Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) that capture the spectrum of disease present challenges due to the frequency of back pain, the relative infrequency of axSpA, and limited physical and laboratory findings in early disease. Several cohorts have reported the performance of the ASAS classification criteria in settings where patients have been selected for certain features such as the presence of inflammatory back pain and/or short symptom duration. We aimed to test the performance of the ASAS classification criteria in unselected patients with undiagnosed back pain who were referred after first presenting with acute anterior uveitis (AAU), psoriasis, or colitis to their respective specialists and whether performance varied according to the presentation of disease.
Methods: The multicenter Screening for Axial Spondyloarthritis in Psoriasis, Iritis, and Colitis (SASPIC) Study is aimed at early detection of axial SpA in patients referred after first presenting with these disorders. Consecutive patients ≤45 years of age with ≥3 months undiagnosed back pain with any one of psoriasis, AAU, or colitis undergo routine clinical evaluation by a rheumatologist for axial SpA and MRI evaluation is ordered per rheumatologist decision. The rheumatologist determines the presence or absence of axial SpA and the degree of confidence in the diagnosis (-10 (definitely not SpA) to +10 (definite SpA)) at 3 consecutive stages: 1. After the clinical evaluation; 2. After the results of labs (B27, CRP) and radiography; 3. After the results of MRI evaluation. Assessment of imaging was conducted by local and central readers. We calculated the sensitivity and specificity of the ASAS criteria and the component imaging and clinical arms using the stage 3 diagnostic assessment by the local rheumatologist as gold standard but using central reads for imaging.
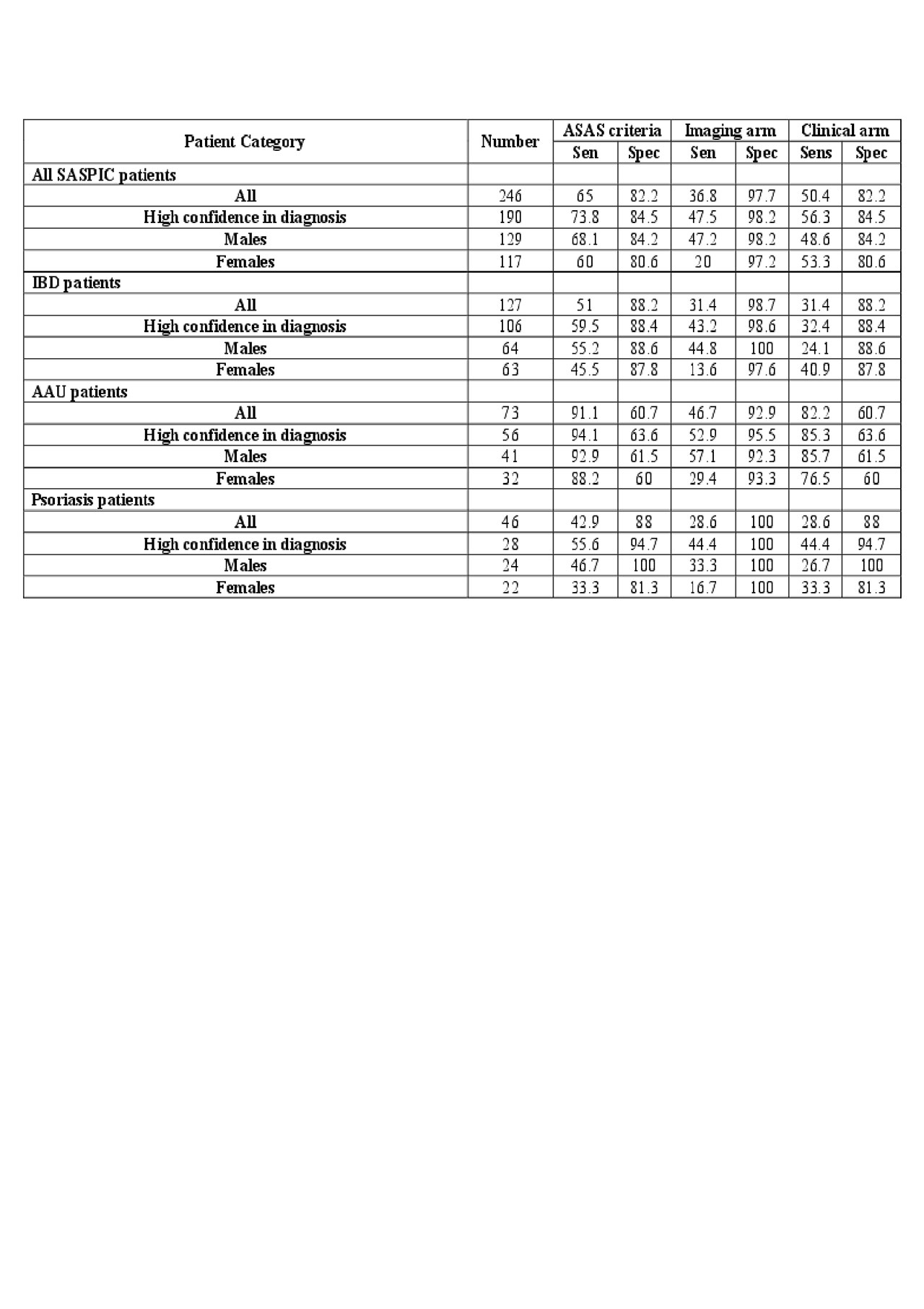
Results: xA total of 246 patients were recruited, 47.6% being diagnosed with axSpA (61.5% male, age 33.7 years, symptom duration 7.6 years, B27 positive 52.1%), after stage 3 evaluation. Sensitivity/specificity of the ASAS criteria, imaging arm, clinical arm were 65/82.2%, 36.8/97.7%, 50.4/82.2%, respectively (Table). For patients diagnosed with a high degree of confidence sensitivity/specificity was 73.8/84.5%, 47.5/98.2%, 56.3/84.5%, respectively. Performance varied substantially according to presentation of disease characterized by much higher sensitivity but markedly lower specificity, especially for the clinical arm, in patients presenting with AAU. This was noted even in patients diagnosed with high confidence. The imaging arm had high specificity ( >90%) in all patient groups and was at least twice as sensitive in males versus females.
Conclusion: The performance of the ASAS criteria in the SASPIC cohort demonstrated lower sensitivity and specificity when compared to published cohorts, even in patients diagnosed with high confidence. This was characterized by much lower specificity for the clinical arm in patients presenting with AAU and raises the potential for ‘diagnostic overcall’ in the setting of a perceived high pre-test probability of axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Carmona R, Chan J, Yeung J, Aydin S, Martin L, Masetto A, Mosher D, Ziouzina O, Keeling S, Rohekar S, Dadashova R, Paschke J, Carapellucci A, Lambert R. Performance of the ASAS Classification Criteria Presenting with Undiagnosed Back Pain: Data from the Screening in Axial Spondyloarthritis in Psoriasis, Iritis, and Colitis Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-asas-classification-criteria-presenting-with-undiagnosed-back-pain-data-from-the-screening-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-psoriasis-iritis-and-colitis-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-asas-classification-criteria-presenting-with-undiagnosed-back-pain-data-from-the-screening-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-psoriasis-iritis-and-colitis-cohort/