Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Dose reduction and discontinuation of TNF inhibitors (TNFi) is feasible in many rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, but leads to (temporary) worsening of disease activity in some patients. We evaluated the predictive value of baseline adalimumab and etanercept serum levels and antidrug antibodies for successful dose reduction or discontinuation in patients with RA and low disease activity.
Methods
Patients with RA and a stable low disease activity, included in the intervention arm of an 18 months randomised controlled trial (DRESS study) assessing non-inferiority of a dose reduction strategy of adalimumab or etanercept compared to usual care were analysed1. Dose was reduced by stepwise increasing the interval between injections every 3 months until flare or discontinuation of the TNFi. Serum levels of adalimumab or etanercept and antidrug antibodies were measured before start of dose reduction2,3. Receiver-operator-curves (ROC) and optimal cut-off drug serum levels were calculated. A sensitivity analyses was done for timing of serum sampling (days after last injection), per tertile. Sensitivity/specificity of anti-drug antibodies were calculated for successful discontinuation and for successful dose reduction separately.
Results
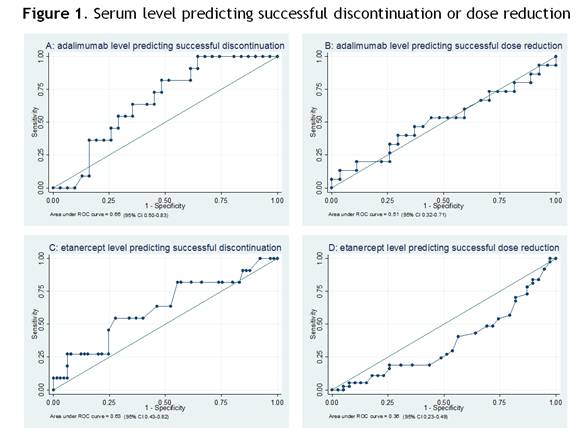
Data was available for 118 of 121 included patients. Mean DAS28-CRP at baseline was 2.2 (SD 0.6). At 18 months follow up TNFi could be stopped in 19% (95%CI 12-27) of patients, the interval increased in 44% (95%CI 35-53) and in 37% (95%CI 29-47) of patients no dose reduction was possible. Mean drug levels and anti-drug antibodies were not different per subgroup (table 1). ROC analyses showed no predictive value of drug levels for successful dose reduction or discontinuation (figure 1). Sensitivity analyses showed no influence of serum sample timing, with the exception of adalimumab trough level (last tertile) predicting successful dose reduction (AUC 0.86, 95% CI 0.58-1.00, optimal cut-off 7.8 μg/ml).
Anti-adalimumab antibodies were detected in 4 patients (10%), and were not predictive for successful discontinuation. No anti-etanercept antibodies were detected.
Conclusion
Adalimumab and etanercept serum levels and antidrug antibodies have no predictive value for successful dose reduction or discontinuation in RA patients with low disease activity, with a possible exception of adalimumab trough levels for predicting successful dose reduction.
References
1: den Broeder et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013 24;14:299
2: Bartelds et al. JAMA 2011;305(14):1460-1468
3: Jamnitski et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:88-91.
Disclosure:
N. van Herwaarden,
None;
C. Bouman,
None;
A. van der Maas,
Roche, MSD, ,
9;
R. F. van Vollenhoven,
Abbott, BMS, GSK, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, UCB ,
2,
Abbott, BMS, GSK, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, UCB ,
5;
J. W. J. Bijlsma,
AbbVie, Roche, Pfizer, MSD, UCB, BMS,
2,
AbbVie, Roche, Pfizer, MSD, UCB, BMS, Jansen,
5;
F. H. J. van den Hoogen,
None;
A. A. den Broeder,
None;
B. van den Bemt,
Roche Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer,
2,
Roche, Pfizer, MSD Abbvie,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-successful-dose-reduction-or-discontinuation-of-adalimumab-or-etanercept-using-serum-drug-levels-and-antidrug-antibody-measurement/