Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome is a rare autoimmune disease with heterogeneous presentation and severe disease burden. Factors influencing the quality of life (QoL) in patients with SAPHO syndrome remained under-recognized. We aim to assess the impact of various current symptoms (osteoarticular, dermatological and nail) on QoL in SAPHO patients.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted based on a previously established single-center dynamic cohort of SAPHO syndrome.1, 2 Electronic questionnaires were distributed to patients recruited from January 2004 and December 2018 via a patient committee. Patients with active disease were asked to report their current clinical presentation (osteoarticular, dermatological and nail) and fill out the EuroQol five dimensions questionnaire (EQ-5D). Health related quality of life results measured by the EQ-5D were converted to a utility score using the Chinese time trade-off value set.3 In addition, for those with osteoarticular manifestations, disease activity was measured using Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI). The Dermatology Quality of Life Index (DLQI) was obtained from the patients with dermatological manifestations.
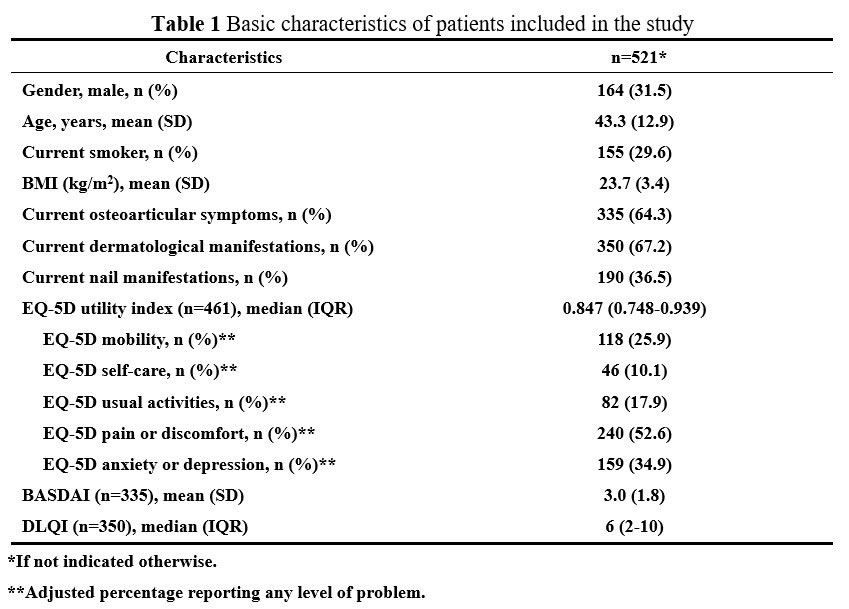
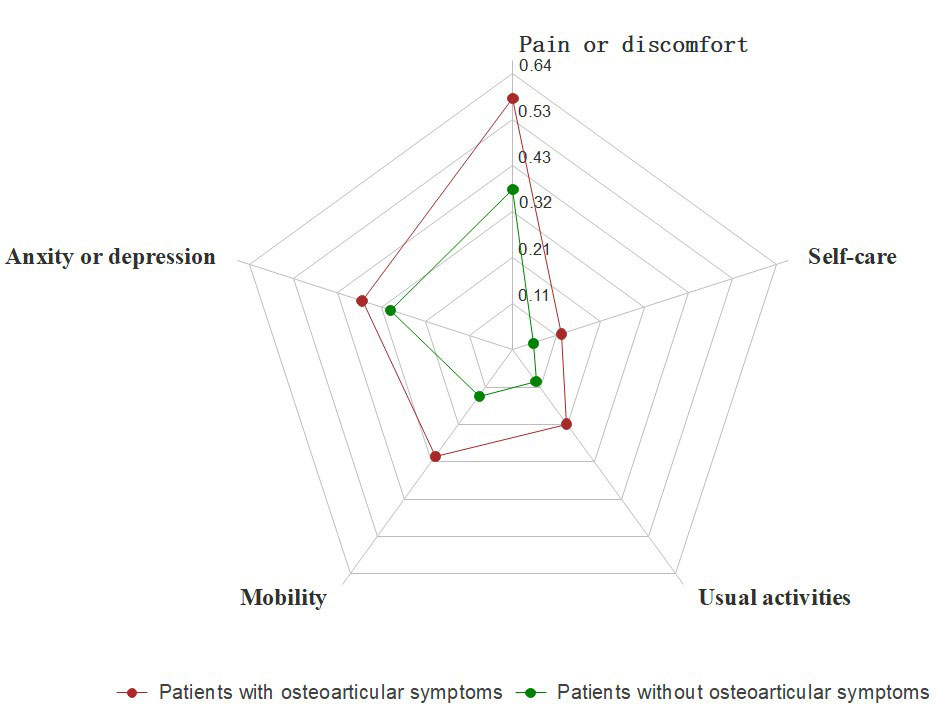
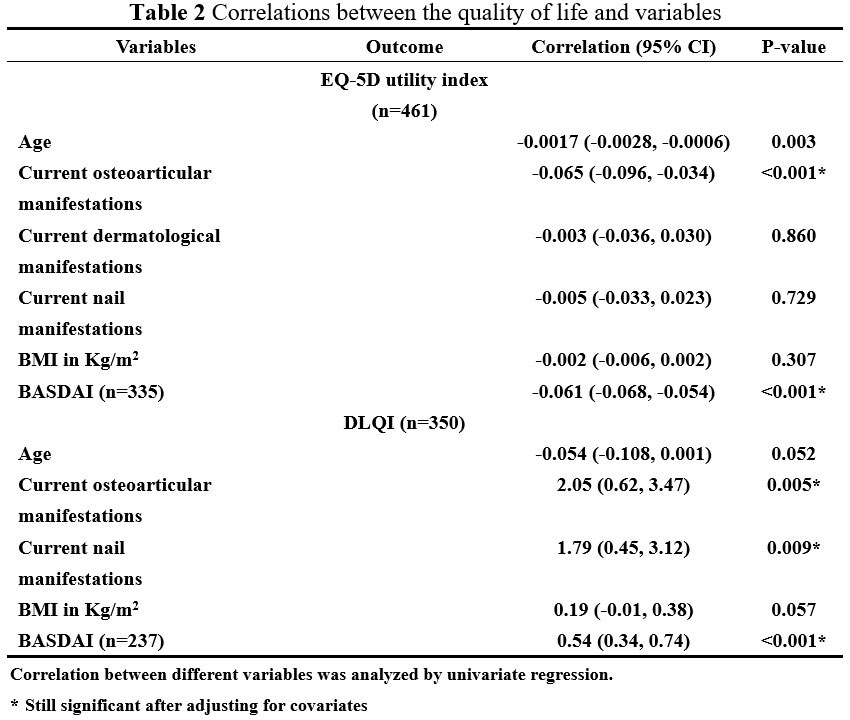
