Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) has evolved substantially in the past decade. In 2011, the FDA approved belimumab, the first targeted monoclonal antibody (mAb) for treatment of SLE. In 2020, belimumab was approved for treatment of lupus nephritis. Voclosporin, a novel calcineurin inhibitor, was later approved for the treatment of lupus nephritis in 2021, followed by anifrolumab, a type I interferon antagonist for treatment of moderate to severe SLE. Given the benefits of these newer treatments, we sought to evaluate the real-world uptake of these medications across the United States.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional analysis of the Medicare Part D database to identify all rheumatologists prescribing belimumab, anifrolumab, and voclosporin between 2017 and 2022 (the most recent available data). We then standardized prescription volume to annual claims per 100,000 Medicare Part D beneficiaries. Our primary outcome of interest was trends in annual prescriptions of these three systemic therapeutics. Secondarily, we analyzed rheumatologist prescription patterns based on U.S region (Midwest, Northeast, South, West) and physician gender (male, female). T-tests and ANOVAs were conducted to further understand the relationship between these therapeutics and the outcomes of interest above.
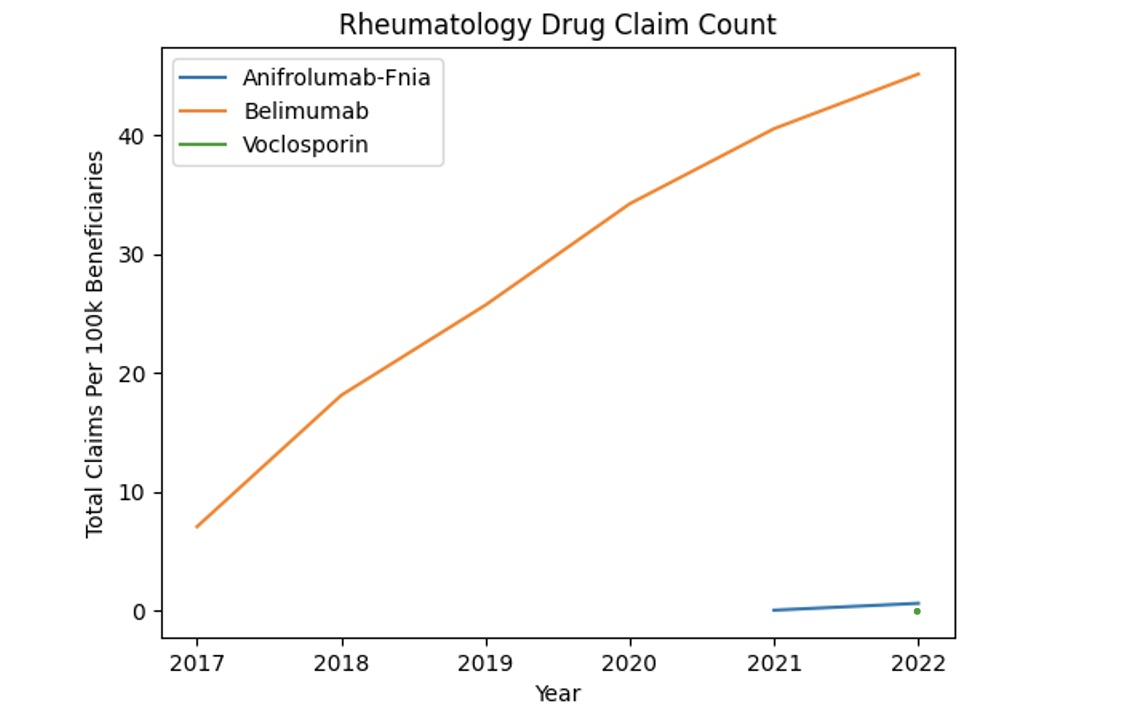
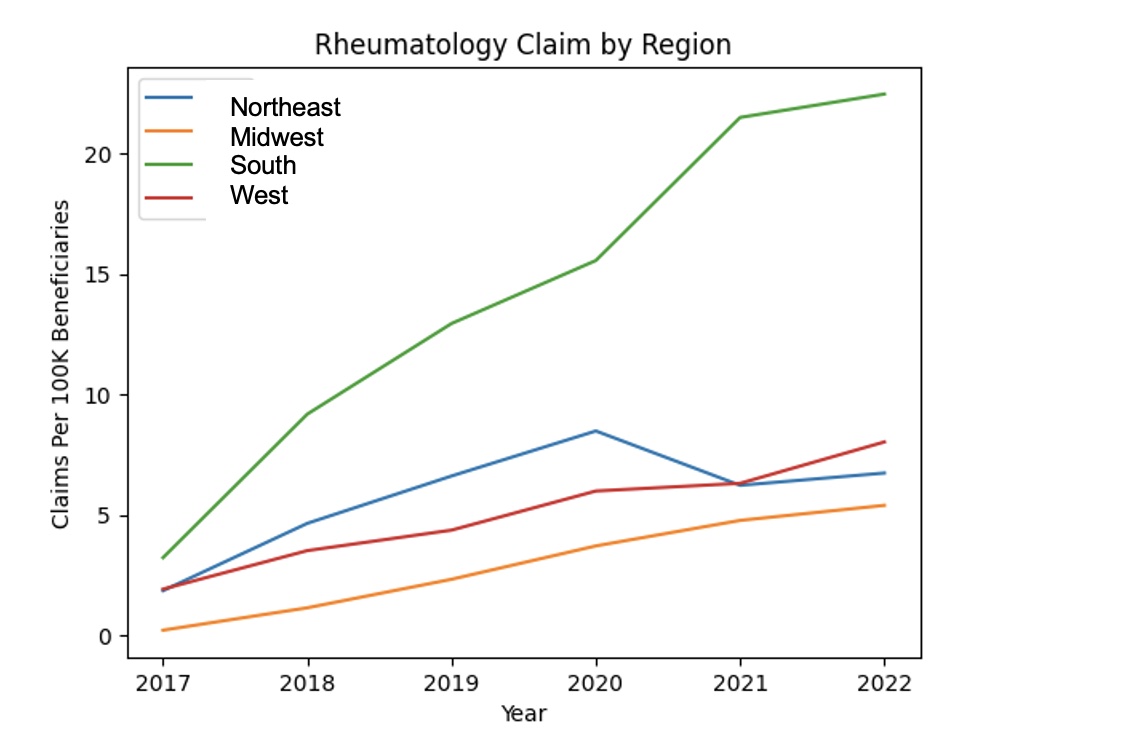
Results: From 2017-2022, total annual claims for belimumab, anifrolumab, and voclosporin combined increased from 3,019 to 21,035. Belimumab prescriptions increased at an average yearly rate of 5.8, from 7.2 in 2017 to 41.9 in 2022 per 100,000 Medicare Part D beneficiaries. There was a total of 17 claims for anifrolumab in 2021 and 282 in 2022. There were zero claims for voclosporin in 2021 and 67 in 2022 (Figure 1). The greatest number