Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
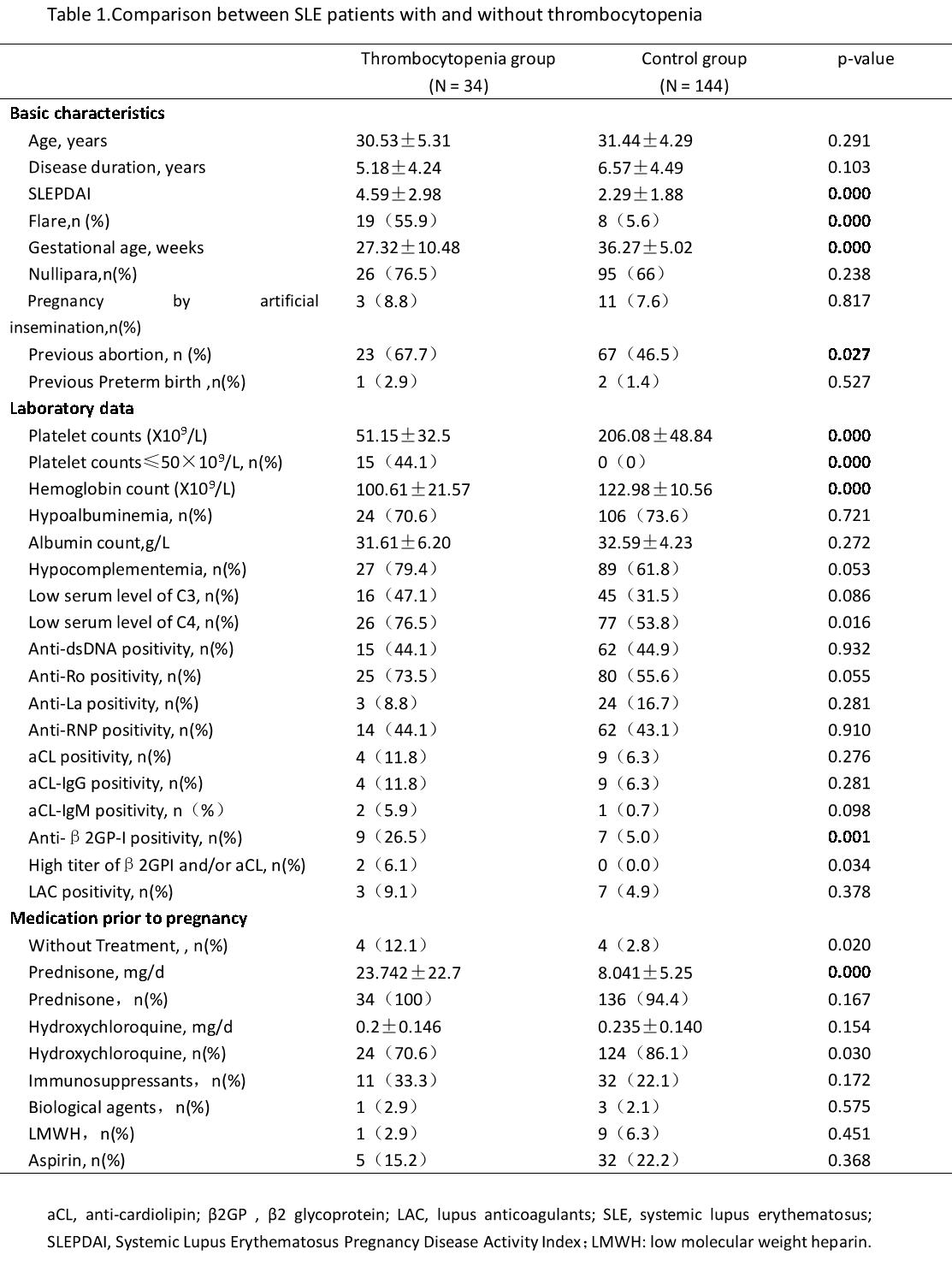
Background/Purpose: To compare the pregnancy outcomes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) complicated with thrombocytopenia and those without, and to analyze the related risk factors.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 178 pregnant patients complicated with SLE who were treated at the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University from February 2012 to October 2023. Patients were categorized into thrombocytopenia group (platelet count < 100×10^9/L) and normal platelet group, and pregnancy outcomes between the two groups were compared. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk factors associated with thrombocytopenia.
