Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster Session III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
To describe
cumulative organ damage in a longitudinal cohort of SLE patients and to
evaluate the impact of key disease-related factors, medical therapies,
demographic variables, and serological biomarkers on the rate of damage
accrual. The relationship between cumulative organ damage and health-related
quality of life (HRQoL) was also examined.
Methods:
A longitudinal
database of SLE patients followed for up to 14 years was analyzed. Patients were
assessed at enrollment and annually for (i) cumulative organ damage (Systemic
Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC)/ACR Damage Index (SDI)) and
(ii) HRQoL (Medical Outcome Survey Short Form-36 (SF-36) subscales and summary
scores). The impact of demographic,
disease-related and treatment-related factors on damage progression was
examined using multivariable Cox
proportional-hazards models. The impact of changes in SDI scores on
HRQoL was assessed using linear
mixed-effects modeling.
Results:
There were 273
SLE patients with a mean (SD) follow-up of 7.3 (4.3) years. Seventy-seven
patients (28.2%) had preexisting damage (baseline SDI > 0) and during follow-up,
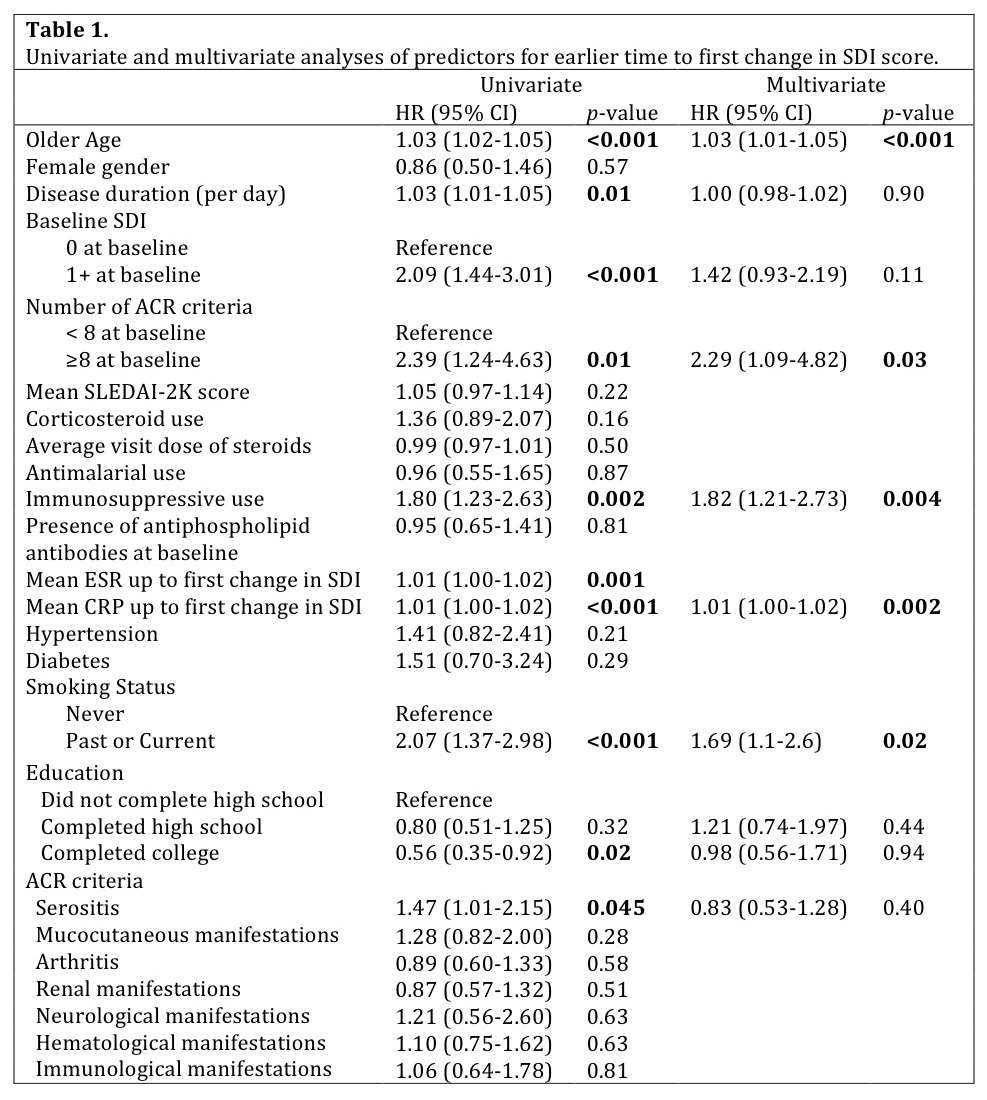