of prescriptions per 100,000 beneficiaries occurred in the South from 2017-2022, while the lowest number of prescriptions was in the Midwest (p< 0.005) (Figure 2). Belimumab and voclosporin mirrored a similar trend, with the greatest number of claims occurring in the South. While all claims for anifrolumab in 2021 came from the West, by 2022, the region with the most claims was again in the South. Unique prescribers for these medications increased from 118 (out of a total of 4,713 rheumatologists) in 2017 to 847 in 2022 (out of a total of 5,159), with an average increase of 121 prescribers per year. Despite having a near equivalent prescriber gender ratio, prescriptions written by male physicians were significantly greater than prescriptions written by female physicians for belimumab (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: Belimumab, anifrolumab and voclosporin exhibited an increase in claims from 2017-2022, with belimumab having a nearly 600% increase over the time-period, reflecting increased physician uptake of these medications. Our data suggests that Southern states have greater prescription rates of these medications, which, among other factors, may reflect regional variations in SLE prevalence. Interestingly, all claims for anifrolumab in 2021 came from the West, which may reflect factors such as different rates of marketing, information dissemination, etc. in different parts of the country.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
He C, Li Z, Chennareddy S, Dobrowolski C. Prescribing Trends for Novel Treatments in Systemic Lupus from 2017 to 2022 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prescribing-trends-for-novel-treatments-in-systemic-lupus-from-2017-to-2022/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prescribing-trends-for-novel-treatments-in-systemic-lupus-from-2017-to-2022/