Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Quantitative analysis of fibrotic patterns provides an objective measurement of treatment efficacy in interstitial lung disease (ILD). We aimed to measure the extent of ILD in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients by computer-aided analysis of high-resolution chest CT (HRCT), and to identify correlation with the visual assessment by radiologist and results of pulmonary function test (PFT).
Methods: Twenty-six RA patients with ILD who had two HRCTs with matched PFT result within 3 months were enrolled in this retrospective study. Demographic, clinical, laboratory information were obtained through a medical chart review. Quantitative analysis of HRCT image was conducted by the Radiology Core at University of California at Los Angeles. Quantitation was expressed as parameters in detail such as ground-glass opacity (QGG), lung fibrosis (QLF), honeycombing (QHC), and their summation (QILD).
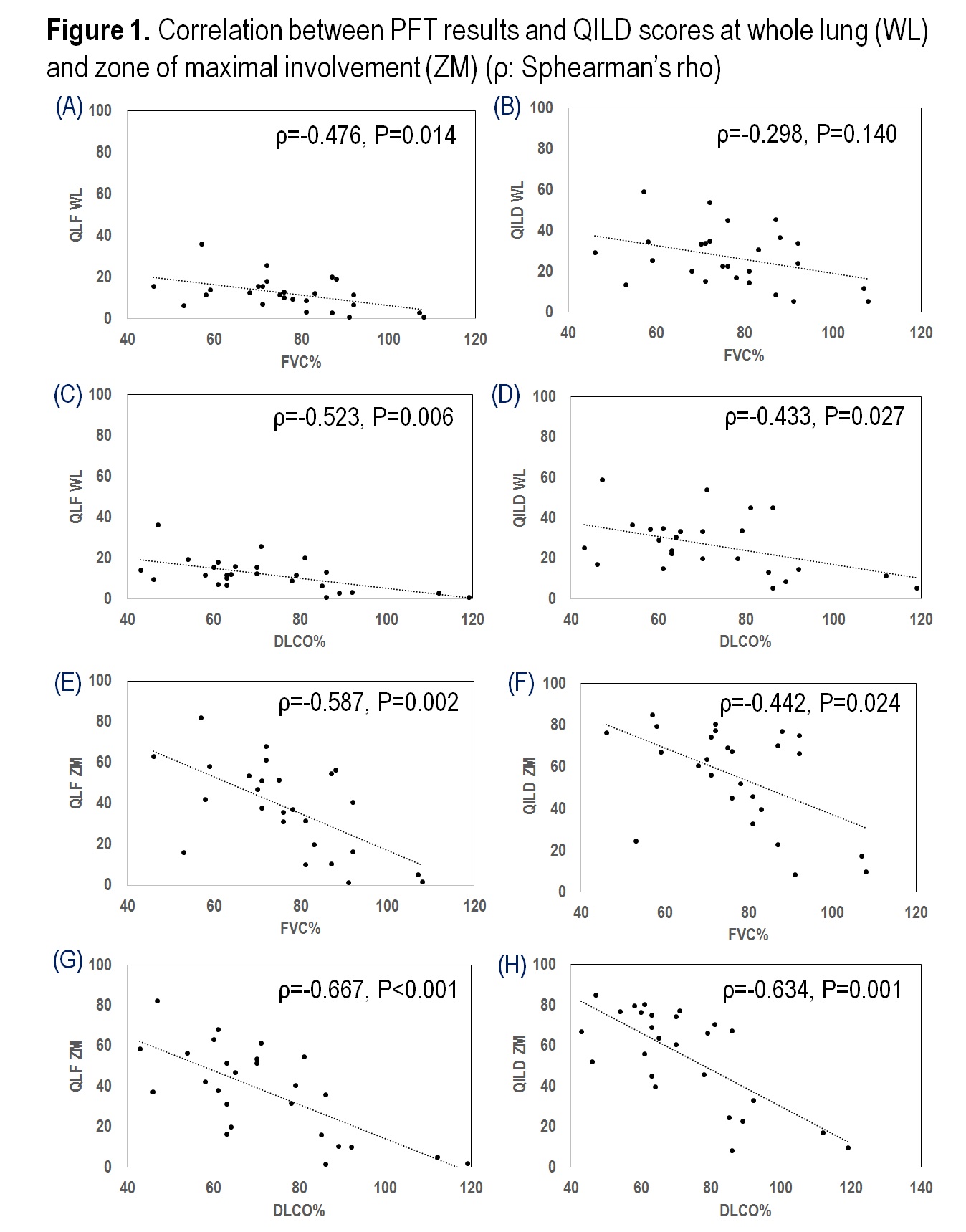
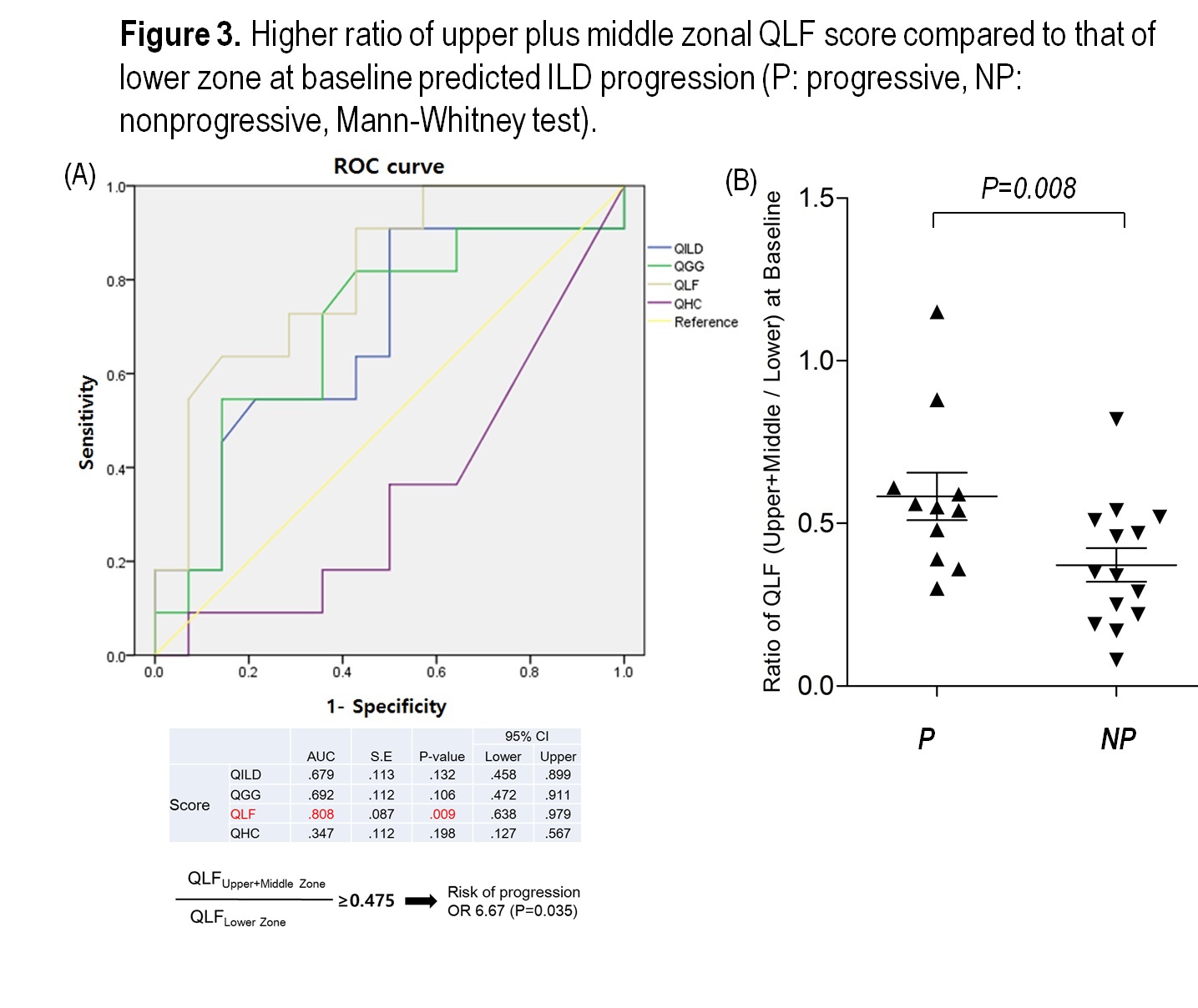
Results: Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics of the patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease were not different when analyzed by interval progression evaluated by radiologist, except for body mass index (progressive group 20.0¡¾3.7; non-progressive group 25.5¡¾3.6 kg/m2, P = 0.001), time interval between HRCTs (progressive group 2.0¡¾1.2; non-progressive group 1.1¡¾0.6 years, P = 0.047), and all-cause mortality (progressive group 50.0%; non-progressive group 7.1%, P = 0.031). Negative correlation between PFT results and QILD scores at whole lung or zone of maximal involvement were significant (Fig. 1). Correlation between the evaluation of radiologist and QILD scores at whole lung was significant on QLF score (progressive group 3.38¡¾4.15; non-progressive group -1.01¡¾2.64, P = 0.004) (Fig. 2). More involvement of ILD on upper and middle zone of lung (versus lower zone) would predict progression of ILD (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: QILD score provides reliable estimate of ILD status and prognosis in RA patients when compared to PFT and assessment of radiologist.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee JS, Kim HJG, Goldin J, Lee W, Ha YJ, Kang EH, Lee YJ, Song YW, Lee EY. Quantitative Radiographic Analysis of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitative-radiographic-analysis-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitative-radiographic-analysis-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/