Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The best packaging of holistic therapy for Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) will involve two components: a potent anti-inflammatory therapeutic and a rationally designed drug delivery vehicle to enrich the target site concentration and sustained release of the drug. The natural product, triptolide (TP), which is an effective anti-inflammatory compound, has been used for RA in clinical. However, the potential clinical application of triptolide is limited due to its poor solubility and high toxicity. Drug delivery systems responding to inflammatory acidic pH environment can be constructed by using nanomaterials as carriers combined with TP. Through targeting and nano-drug sustained release, the toxic and side effects of drugs can be reduced and therapeutic effects can be improved.
Methods: The effects of TP@NPs on cell survival, apoptosis and ROS production were detected in RAW264.7 cells. NPs group and saline group were used as control group, TP@NPs group and free TP component of the same amount of TP were given high and low doses (0.15mg/kg/3 days and 0.075mg/kg/3 days) to treat collagen induced arthritis mice for 30 days. ABOG staining,TRAP staining and micro-CT were used to observe bone destruction. HE staining and biochemical indexes of liver and kidney (ALT, AST, CRE, BUN) were used to observe drug toxicity.
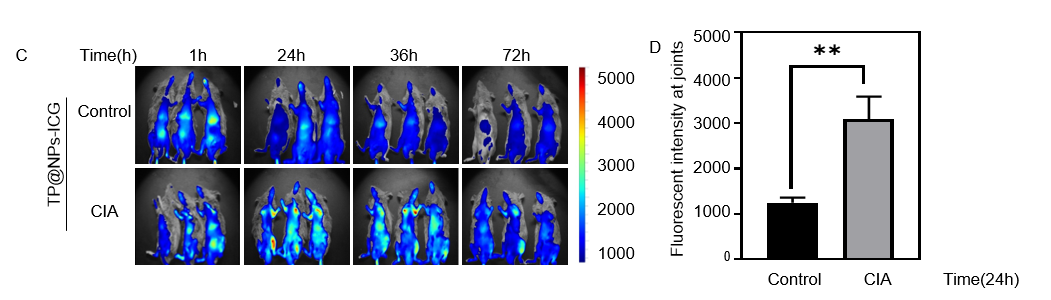
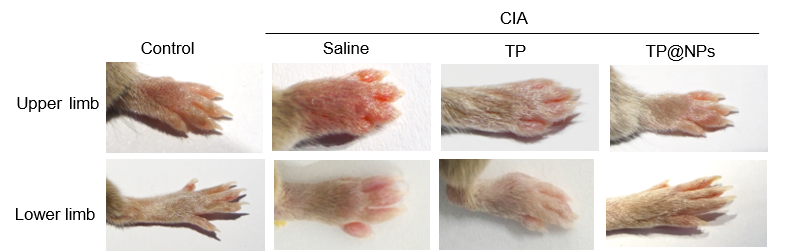
Results: Compared with TP, TP@NPs could effectively improve the survival rate of RAW264.7 cells(P< 0.05).The apoptosis rate of TP was 26.6±8.052, while that of TP@NPs was 1.693 ±0.1617 (P< 0.01).The proportion of ROS produced by TP was 10.97±0.5774, which was reduced to 3.68±0.51 by TP @NPs (P< 0.01). Q-PCR showed that TP@NPs and TP had the similar effect on inhibiting inflammation in vitro (P >0.05). In vivo study, the serum AST (n=5, P=0.0083), ALT (n=5, P=0.0013), CRE (n=5, P=0.0069) and BUN (n=5, P=0.0312) in TP@NPs (containing high dose TP) treated CIA mice were significantly lower than those in high dose TP group. HE staining showed histomorphological abnormalities of liver, kidney and spleen in high dose TP treated CIA mice, while the structure of those organs in TP@NPs (containing high dose TP) group maintained normal. Furthermore, the score of CIA mice (n=10, P< 0.05), and the serum level of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α(n=5, P< 0.05) of TP@NPs (containing low dose TP) group were lower than low dose TP group. ABOG and TRAP staining and micro-CT showed that TP@NPs (containing low dose TP) effectively reduce the destruction of articular cartilage, synovial hyperplasia and osteoclast production (n=10, P< 0.05), and the loss of talus bone mass (0.95±0.1108 VS 1.133 ±0.09074 n=9, P=0.007). In vivo imaging showed that TP@NPs was able to target inflammatory joints of CIA mice, but not normal mice (the fluorescence intensity was 1247 ± 108.2, n=3, 12 limbs VS 3093 ± 496.4, n=3, 12 limbs) at 24 h.
Conclusion: The nano-drug can achieve the sustained release of TP, maintain a good blood concentration, improve water solubility, improve the efficacy, reduce toxic side effects, and can be candidate therapy for RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang L, JianQiu J, Hao X, HaiHui H, Tong H, WeiAn Z, QianQian L. pH-Sensitive Nanoformulated Triptolide as a Targeted Therapeutic Strategy for Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ph-sensitive-nanoformulated-triptolide-as-a-targeted-therapeutic-strategy-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ph-sensitive-nanoformulated-triptolide-as-a-targeted-therapeutic-strategy-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/