Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary involvement in rheumatoid
arthritis (RA) patients is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Nevertheless,
limited data are available regarding such lung complications in the Middle East,
especially in the Kingdome of Saudi Arabia. The objective of the current study
were to determine the prevalence of pleuropulmonary manifestations and to
identify the risk factors predicting lung involvement.
Methods: This was a retrospective
study involving 419 RA patients diagnosed at a tertiary center over a 12.5-year
period. RA was diagnosed on the 2010 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)
criteria. The frequency of pulmonary manifestations were recorded based on
combined results from the chest X-rays, pulmonary function tests, and high
resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan on the chest.
Results: The overall
frequency of lung involvement in RA was 25.8%. Pneumonia
and bronchiectasis
were
the
most common abnormalities (36% and 35% respectively). HRCT scan was more sensitive in detecting of pleuropulmonary
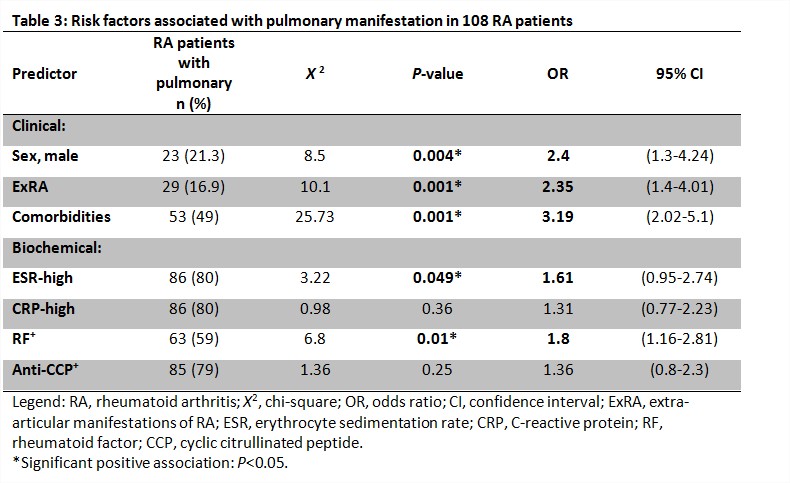
abnormalities. . The presence of comorbid illness (OR=3.19, 95% CI: 2.02–5.1),
male gender (OR=2.4, 95% CI: 1.3–4.24), and the presence of extra-articular manifestations (OR=2.35, 95% CI:
0.4–4.01) were significantly predicting lung involvement .
Conclusion: Pneumonia and bronchiactasis were the most common
abnormalities seen in RA patients in Saudi Arabia. This finding were comparable
with other studies.. The presence of comorbidity , male gender and
extra-articular manifestation were statistically associated with lung
involvement .
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Attar S, Amoudi O. Pleuropulmonary Manifestations in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pleuropulmonary-manifestations-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pleuropulmonary-manifestations-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/