Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Fibromyalgia & Other Clinical Pain Syndromes Poster (0118–0127)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia (FM), a condition characterized by chronic widespread pain, has implications beyond functional disability. FM has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in multiple studies, however, there is a paucity of studies looking for dyslipidemia in diagnosed cases of FM. This study sought to explore the association between FM and dyslipidemia.
Methods: This was a case-control study conducted at a tertiary care center in South India from March 2018 to December 2020. FM patients and healthy controls were enrolled in a 1:3 ratio. FM was diagnosed as per the 2016 modified ACR 2010/2011 criteria. Healthy controls who were age, gender, ethnicity and body mass index (BMI) matched were recruited in the study. Fasting lipid profile was obtained from study participants and dyslipidemia was defined by the “Adult treatment panel III criteria”. (1)The revised fibromyalgia impact questionnaire (FIQR) was used as a tool to ascertain disease severity in FM at diagnosis. The prevalence of dyslipidemia in FM was compared with that of healthy controls and odds ratio was calculated. We also studied the correlation of FIQR with fasting lipid profile. Chi- square test and Pearson correlation coefficient was computed and linear regression t test were applied to test statistical significance. A p value < 0.05 was considered significant.
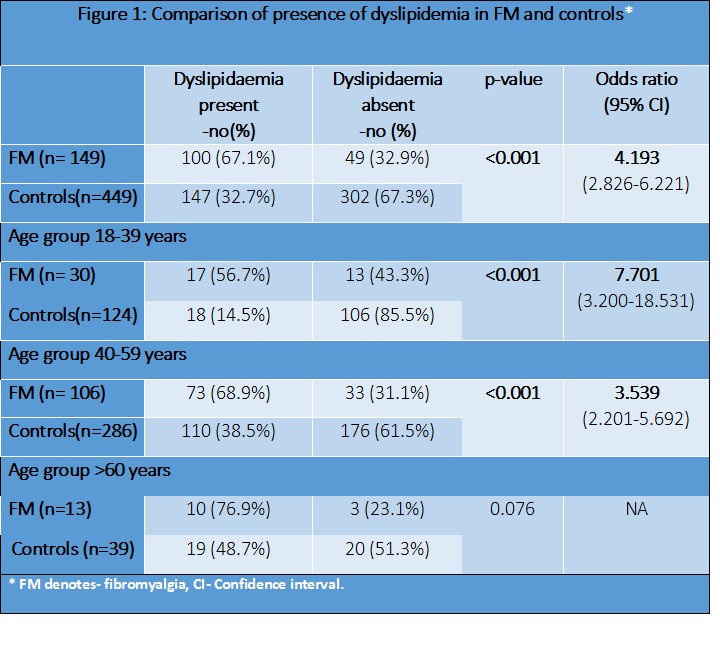
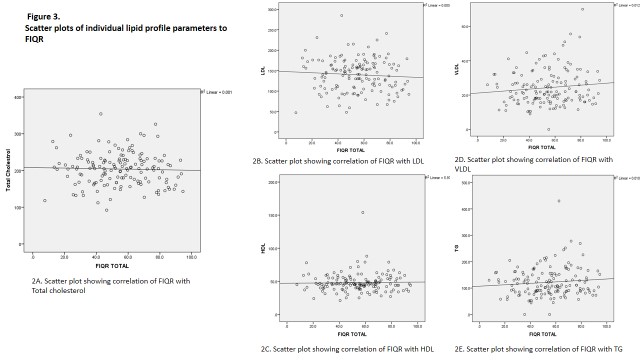
Results: A total of 149 (females- 147) FM cases and 449 healthy controls were enrolled in the study. We noted that dyslipidemia was present in 100 (67%) FM cases and 147 (33%) controls, their difference was statistically significant (p< 0.001; OR 4.193). Subgroup analysis amongst individual age groups showed an increased prevalence of dyslipidemia in the 18-39 years with 17 (57%) amongst FM cases as compared to 18 (15%) in control group (p< 0.001; OR 7.701). In the 40-59 years age group, 73 (68%) FM patients were dyslipidemic as compared to 110 (39%) of the controls (p< 0.001, OR: 3.539). There was no statistically significant difference in prevalence of dyslipidemia between cases and controls of age greater than 60 years. (Figure 1, Figure 2). There was also no statistically significant correlation between FIQR and individual components of lipid profile (p >0.05). (Figure 3)
Conclusion: In this study, dyslipidemia was more prevalent in FM patients as compared to general population. The findings were consistent in subgroup analysis of age groups 18-39 and 40-59 years. However, FM disease severity did not correlate with individual components of fasting lipid profile in our study. These findings emphasize the need for evaluation of dyslipidemia in fibromyalgia patients.
Reference:
1. National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III)Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 2002; 106:3143–421.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
CB M, Surendran S, Madan S, Tiwari A, Raj S, Easwar S, Ravindran G. Prevalence of Dyslipidemia in Fibromyalgia: A Single Center Case Control Study from South India [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-dyslipidemia-in-fibromyalgia-a-single-center-case-control-study-from-south-india/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-dyslipidemia-in-fibromyalgia-a-single-center-case-control-study-from-south-india/