Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster II: Clinical/Epidemiology Studies
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Assessment of SpA international Society Health Index (ASAS HI) was developed to assess function, disability, and health in patients (pts) with SpA. This is the first time that the ASAS HI has been included in a Phase 3 clinical study. Psychometric properties of the ASAS HI in pts with active radiographic axial SpA (r-axSpA) in a Phase 3 study of ixekizumab, an IL-17A monoclonal antibody (COAST-V [NCT02696785]) are presented.
Methods: The ASAS HI questionnaire consists of 17 items, total score ranging from 0 (good health) to 17 (poor health). The psychometric properties of the questionnaire, including test-retest reliability, convergent and discriminant validity, as well as responsiveness, were evaluated using pooled data from 4 treatment groups (placebo, adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks, and ixekizumab 80 mg every 2 or 4 weeks). COAST-V enrolled biologic DMARD-naive adults with active r-axSpA per ASAS criteria (sacroiliitis defined centrally by modified New York Criteria and ≥1 SpA feature), BASDAI ≥4, back pain ≥4, and inadequate response or intolerance to NSAID therapy.
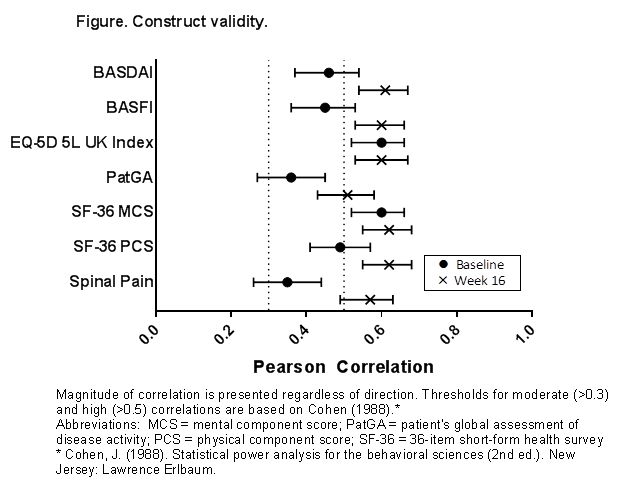
Results: A total of 341 pts were randomized at Week 0. Mean (SD) ASAS HI score at baseline in the pooled group was 8.05 (3.6). Test-retest reliability of ASAS HI between screening and baseline was evidenced by intraclass correlation (0.76). Construct validity analyses demonstrated that the ASAS HI score is moderately correlated with Spinal Pain, Short-Form 36 physical and mental component scores, EQ-5D 5-Level UK Population-based Index, Patient’s Global Assessment, BASDAI, and BASFI at baseline (|r│>0.30, Figure [circles]) and strongly correlated at Week 16 (|r|>0.50; Figure [crosses]). Known-group validity of ASAS HI was demonstrated by significant difference among ASDAS categories at baseline and Week 16 (p<.001 for all comparisons). Greater improvements in disease activity were associated with greater improvements in ASAS HI scores at Week 16 (Table). Changes in ASAS HI from baseline at Week 16 were highly correlated with ASDAS, BASDAI, and BASFI changes (all correlations >.50).
Conclusion: The ASAS HI demonstrated reliability, construct validity, and responsiveness in adults with r‑axSpA, supporting measurement properties of this instrument in an external study. Based on its content validity, the data suggest that the ASAS HI provides additional information beyond core disease activity and response criteria traditionally used in randomized clinical studies. This includes a balanced characterization of treatment effects from the patient perspective.
|
Table. Association between ASAS HI Change from Baseline and Disease Activity at Week 16 (Pooled Treatment Groups) |
|||
|
|
ASAS20 Nonresponder |
Patient Achieving ASAS20, But Not ASAS40 |
ASAS40 Responder |
|
N |
143 |
67 |
130 |
|
ASAS HI (LSM [SE]) |
-0.7 (0.2) |
-1.6 (0.3)* |
-4.2 (0.2)***,§ |
|
|
ASDAS Improvement <1.1 |
ASDAS Improvement ≥1.1 but <2.0 (CII) |
ASDAS Improvement ≥2.0 (MI) |
|
N |
171 |
101 |
68 |
|
ASAS HI (LSM [SE]) |
-0.9 (0.2) |
-2.5 (0.2)*** |
-4.9 (0.3)***,§ |
|
|
BASDAI50 |
BASDAI50 |
|
|
N |
226 |
114 |
|
|
ASAS HI (LSM [SE]) |
-1.2 (0.2) |
-4.3 (0.2)*** |
|
|
ASAS HI = Assessment of SpA International Society Health Index; ASDAS = AS Disease Activity Score; CII = clinically important improvement; LSM = least-squares mean; MI = major improvement. *p<.05; ***p<.001 versus lowest response group. §p<.001 versus middle response group. Note: An analysis of covariance model with change in ASAS HI score as dependent variable and clinical outcome (ASAS, ASDAS, or BASDAI50) response and baseline ASAS HI as independent variables was applied. Post hoc comparison was conducted with Scheffe’s correction. |
|||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiltz U, van der Heijde D, Boonen A, Gensler LS, Hunter T, Dong Y, Wyrwich K, Carlier H, Braun J. Psychometric Properties of the Assessment of Spa International Society Health Index in Patients with Active As/Radiographic Axial Spa in a Phase 3 Clinical Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psychometric-properties-of-the-assessment-of-spa-international-society-health-index-in-patients-with-active-as-radiographic-axial-spa-in-a-phase-3-clinical-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psychometric-properties-of-the-assessment-of-spa-international-society-health-index-in-patients-with-active-as-radiographic-axial-spa-in-a-phase-3-clinical-study/