Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
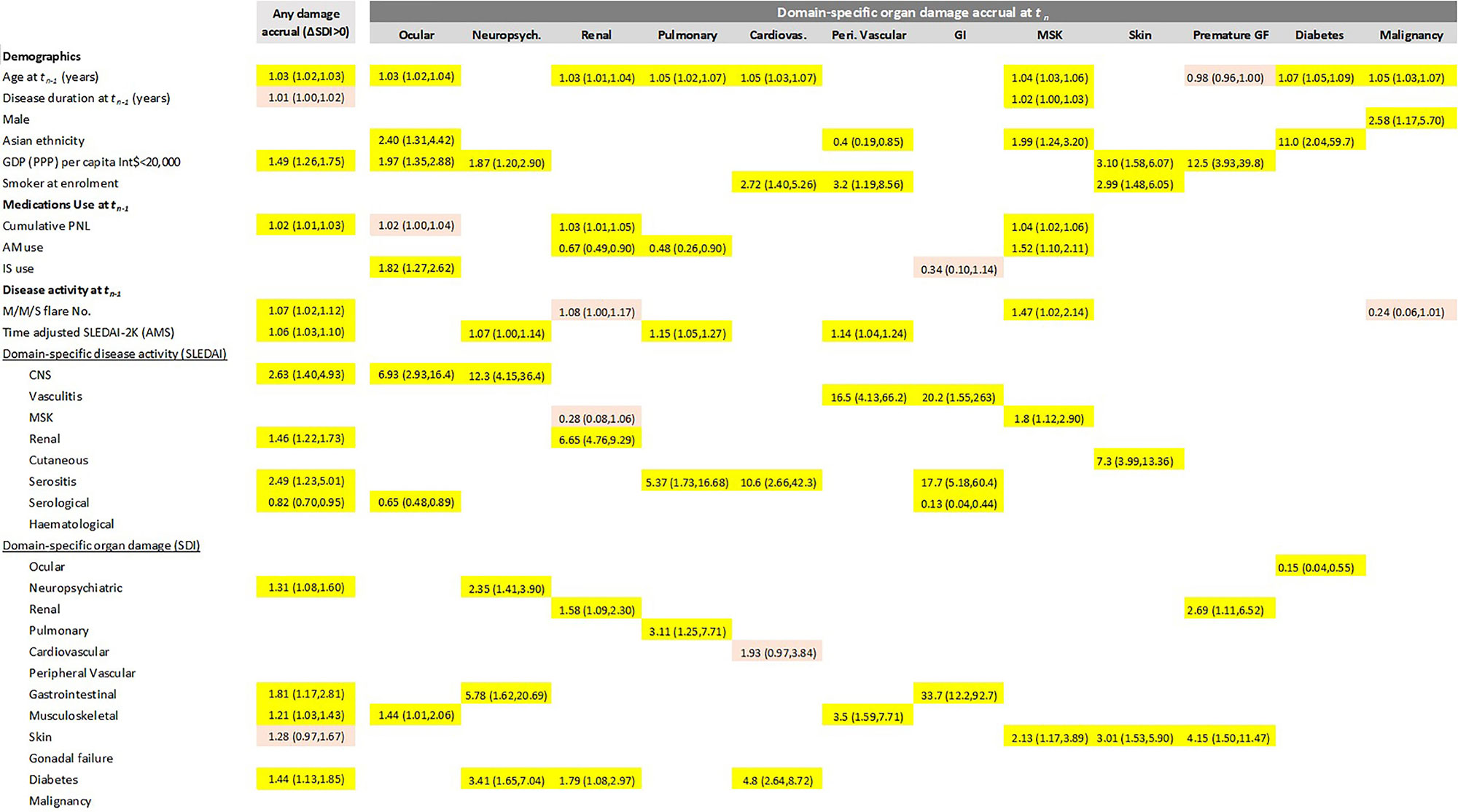
Background/Purpose: Prevention of organ damage is one of the main treatment goals in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).The SLICC/ACR Damage Index (SDI) is used to quantify damage in 12 organ systems; ocular, neuropsychiatric (NP), renal, pulmonary, cardiovascular (CV), peripheral vascular (PV), gastrointestinal (GI), musculoskeletal (MSK), skin, premature gonadal failure (PGF), diabetes and malignancy [1]. Most studies report a summed damage score >0 as an indication of organ damage. However, few studies report the frequency and predictors of damage according to organ system domains.
We examined the predictors of overall damage accrual (DA) as well as DA in organ domains and assessed whether risk factors for overall DA capture those associated with domain-specific DA.
Methods: Data from a 13-country longitudinal SLE cohort were collected between 2013 and 2020 using standard templates. Organ damage was assessed annually using SDI; at each visit disease activity was assessed using SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI-2K), physician global assessment (PGA) and flare (SELENA-SLEDAI Flare Index). A series of multi-failure, multivariate models were carried out to examine the risk factors associated with overall and domain-specific DA. Total time from cohort entry to the occurrence of new damage accrual was fitted using the Prentice, Williams and Peterson (PWP-TT) models.
Results: For overall DA, older age and living in a low gross domestic product (GDP) country were strong predictors, as was cumulative prednisolone dose (Figure 2). Flare number and time adjusted mean SLEDAI-2K (AMS) increased the risk of subsequent overall DA by 7% (HR=1.07 (95%CI: 1.02, 1.12), and 6% (HR=1.06 (95%CI: 1.03, 1.10), respectively, as did CNS, renal, and serositis activity. Likewise, the presence of organ damage in several domains including NP, GI, MSK and diabetes was strongly associated with subsequent overall DA. For organ domain specific DA, Figure 2 shows that risk factors differed between domains. Existing organ damage in diabetes and skin domains was strongly predictive of subsequent DA in multiple domains. Smoking was a significant risk factor for CV, PV and skin DA. Male sex was associated with malignancy DA, while Asian ethnicity conferred greater risk of ocular, MSK, and diabetic DA but was protective against PV DA. Anti-malarial (AM) use was protective from renal and pulmonary DA but was a significant risk factor for MSK DA. Immunosuppressant use was strongly associated with ocular DA (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In SLE, risk factors for overall DA have highly variable associations with domain-specific DA. Domain-specific damage should be reported in studies of SLE outcomes.
References
1. Stoll T, Seifert B, Isenberg DA. SLICC/ACR Damage Index is valid, and renal and pulmonary organ scores are predictors of severe outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Mar; 35(3):248-254.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kandane-Rathnayake R, Li N, Golder V, Louthrenoo W, Chen Y, Cho J, Lateef A, Hamijoyo L, Fen L, Wu Y, Navarra S, Zamora L, Li Z, Yuan A, Sockalingam S, Katsumata Y, Harigai M, Hao Y, Zhang Z, Chan M, Kikuchi J, Takeuchi T, Oon S, Bae S, Goldblatt F, O'Neill S, Gibson K, Ng K, Law H, Basnayake D, Tugnet N, Kumar S, Tee C, Tee M, Tanaka Y, Sing C, Nikpour M, Hoi A, Morand E. Predictors of Organ Damage Accrual by Domains [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-organ-damage-accrual-by-domains/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-organ-damage-accrual-by-domains/