Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
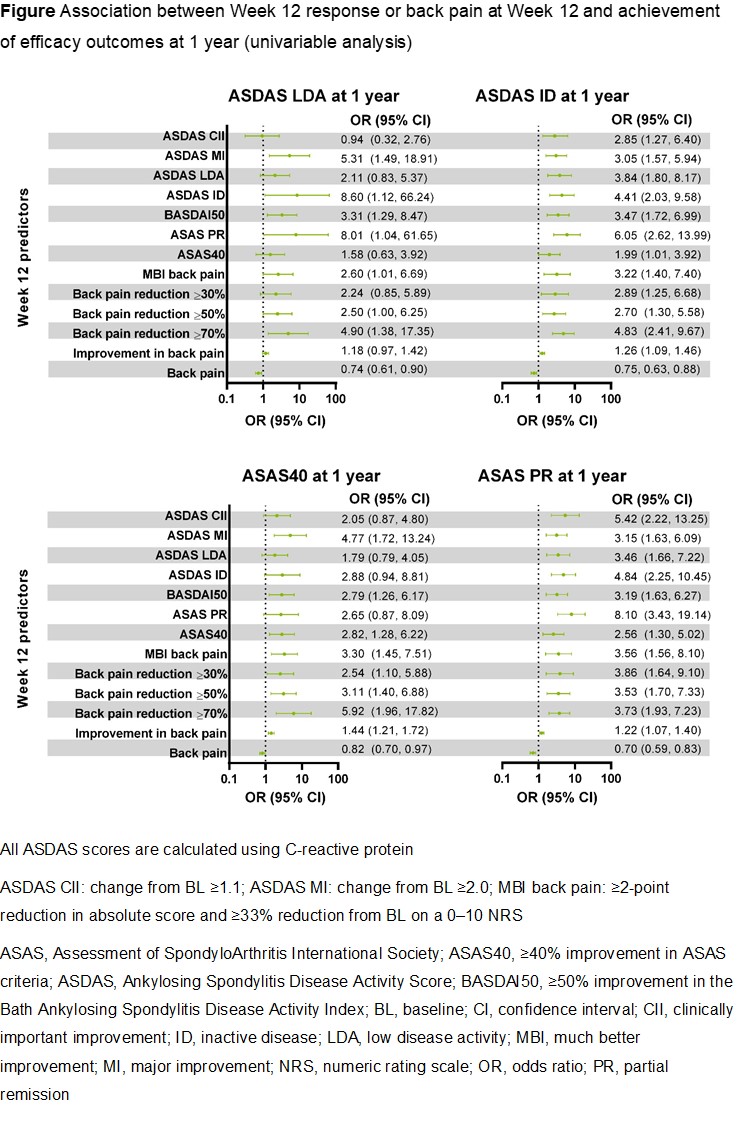
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor that has demonstrated efficacy and safety among patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in the phase 2/3 SELECT-AXIS 1 study.1 If identified, early predictors of treatment response may inform treat-to-target strategies and optimize patient outcomes in AS. The objective of this analysis was to determine whether baseline (BL) characteristics or early responses predict clinical response at 1 year in UPA-treated patients with AS.
Methods: In the double-blind, randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled SELECT-AXIS 1 study, patients received UPA 15 mg once daily or PBO until Week 14.1 At Week 14, PBO-treated patients switched to UPA 15 mg; patients originally randomized to UPA continued UPA therapy. Data from patients in the PBO and UPA arms were combined based on overall exposure to UPA; in the switch arm, exposure was defined as current visit minus 14 weeks (time of switch). The following outcomes were assessed at 1 year: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with C-reactive protein (ASDAS[CRP]) inactive disease (ID; < 1.3) and low disease activity (LDA; < 2.1), Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) partial remission (PR), and ≥40% improvement in ASAS criteria (ASAS40) response. The ability of BL characteristics, efficacy at Week 12, and back pain at Week 12 to predict 1-year outcomes was assessed using a univariable logistic regression model generating odds ratios (ORs; 95% confidence intervals). LASSO regression was used to select the best-fitted multivariable model at Week 12 for each outcome measure.
Results: Among 187 patients who received or switched to UPA 15 mg, 70 (37.4%), 134 (71.7%), 73 (39.0%), and 131 (70.1%) achieved ASDAS(CRP) ID, ASDAS(CRP) LDA, ASAS PR, and ASAS40, respectively, following 1 year of UPA treatment. No meaningful predictors of 1-year efficacy outcomes were identified based on BL demographics (including disease duration, gender, and human leukocyte antigen B27 status) or BL disease characteristics (including ASDAS, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, and CRP levels). In univariable analyses, Week 12 responses based on several disease activity measures and patient-reported outcomes (PROs), including reductions (much better improvement [MBI], ≥30/≥50/≥70% reduction, or improvement) in back pain score, along with lower scores for back pain at Week 12, were associated with the achievement of ASDAS(CRP) ID, ASDAS(CRP) LDA, ASAS PR, and ASAS40 at 1 year (Figure). In a multivariable analysis, improvement from BL to Week 12 in back pain score consistently predicted several efficacy outcomes at 1 year.
Conclusion: In upadacitinib-treated patients with AS, improvement in PROs and reduction in back pain score at 12 weeks predicted clinical outcomes at 1 year.
Reference: 1. van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet 2019;394:2108–17.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Magrey M, Ramiro S, Pinheiro M, Gao T, Ganz F, Song I, Biljan A, Haroon N, Rudwaleit M. Predictors of 1-Year Treatment Response Among Upadacitinib-Treated Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Post Hoc Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-1-year-treatment-response-among-upadacitinib-treated-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-post-hoc-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-1-year-treatment-response-among-upadacitinib-treated-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-post-hoc-analysis/