126 patients (46.1%) had an increase in SDI scores. Multivariate analysis
revealed that older age, 8 or more ACR classification criteria,
immunosuppressive drugs, cigarette smoking, and higher C-reactive protein (CRP)
levels up to time of first SDI change were associated with an increase in SDI
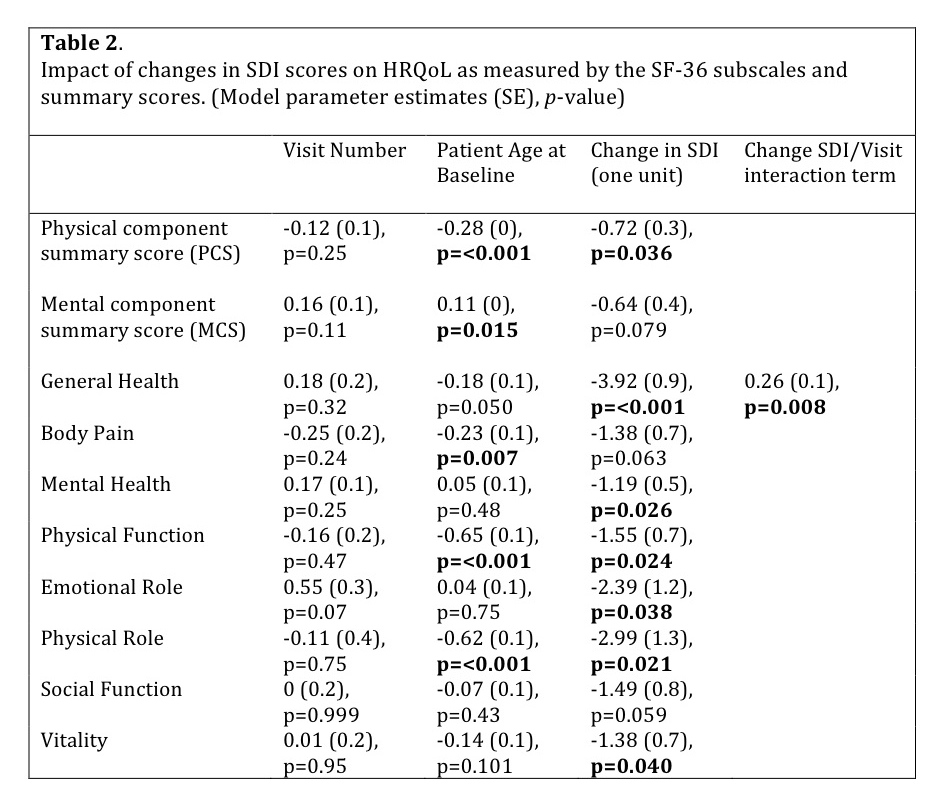
scores (Table 1). Changes in SDI scores were associated
with initial declines in SF-36 scores at the time that damage occurred, with subsequent
change in HRQoL comparable to that seen in patients without damage progression (Table 2).
Conclusion:
Pre-existing
organ damage and other risk factors, some modifiable, predict additional damage
accrual in SLE patients. The negative impact of damage progression on HRQoL emphasizes
the need to target modifiable risk factors and develop effective prevention and
treatment strategies to reduce organ damage over time.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Legge A, Doucette S, Hanly JG. Predictors of Organ Damage Progression and Impact on Health-Related Quality of Life in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-organ-damage-progression-and-impact-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-organ-damage-progression-and-impact-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/