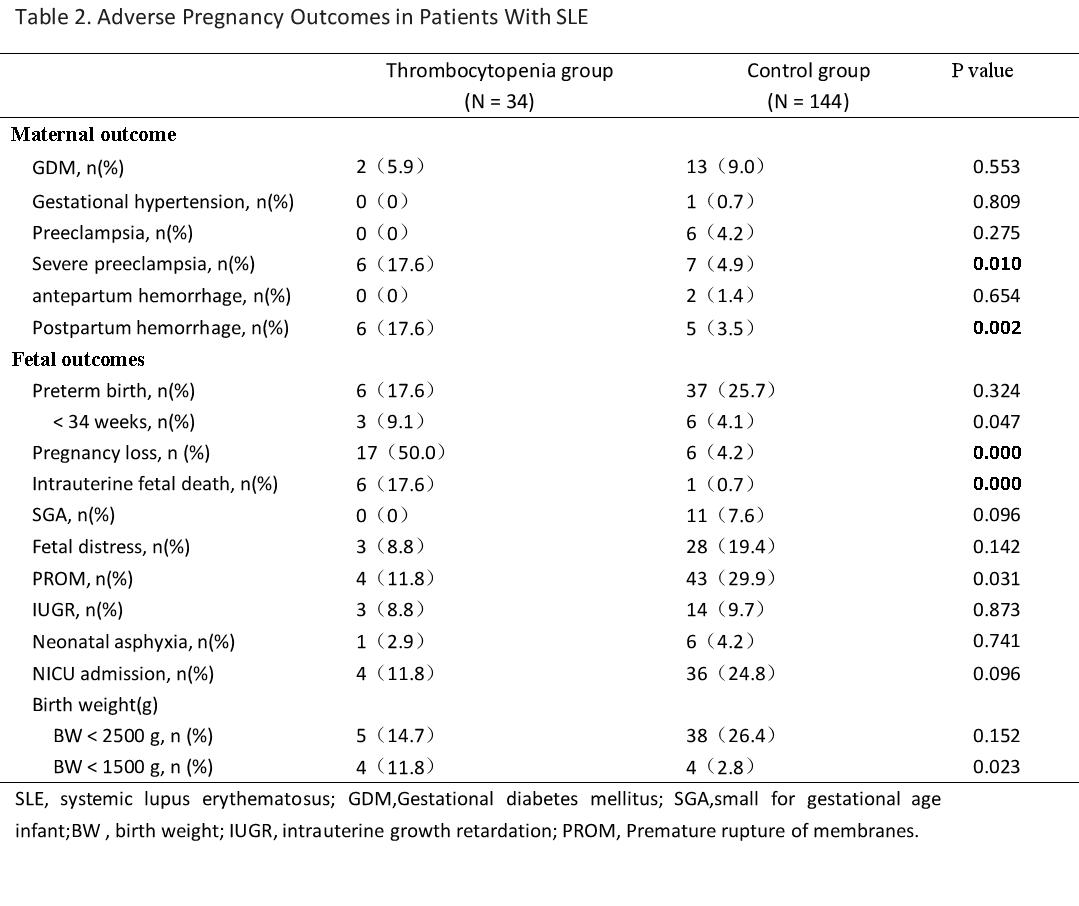
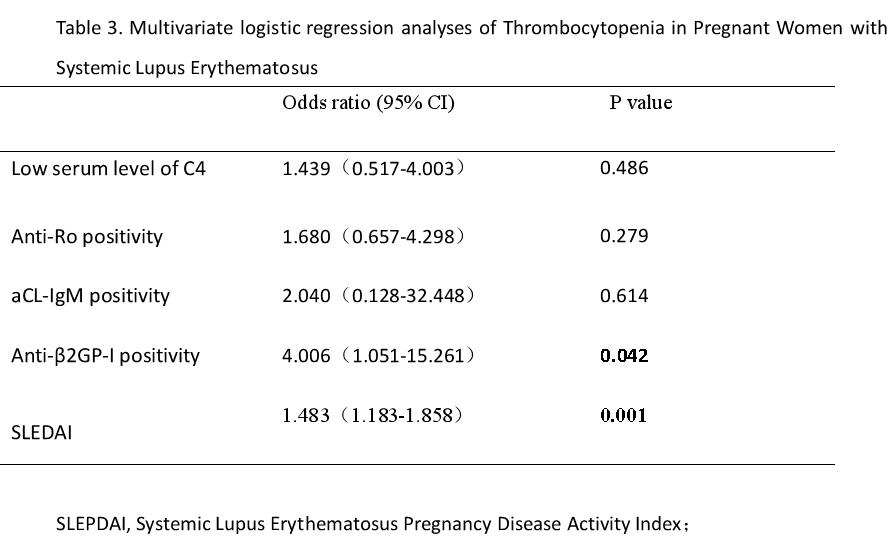
Results: Out of the 178 SLE patients, 34 (19.1%) were found to have thrombocytopenia during their pregnancy. Compared with the control group, SLE patients with thrombocytopenia during pregnancy had a higher percentage of disease flaring rate (55.9% vs 5.6%, P< 0.001) and a higher SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)(4.59±2.98 vs 2.29±1.88, P< 0.001). There were significant differences in the incidence of severe preeclampsia (17.6% vs 4.9%, p=0.010) and postpartum hemorrhage (17.6% vs 3.5%, p=0.002). The rates of pregnancy loss (50.0% vs 4.2%, p< 0.001), stillbirth (17.6% vs 0.7%, p< 0.001), and the birth of low birth weight infants (12.1% vs 2.8%, p=0.001) were higher in patients with thrombocytopenia. In our study, Anti-β2GP-I positivity (OR=4.006, 95% CI 1.051-15.261, P = 0.042) and higher SLEDAI score (OR =1.483, 95% CI 1.183-1.858, P=0.001) were identified as independent risk factors for thrombocytopenia in pregnant patients with lupus.
Conclusion: Pregnancy complicated with thrombocytopenia in patients with SLE predicts higher disease activity, higher rates of pregnancy failure, and stillbirth.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lian F, Fang Q. Pregnancy Outcome and Risk Factors Analysis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Complicated with Thrombocytopenia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pregnancy-outcome-and-risk-factors-analysis-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-complicated-with-thrombocytopenia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pregnancy-outcome-and-risk-factors-analysis-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-complicated-with-thrombocytopenia/