Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is a novel, oral Janus kinase inhibitor being investigated as a targeted immunomodulator and disease-modifying therapy for RA. This Phase 3, 24-mo study (ORAL Start; NCT01039688) compared efficacy, including inhibition of structural damage, and safety of tofacitinib vs methotrexate (MTX, 10-20 mg/wk) in MTX-naïve patients (pts) with active RA.
Methods: Pts were randomized 2:2:1 (double-dummy, double-blind) to: tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID); tofacitinib 10 mg BID; or MTX 10 mg/wk with 5 mg/wk increments every 4 wks to 20 mg/wk. Predetermined primary endpoints (Mo 6) compared tofacitinib vs MTX for: 1) mean changes from baseline (BL) in van der Heijde modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS); 2) ACR70 response. Evaluation of safety and tolerability was also a primary objective. Results are from planned 12‑mo interim analyses.
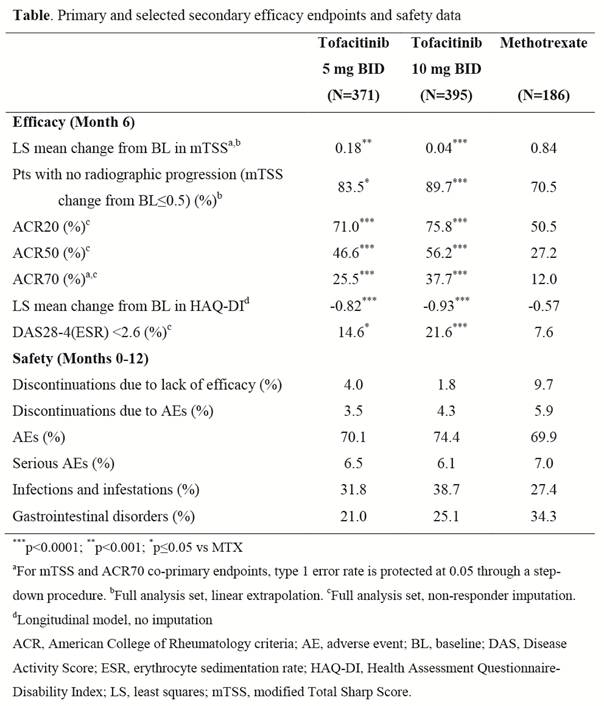
Results: Overall, 952 pts were randomized and treated with tofacitinib 5 mg BID (N=371), 10 mg BID (N=395), and MTX (N=186). Demographic and BL RA disease characteristics, including radiographic scores (mTSS: 20.30, 18.85, and 16.51 for 5 mg BID, 10 mg BID, and MTX, respectively), were similar across groups. Mean changes from BL in mTSS and ACR70 rates at Mo 6 were statistically superior for both doses of tofacitinib vs MTX (Table). There was a statistically significant difference in ACR70 response for both doses of tofacitinib vs MTX by Mo 1 (first post-BL visit) with increasing efficacy over time. Secondary radiographic endpoints were also significantly different for tofacitinib vs MTX: smaller changes in erosion and joint space narrowing scores and greater proportions of pts with no progression from BL (mTSS change ≤0.5) at Mo 6. Other secondary endpoints, including ACR20 and ACR50 responses, mean change in DAS28-4(ESR), DAS28-4(ESR) <2.6 rates, and mean change in HAQ-DI, were significantly better with tofacitinib vs MTX at all timepoints.
The incidence of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs was similar across groups (Table). Most AEs were mild or moderate; the most frequently reported AEs in all groups were infections. Herpes zoster occurred in 2.2%, 2.5%, and 1.1% of tofacitinib 5 mg BID, 10 mg BID, and MTX pts, respectively; 1 pt had bone tuberculosis (10 mg BID) and 1 had cytomegalovirus infection (MTX); 2 tofacitinib pts died later in the same trial. Decreases in mean neutrophil counts and small increases in mean serum creatinine were seen in all groups. Increases were seen in mean LDL- and HDL-cholesterol levels with tofacitinib. The incidence of aspartate and alanine aminotransferase elevations ≥3x the upper limit of normal was low.
Conclusion: In this Phase 3 study tofacitinib monotherapy significantly inhibited progression of structural damage and improved RA signs and symptoms and physical functioning vs MTX in MTX-naïve pts. The safety of tofacitinib was similar to that reported in other Phase 3 trials reported previously.
Disclosure:
E. B. Lee,
Pfizer Inc.,
5;
R. Fleischmann,
Pfizer Inc.,
2,
Pfizer Inc.,
5;
S. Hall,
None;
R. F. van Vollenhoven,
Abbott, BMS, GSK, HGS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, UCB,
2,
Abbott, BMS, GSK, HGS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, UCB,
5;
J. Bradley,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
D. Gruben,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
T. Koncz,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
S. Krishnaswami,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
G. Wallenstein,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
S. H. Zwillich,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
B. E. Wilkinson,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/radiographic-clinical-and-functional-comparison-of-tofacitinib-monotherapy-versus-methotrexate-in-methotrexate-naive-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/