired t-test. The association between changes in MHQ and imaging measures from baseline to 3-months were evaluated using PearsonÕs correlation coefficient.
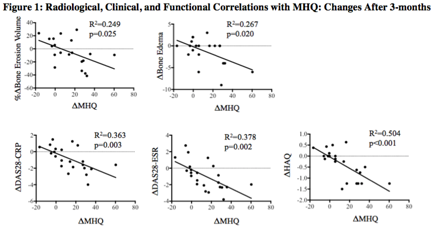
Results: Twenty patients were studied (9 group I and 11 group II, Table 1). Significant increases in MHQ (suggesting improvement) and significant decreases of DAS and erosion volumes from baseline to 3-months were observed in group II (Table 1); while significant increases in DAS28-CRP and erosion volumes were observed in group I. 3-month changes in bone erosion volume and edema had a significant correlation with changes in MHQ score (Figure 1 top). Significant correlations with 3-month changes in MHQ and DAS28 and HAQ were also found (Figure 1 bottom).
Conclusion: Advanced imaging measures such as bone erosion volume and bone marrow edema show great potential to serve as biomarkers to determine disease progression, therapy response, and specific hand functions in patients with RA. The study is recruiting more patients and will follow up patients at 12-months to evaluate potential imaging markers that may predict hand functional outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cruz A, Shimizu T, Tanaka M, Mamoto K, Burghardt AJ, Heilmeier U, Link T, Graf J, Imboden JB Jr., Li X. Radiological Changes Measured By MRI and High-Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography (HR-pQCT) Show Correlation with Michigan Hand Outcome Questionnaire (MHQ) in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/radiological-changes-measured-by-mri-and-high-resolution-peripheral-quantitative-computed-tomography-hr-pqct-show-correlation-with-michigan-hand-outcome-questionnaire-mhq-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-p/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/radiological-changes-measured-by-mri-and-high-resolution-peripheral-quantitative-computed-tomography-hr-pqct-show-correlation-with-michigan-hand-outcome-questionnaire-mhq-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-p/