Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease 12-item questionnaire (PsAID12) has been developed to measure impact of Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) for purposes of monitoring and clinical management. We aim to investigate the relation between change in disease activity and change in PsAID, and which domains of the PsAID are main drivers of change in score.
Methods: Newly diagnosed PsA patients were included in the Dutch southwest Early Psoriatic Arthritis cohoRt (DEPAR). For this analysis, patients that have answered the PsAID12 (range 0-10) at two consecutive visits (i.e. 3 months apart) within the first year were included. In case longer periods per patients were available, data from the first period of three months was used. The change in PsAID was compared to the change in disease activity over this period, measured with the Composite Psoriatic Disease Activity Index (CPDAI) using Spearman’s correlation. Change in score on PsAID domains was analyzed in subgroups of patients that perceived improvement in health and those that perceived worsening. The Short Form-36 question on self-perceived change in health was used to determine these subgroups.
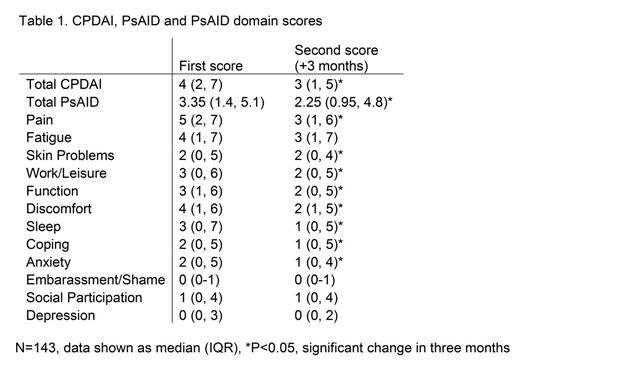
Results: 143 unique patients had at least one period with two PsAID and CPDAI measurements (Table 1). Mean age was 51 (SD 13.7) and 70 (49%) were male. The difference in PsAID score was significantly but moderately correlated with the difference in CPDAI (Spearman’s rho 0.267, P=0.0013). 58 patients (41%) reported a better health status compared to 3 months ago and 29 worsening of health status. Figure 1 shows that improved patients had higher scores in almost all domains, with the biggest improvement in pain. Domains of skin problems and embarrassment/shame did not improve significantly. Worsened patients only had significantly lower scores in fatigue, discomfort and social domains.
Conclusion: Improvement in CPDAI disease activity was significantly but moderately associated with improvement in PsAID score. This reflects that the PsAID partially measures disease activity, but measures other constructs of disease as well. In early PsA, a state of improved health is reflected in the PsAID in almost all domains, with the strongest effect in pain.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wervers K, Luime JJ, Tchetverikov I, Gerards AH, Kok MR, Appels CWY, van der Graaff WL, van Groenendael JHLM, Korswagen LA, Veris J, Hazes JMW, Vis M. Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PSAID12) in Early Psoriatic Arthritis: Pain As One of the Main Determinants of Disease Impact [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-psaid12-in-early-psoriatic-arthritis-pain-as-one-of-the-main-determinants-of-disease-impact/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-psaid12-in-early-psoriatic-arthritis-pain-as-one-of-the-main-determinants-of-disease-impact/