Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: We have previously demonstrated that Fc gamma receptor(FcgR)
Methods: Heparinized venous blood was obtained from 48 RA patients and 12 healthy controls(HC). Surface expression of CD16(FcgR
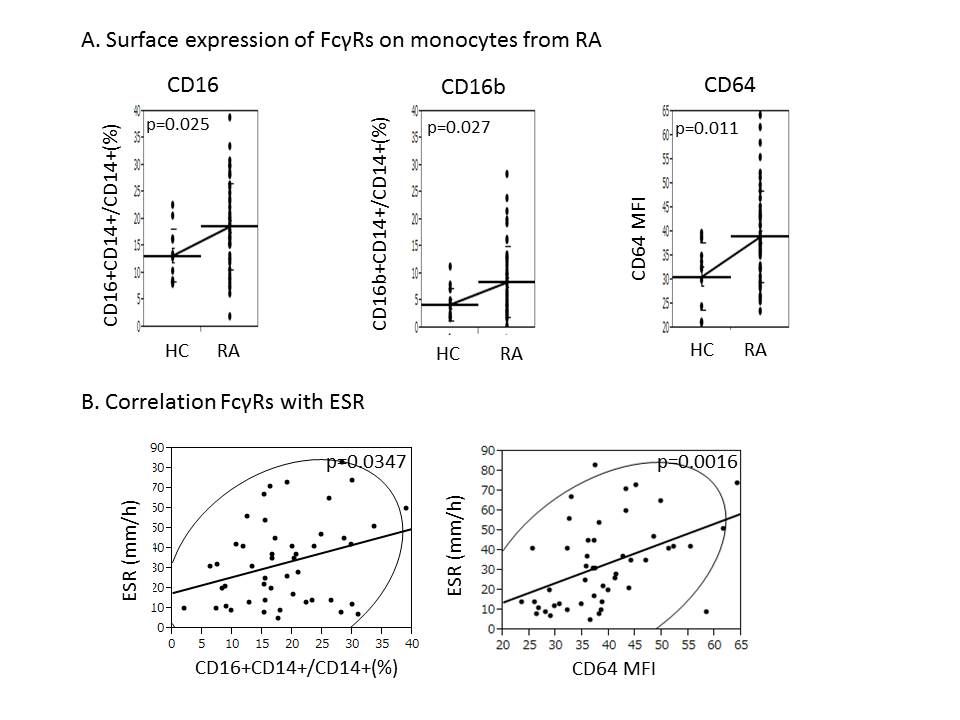
Results: Both percentages of CD16+ and CD16b+ cells on CD14+ monocytes were significantly increased in RA patients(18.7±8.0% and 8.5±6.5%) compared with HC(13.3±4.9% and 4.4±3.0%)(p=0.025 and p=0.027). These results suggest that CD16 is upregulated, completely different from CD32 on monocytes in RA. Moreover, CD64 MFI on CD14+ monocytes from RA patients(39.0±9.4) was significantly higher than that of HC(30.8±7.1)(p=0.011). Interestingly, CD64 MFI and percentage of CD16+ cells strongly correlated with ESR(p=0.0016 and p=0.035). CD64 expression itself also correlated with ACPA(p=0.044). On the other hand, CD64 MFI correlated with CD16-expressing cells(p=0.049), but didn’t correlated with CD16b(p=0.24).
Conclusion: We found CD16 and CD64 were aberrantly upregulated on CD14+ monocytes in RA patients. Clinically, CD16b upregulation together with its functional polymorphism may participate in adverse reaction such as infusion reaction, and CD64 and CD16a rather may relate to inflammation and autoantibody production in RA.
Disclosure:
M. Tsukamoto,
None;
K. Suzuki,
None;
K. Yoshimoto,
None;
H. Kameda,
None;
T. Takeuchi,
Astra Zeneca K.K., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., and Asahi Kasei Medical K.K,
5,
AbbVie GK., Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,
8,
AbbVie GK., Astellas Pharma, Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Sanofi–Aventis K.K.,
2,
Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Teijin Pharma Ltd.,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pleiotropic-roles-of-fc%ce%b3-receptors-upregulated-on-circulating-monocytes-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/