Results: A total of 588 questionnaires were issued and 521 were retrieved. 60 were in remission at the time of examination. For the EQ-5D dimensions, patients reported the most problems (of any level) with pain or discomfort (52.6% [95% CI 48•0–57.2]) and fewest problems with self-care (10.1% [7.6–13•2]). Patients with current osteoarticular symptoms had a significant lower EQ-5D score than those without, which remained significant after adjustment for covariates (age, gender, smoking, and BMI). Meanwhile, such a relationship was not shown for dermatological and nail manifestations. For patients with skin lesions, DLQI was significantly lower at the presence of osteoarticular symptoms or nail lesions, even after adjusting for covariates.
Conclusion:
Our findings suggested a negative correlation between osteoarticular symptoms and QoL in SAPHO syndrome. Effectively controlling osteoarticular symptoms may be pivotal in improving patient QoL. Nail involvement, which is under-recognized previously, also had a negative influence on QoL in SAPHO patients.
References:
- Li C et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(6):1023-30.
- Cao Y et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;48(6):990-6.
- Liu GG et al. Value in health : the journal of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research. 2014;17(5):597-604.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li Z, Li C, Cao Y, Xiang Y, Li Y, Zhang W. Quality of Life in Patients with SAPHO Syndrome: A Single-center Survey of 588 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-in-patients-with-sapho-syndrome-a-single-center-survey-of-588-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-in-patients-with-sapho-syndrome-a-single-center-survey-of-588-patients/